False chanterelle - what does it look like, where does it grow? The generally recognized mushroom is the “double” of the real yellow chanterelle - is it really that similar to it? Let's compare the false fox with the real one. Is the false chanterelle as dangerous as it is sometimes “painted”, and is it worth eating?
Hello dear reader!
The story about “terribly poisonous false mushrooms” - “doubles” of good edible mushrooms appeared a long time ago. The Internet has only breathed new life into this old story.
And they travel from site to site, and especially on social networks, the terrible “false honey mushrooms”, “false boletus”, “false whites” and even, sorry, “false saffron milk caps”. And recently I discovered a “false russula”...
One can, of course, declare the gall mushroom (gorchak) to be a “false white”; A “false butter dish” is either a grainy butter dish (since it has no ring on the stem), or a valua at all.
But in the scientific names of mushrooms, the word “false” is extremely rare. Namely, the scientific names of mushrooms (including Latin) are the only reasonable ones to use on the Internet to identify and discuss a mushroom. After all, we live in different regions, sometimes even in different countries.
Local, regional names of mushrooms can be interesting. And no more. Using them, it is hardly possible to discuss anything constructively. To argue about this or that mushroom using these names, to argue, even to the point of insults, is simply stupid.
Real and false chanterelles: similarities and differences
Both varieties of chanterelles grow in wooded areas: coniferous and coniferous-deciduous forests. The real chanterelle likes to hide in moss or under leaves, and can grow in an open area of soil or on a mossy stump. The false variety is found in moss, on fallen rotting trees, and on the forest floor. False chanterelle can grow in groups or alone. A real chanterelle is not found one at a time, but grows in close groups, so if you encounter one single mushroom in the entire clearing, you should take a close look at it - perhaps it is better not to touch it. In addition, this useful mushroom is a frequent inhabitant of the soil near pine trees, oak trees, beech trees and spruce trees.
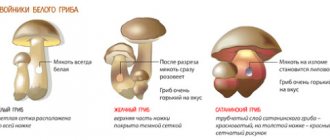
The main difference between chanterelles, which will immediately catch your eye, is that the poisonous one has a bright orange cap with edges of a lighter, reddish color. The useful species has a uniform light yellow or orange-yellow color, and the younger the mushroom, the paler its color looks.
The hat of the false chanterelle is of a regular round shape in the form of a funnel, with rounded edges and a velvety surface to the touch, in contrast to its useful sister - its hat is always wavy, has a smooth surface and a larger diameter.
Another external sign is the leg. In a healthy mushroom it is thicker and does not have a clear transition to the cap. It is usually the same color as the whole mushroom, or a little lighter. It is not hollow inside. Thick and dense plates of the cap extend onto the stem.
A thin and straight leg of a reddish-brown or brownish color immediately gives away a false chanterelle. The transition boundary is visually noticeable between the cap and the stem. The plates of the cap are frequent and thin, have a bright orange color.
For those who do not fully rely on their own eyes, there remains the sense of smell. False mushrooms have a sharply unpleasant odor, which is difficult to confuse with the aroma of good mushrooms.
If the mushroom is already in the basket, you can determine its suitability for consumption using a knife - if you make a cut on the stem and press, the whitish flesh of a real mushroom will turn slightly pink. False chanterelles have a yellow or orange cut and do not change color.
A sign that will become noticeable as soon as the mushroom is in your hands is the presence of parasites in it. Real chanterelles are not affected by them, as they contain a substance – chitinmannose, which repels insects and pests. If the mushroom is worn out and wormy, then it is definitely a false relative of the edible species.
Spreading
The common chanterelle is found in all areas with a temperate climate (for example, Belarus, Ukraine and central Russia), developing from the beginning of summer in deciduous, coniferous and mixed forests. Most of these mushrooms can be collected in mid-summer, but individual specimens are found until late autumn. It is noteworthy that in Belarusian forests, in addition to the standard orange chanterelle, its gray variety, listed in the Red Book of the Republic of Belarus, also grows. It is very rare in neighboring countries.
False chanterelle is widespread in the forests of the Northern Hemisphere, growing in the soils of coniferous or small-leaved mixed forests. Most of all, she likes mossy areas with a lot of fallen leaves and rotting wood, under which it is quite humid and cool. Mushrooms can grow both in groups and individually (even when placed in groups, they are located at a certain distance from each other). The fruiting period depends on the weather, but usually occurs in late summer or early autumn.
Did you know? Chanterelles are used in folk medicine in several main ways: as a good anthelmintic, and also as an auxiliary medicine in the treatment of hepatitis, fatty liver degeneration and hemangiomas.
Taste properties and use in cooking
Usually, both doctors and mushroom pickers advise against collecting this type of mushroom, except in very extreme cases, when it is simply impossible to find others.
However, oddly enough, the false fox has its fans. Basically, reviews about their taste are not the most flattering - they are bland, viscous and do not have a very pleasant smell. But some mushroom pickers still collect and prepare this type of mushroom, pickling or pickling them for the winter.
The main rule for their preparation is complete primary processing. First of all, mushrooms need to be thoroughly washed and sorted; spoiled and eaten by insects should be thrown away. After this, they must be soaked for three days in clean water. The water needs to be changed twice a day, morning and evening. After this procedure, they are boiled in boiling water with the onion for about 15-20 minutes.
Drying them is usually useless, but you can fry, stew, pickle, or make mushroom sauce with them.
Why are chanterelles bitter, how to remove the bitterness?
Chanterelles have a natural bitterness
, therefore they are not liked by pests and insects, but are valued in cooking. If the mushrooms are not processed immediately after harvesting, the bitterness will increase. Also, increased bitterness of chanterelles is possible due to the influence of some natural factors.
Chanterelles have more bitterness
, collected in dry weather, under coniferous trees, near highways and enterprises, overgrown mushrooms growing in moss, if these are false chanterelles.
It is better to collect and cook young chanterelles; the bitterness content in them is minimal. To remove the bitterness, you need to soak the chanterelles for 30-60 minutes in water and then boil them. Drain the water after cooking.
To freeze, use boiled chanterelles - they will not taste bitter and take up less space. If you froze them fresh and when you defrost them you find that the mushrooms are bitter, boil them in salted water, the bitterness will go into the water.
Return to contents
Recipes for dishes with false chanterelles
Not only healthy and edible mushrooms can be used to prepare delicious dishes. There are a number of recipes using these conditionally edible mushrooms.
Mushroom julienne is especially tasty when cooked in portioned pots. It requires:
- 500 g mushrooms;
- 1 cup sour cream 15% fat;
- 50 g hard cheese;
- 2 tablespoons olive oil;
- 1 teaspoon flour;
- salt, pepper, seasonings to taste.
Pre-processed mushrooms are doused with boiling water and the water is allowed to drain. The onion is cut into half rings, the mushrooms into medium-sized strips. First, the onions are lightly fried in a frying pan, mushrooms are added to them, the mixture is salted, peppered, seasonings are added and simmered until half cooked under the lid. Add flour to the future dish and, stirring constantly, wait until it browns. Mushrooms with onions and flour are placed in pots, filling approximately 2/3 of the volume. Next, they are poured with sour cream and placed in the oven for 5 minutes at 180 degrees. After this, the dish is sprinkled with grated cheese and sent back to the oven until the cheese melts. It must be served hot.
Pickled mushrooms are prepared for the winter - such an appetizer takes pride of place on tables next to sauerkraut and sour cucumbers. It can also be prepared from false chanterelles.
For 1 liter of marinade you need:
- 1 teaspoon sugar;
- 1/2 tablespoon salt;
- 2/3 cup vinegar;
- 2 carnation umbrellas;
- 1 bay leaf;
- 3-5 black peppercorns.
1 kilogram of mushrooms is soaked and boiled in advance, then boiled in new clean water for 30 minutes. The liquid is drained and sugar, salt and spices are added. It is better to keep the bay leaf in the marinade for no more than 20 minutes. Next, vinegar is poured into the marinade, the mushrooms along with the liquid are sent into sterile glass jars and sealed with lids. The product is stored in a cool, dark place for no longer than 3 months.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
How long can chanterelles be stored fresh?
After collecting mushrooms, they can be stored at a temperature not exceeding +10 degrees. Do not store in the refrigerator for more than two days after collection; it is better to start processing immediately.
Chanterelles - how to clean
Before processing, chanterelles must be cleared of debris and damaged mushrooms must be discarded. Dirt does not stick strongly to the surface of the chanterelles, so you can remove it with a soft brush or sponge.
Use a knife to cut off the damaged, rotten parts of the mushroom. For subsequent drying, debris is also removed from the records using a brush.
After clearing the mushrooms of debris, rinse them in water, paying special attention to the cap plates. Rinse should be changed by changing the water several times. If the taste remains bitter, soak the mushrooms in water for 30 minutes.
Possible harm from consuming the product
False chanterelles do not cause fatal poisoning. Their unpleasant properties are neutralized by soaking and heat treatment. However, for those who have problems with the digestive tract, it is better not to risk trying dishes with false chanterelles in their composition. Mushrooms themselves are difficult to digest and poorly digested food; they can cause a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and intestines, heartburn, and nausea.
We must not forget about botulism - with improper and insufficient processing, and unscrupulous adherence to conservation rules, there is a chance of becoming infected with this deadly bacterium. The consequences of the disease can be extremely sad.
What to do if poisoning occurs
For people with a sensitive gastrointestinal tract, eating false chanterelles can result in food poisoning of varying severity - it all depends on the amount of mushrooms eaten. Its main symptoms are stomach upset, nausea, vomiting; in severe cases, the temperature may rise, chills, dizziness, and loss of consciousness may appear. In any case, if such symptoms appear after a meal with mushrooms, the first aid will be gastric lavage. It is necessary to constantly drink warm boiled water in large quantities, inducing vomiting until the stomach is cleared. Of course, all this should happen after an ambulance is called, because mushroom poisoning is severe and can cause significant harm to human health.
False chanterelles are mushrooms that were categorically forbidden to be eaten for a long time, considering them dangerous. Today they are classified as more or less edible products, but in order to be able to prepare dishes for the table from false chanterelles, you will have to tinker with them - soak and boil until the mushrooms become suitable for food. Each lover of mushrooms and dishes made from them decides for himself whether the effort expended is worth the resulting result. Usually, the taste of the mushrooms themselves is not very impressive to chefs, but they are used to prepare julienne, pies, sauces and pickles for the winter.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
The nutritional value
Information about the suitability of this mushroom is contradictory; some sources claim that after heat treatment, cocos are suitable for consumption. However, the majority is still convinced of the opposite. As arguments, facts are given about the low nutritional value of the mushroom and the high risks of poisoning.
In order to protect themselves, orange talkers are soaked for several days, then boiled for about half an hour, and only then used for cooking. It has been scientifically proven that when exposed to temperature, the toxins in their composition are destroyed, but the likelihood of poisoning remains. In addition, after so many treatments, the tender pulp of the mushroom turns into a porridge-like mass.