All experienced mushroom pickers are familiar with a very simple rule: if there is warm rain, you can soon go on a “quiet hunt.” The physiology of mushrooms is such that after rain, boletus grows very, very quickly, being one of the fastest growing species in the Russian climate. Next we will consider how many days this species develops to reach an acceptable size for collection.
Processing oil after collection
Butter is useful in any form and is suitable for subsequent culinary processing.
They can not only be boiled or fried, but also pickled, and also create full-fledged culinary masterpieces. Young autumn mushrooms are the most delicious. Before you start cooking, the butter should be peeled from the brown skin and washed in warm water. There is a coloring substance on the cap that does not have the most pleasant taste, so it should be removed.
If the skin is difficult to remove from the mushroom, then you should put it in boiling water for a few minutes, and then quickly splash it with cold water - then it will fall off by itself.
What is a mushroom
To answer the question of how quickly mushrooms can grow, you first need to talk about the features of their development
First of all, it is important to know that they are representatives of one of the three kingdoms of the classification of biological species of living organisms
Therefore, let us draw your attention to the fact that mushrooms are not plants, and certainly not animals. These are completely separate organisms
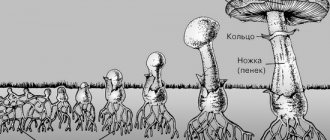
In fact, mushrooms are a fruit that grows from a special vegetative body - the mycelium. What you see on the outside is only a tiny part of what a given organism actually is. In reality, the mycelium is a whole system, the branches of which can go deep underground. It constantly grows, accumulating nutrients, but begins to bear fruit only at a specific period.
Most of the mushrooms that we collect in the forests of our country fully grow within 14 days. This period is often enough for the fruit to fully ripen and take on the required size and shape. However, in some cases, 5-7 days are enough for complete ripening.
It should be noted that the mushroom grows not only in height, but also in width. Moreover, both the stem and the cap continue to increase in diameter even after the upward growth of the fetus ends. However, the cap does not stop growing even after the lower part of the mushroom has finally matured. The fact is that the stem connects the top of the fruit with the mycelium, which is a source of nutrients. The mycelium threads, rising upward, intertwine with each other and form something resembling a fruiting body. Thus, literally in 5-14 days we will see a full-fledged, formed mushroom that can be taken home.
Remember, before cutting a mushroom, it must be inspected. Pre-screening is a critical step to help you stay healthy. Every mushroom picker knows that they are divided into two main types:
- Edible.
- Inedible.
Everything is clear with inedible mushrooms. They contain poison of such strength that even the most poisonous animals and plants on our planet can envy. But as for edible mushrooms, do not under any circumstances collect them near roads. A feature of organisms of this type is the ability to accumulate all the toxic substances that settle in the soil. Poisonous metals from exhaust gases enter the ground and then accumulate in the ground. The mycelium absorbs them in search of nutrients. Therefore, if you decide to go mushroom picking for the first time, try to get as far away from the roads as possible. In addition, most forests have special trails used by mushroom pickers, learn as much as you can about them.
So, we figured out what mushrooms are and found out some of their features. Next, let's talk about how long you need to wait for them to grow after a good rain.
How long does it take for mushrooms to grow after cutting?
Perhaps none of the plants widely used by humans for food grows as quickly to a ripe state as a mushroom. Hence the expression “grows like a mushroom.” However, in the minds of mushroom pickers, the growth rate of mushrooms is usually exaggerated. This happens because some of the mushrooms go unnoticed during collection. When visiting the site again after a day or two, mushroom pickers find mushrooms of considerable size. Cap mushrooms grow very quickly. Over the course of one, several days, and even part of a day, porcini mushrooms, aspen mushrooms and boletus mushrooms significantly increase in size. Most mushrooms grow to medium size in 3-6 days. Under favorable weather conditions, boletus, boletus, and russula can be collected within a day or even a night after they appear on the soil surface. The fact is that the fruiting bodies of the most famous cap mushrooms first form underground, grow there for a long time and emerge almost fully formed to the surface. However, even after this, their growth until full ripening can continue for 8-12 days. Infection with fly and mosquito larvae slows down or stops the growth of mushrooms. During the day, the mushrooms grow by an average of 1-1.5 centimeters in the total height and diameter of the cap. But even among mushrooms of the same species, for example, boletus, the daily growth ranges from 3 millimeters to 3 centimeters, which is due to their individual characteristics and condition. In the first 5-8 days, the growth of the mushroom, both in total height and in diameter of the cap, occurs quite evenly. The growth of mushrooms in height stops one to two days earlier than the growth of the cap in diameter. A day after growth stops, the mushroom is destroyed. Some argue that there is no significant difference in the growth rate of mushrooms at night and during the day. Sometimes there is a noticeable increase in fungal growth after precipitation. And yet, mushrooms appear to grow most at night. You walk through the forest in the evening - there are no mushrooms, it’s empty. And in the morning, the young mushrooms are right there, asking to be put in the basket. So light has little effect on the development of mushrooms, because the mushroom is a child of the shadow. In the summer-autumn period, the average weight of fresh mushrooms on the fourth day of their growth is expressed by the following values: porcini mushroom - 160 grams, boletus - 74, boletus - 45, oiler - 35, moss - 33, chanterelle and goat - 9, milk mushroom - 79 , volushka—17, russula—12 grams. In which forests are the conditions most favorable for mushroom growth? Some argue that mushrooms grow better in young forests, in which the mycelium filaments get along better with young, small, soft-barked tree roots. These roots are located in the top layer of soil and are accessible to fungi. In older trees, the roots are located deep in the ground, so they are less accessible to the mycelium. The practice of mushroom pickers confirms the opposite. There are fewer mushrooms in young forests than in old ones. The first porcini mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, boletus mushrooms and others, as a rule, appear on large trees and most often in the immediate vicinity of them, where there are significantly fewer young, small roots at the soil surface. At the same time, these mushrooms are almost impossible to detect in young forests. Somewhat later, approximately in the second half of August - early September, mushrooms grow relatively evenly in both forests. At the end of the season, mushrooms are again found more in old forests than in young ones. The only exceptions are boletus and saffron milk caps, which grow better in young growth and on the edges. The collector is sometimes struck by the unevenness of the mushroom harvest, that they seem to “wander” from one place to another, from one forest to another. This is explained by changes in fungal growth factors. For example, dry, hot weather set in, and there were almost no mushrooms in the elevated, dry places, but in the lower areas of the forest, where excess moisture from the soil evaporated, mushrooms appeared as if by magic. Therefore, mushrooms cannot tolerate either excessive dampness or dryness.
How to prepare boletus
Depending on which appliances you use, the butter will cook for different lengths of time. For example, if you take a standard pan, the mushrooms will be ready half an hour after they were thrown into boiling water.
If you use a slow cooker for cooking, the butter will cook for 40 minutes. Before frying, you should also boil the butter - 15 minutes will be enough for this. If you plan to marinate mushrooms, then you should place them in boiling water for 20 minutes.
You can prepare many dishes from butter, for example:
- baked potatoes with mushrooms;
- butter in sour cream;
- fresh butter soup;
- zrazy with mushrooms and egg;
- marinated or fried boletus;
- butter with onions and mustard and so on.
Butterflies are universal mushrooms, since they are not only used to prepare delicious dishes, but also festive desserts. They are one of the most popular varieties of mushrooms, growing mainly in coniferous forests and throughout the summer and autumn months
You can prepare a wide variety of dishes from them, but before that it is important to pay attention to quality processing
How to collect correctly
It is best to collect butter beans early in the morning, when the sun has not yet had time to heat them, as they are better preserved this way. If you notice just one mushroom, then look around - there should be at least several more nearby. Butterflies do not grow alone.
There is no point in uprooting boletus; it is better to carefully cut off the stem at the very roots and leave them in the ground. This way you will prepare the soil for next year, because it is from this rhizome that a new mushroom will later grow. Place cut mushrooms cap side down or on their side as this will keep them fresh longer.
Be sure to take a basket or hard bucket with you - do not collect mushrooms in a backpack or soft bag, as this will cause them to rub against each other and crumble. Immediately after the “hunt,” the boletus should be washed and cleaned of dirt, and then begin to cook. They cannot be stored for a long time.
Is it possible to collect large boletus
Adult boletus mushrooms in caps reach 4-10 cm. However, experienced mushroom pickers advise collecting young mushrooms whose caps are no more than 2-4 cm, since they are tastier.
Is it possible to collect dried boletus mushrooms?
It is not recommended to collect dried and old mushrooms, especially near production plants, since such specimens have already absorbed harmful substances.
How fast do mushrooms grow?
Mushrooms are fast-growing organisms and 3 days after their appearance they grow to a marketable state and continue to grow for 10 days, increasing in diameter, without making any allowances for day and night. The growth of the cap along the periphery continues even after the end of growth of the stalk. The process occurs due to the fact that the stalk is an fused filament of micelles and serves as a connecting element of the mycelium with the cap. This is a distinctive feature from other representatives of the natural world. The growth rate of mushroom bodies increases significantly after warm, light, prolonged rain or fog.
During the day, fruiting bodies can grow several centimeters. The slowest growing category includes the chanterelle, which grows by about 1 cm in 1 day, in contrast to the boletus, which grows 15 cm in 5 days. But we cannot discount the periods of mushroom growth, and as autumn approaches, the growth rate of fruiting bodies decreases:
- the first period begins at the end of May and ends at the end of June;
- the second period begins at the end of July;
- the third period begins with leaf fall.
Boletus appear the fastest after rain. They can be collected the day after heavy summer rains. These mushrooms are very tasty fried and pickled, but they dry out in hot weather and are attacked by worms in rainy weather, so they are collected when they are very tiny. begin active growth in the second half of summer. They grow in sunny forest clearings and love coniferous forests.
The most beloved and delicious mushroom is rightfully called the white one, which begins to be found in late June - early July. But for its growth, air humidity of about 60% is required. If drought occurs, the fruiting body of the mushroom dries up. You need to look for it in the litter under the moss. Porcini mushrooms live for about 12 days, after which the fruiting body ages and spores form. You can go to the forest for them, as well as boletus and aspen boletuses the day after the rain, but for chanterelles no earlier than a week later.
Where do mushrooms grow?
Mushrooms like to grow in sparse forests in a little shade, along roadsides, on slopes. They do not like lowlands with standing water. Each fruiting body has chosen its own favorite tree, under which it is most comfortable to grow:
- Under the beautiful birch, white boletus, boletus, and chanterelles are often found.
- In the pine forest you can find russula, boletus, boletus, rower, boletus, and boletus.
- Russula, milk mushrooms, chanterelles, and moss mushrooms are found under the aspen.
- Near the oak tree there are oak trees, moss mushrooms, chanterelles, and honey mushrooms.
Dangers
Even an edible mushroom sometimes becomes a cause of poisoning. Therefore, when collecting fruiting bodies, follow simple rules:
- Do not quietly hunt near highways, railway lines, businesses, cemeteries or burial grounds. The mushroom, like a sponge, absorbs radioactive waste and exhaust gases.
- Do not pick old rotten mushrooms. The fruiting body undergoes a process of destruction.
- Collect young, strong mushrooms, inspecting them for worminess.
- Poisonous (for the preparation of tinctures and ointments) and edible representatives are not collected together.
- Follow the rules for preparing canned food to avoid botulism.
- Do not buy ready-made pickled or salted canned fruiting bodies from strangers in the markets.
- Do not collect suspicious mushrooms.
Mushrooms in the forest can and should be collected. A walk through the forest on a warm summer or autumn day will bring not only moral satisfaction from clean air, but also the opportunity to taste delicious dishes and make preparations for the winter period. Mushrooms are dried, frozen, salted and pickled; many dishes are prepared with the fruiting bodies. You just need to follow the collection rules and not cut off unfamiliar fruiting bodies.
How many days does boletus grow?
Some types of mushrooms are very beautiful, and butterfly (Suillus) is one of them. Butterflies look especially beautiful after warm autumn rains, when they grow in stunning numbers. Butternuts are tasty and quite healthy. This article will give you useful information about when to harvest these edible mushrooms, how long it takes to grow them, and where to find them.
Growing conditions are oily
It must be taken into account that the underground part of the mycelium spreads almost constantly. It does not depend on external weather conditions or the season: summer and autumn.
But for young mushrooms to begin to appear, the right conditions must be present:
- daytime temperature: not lower than +18°C;
- air humidity: about 60–80%;
- soil moisture: 70%;
- soil temperature: from +16°C.
This weather should last for at least a couple of summer days. The above-ground part will grow quickly in sunny weather after a warm shower. To understand where and why boletus grows, you need to consider that it is a mycorrhizal fungus - that is, it is found near the host tree.
Mycorrhiza (symbiosis of mycelium with roots) forms with coniferous trees, in particular with Scots pine. The fungus is embedded in its roots, feeding it with useful substances obtained from the soil within the radius of the mycelium, which is much larger than the root system of trees. In exchange, he receives chlorophyll.
Video: Observing the growth of butter
Distinctive features of boletus include:
- growing near pine trees;
- the presence of a sticky cap with easily removable skin;
- the appearance of hard spots on the stem (oily discharge that hardens when dried), and sometimes there is a ring;
- the presence of large pores located radially.
Few people know that all these signs appear at the same time in oilfish. And this makes it easy to distinguish them from other varieties of mushrooms.
How long does it take to grow after rain?
The first specimens can be collected 12 hours after the rain. But the main thing is that these mushrooms grow in large groups and after 2-3 days in one clearing you can collect a whole basket of them.
In sunny weather
If the weather is sunny, the first specimen will appear in the clearing within 5 hours. But it’s unlikely that you’re going to bring just a couple of mushrooms from the forest, so wait the required 3 days and you’ll get a large selection of wonderful boletus.
Rain and other factors affecting mushroom growth
The fact that mushrooms grow rapidly after rain is not a completely true statement. Rain alone cannot cause massive mushroom growth. A lot of other factors also influence the growth rate. The most significant of them are the following:
- Temperature.
- Humidity.
- Lighting.
- Chemical composition of the soil.
- Harmful insects.
The humidity factor involves two components: air humidity and soil moisture. Each species has its own preferences in this regard, but, if we take the statistical average, the optimal humidity level for good growth is considered to be 70%. Soil moisture should correspond to air humidity. If a prolonged drought occurs after heavy rains, the mushrooms will grow slowly because the moisture in the soil will evaporate quickly. Thus, the soil will become dry and the air will become waterlogged, which will upset the balance.
Mushroom growth
Proper lighting plays an important role in active mushroom growth. Many species prefer to grow in sunny meadows or partial shade. If the forest grows too much, they don't have enough light. As a result, they slow down their growth and become deformed, losing their visual appeal.
Most edible mushrooms prefer slightly acidic soil. The only exceptions are a few species that grow well in sandy, limestone or other types of soil. Interventions in the chemical composition of the soil lead not only to growth stagnation, but also to the extinction of entire fungal families.
Indicators of optimal temperature and humidity for mushroom growth
Mycelium with its terrestrial parts are at risk of infection by the larvae of some types of harmful insects. Affected myceliums bear fruit poorly, and the mushrooms are small and grow very slowly. Mechanical damage provokes rot and other serious diseases. Active growth of most mushroom species occurs in the fall. Then the process of mass decay begins.
In the understanding of most, mushrooms are fruiting bodies, most often consisting of a stem and a cap. In fact, it is only the terrestrial part of a complex organism. The mycelium, or mushroom place, is located under a layer of soil, growing systematically throughout its life. The growth of mycelium is not affected by weather conditions; it grows equally both after heavy rain and during severe frosts.
Dependence of the number of mushrooms in the forest on various factors
In order for mushrooms to grow by leaps and bounds, they need:
- warm weather;
- moisture;
- soil acidity;
- illumination
Suitable air temperature is one of the main factors for the rapid growth of mushrooms.
In order for the spores to germinate and the fruiting bodies to quickly increase in size, an air temperature of about 18-27 degrees is required. In the spring, when the soil at a depth of 10 cm warms up to +1 degree, the daily air temperature is summed up. When its value approaches 500 degrees, the mycelium of early mushrooms begins to develop intensively. If this moment coincides with the beginning of warm rains, a large harvest is observed. The period of growth and maturation of summer species occurs at a total temperature of about 800 degrees, autumn ones from 1000 to 1200 degrees. In different years, there are some shifts in the timing of ripening due to temperature fluctuations and the presence or absence of rain at the moment when the mycelium develops. With increasing temperature, the period of development of fruiting bodies decreases, and with decreasing degrees it increases. The amount of precipitation plays a decisive role. Sometimes mushrooms bear fruit in waves, and this happens as many times as it rains. In the absence of rain, the fruiting bodies are dry and small or do not develop at all. But, if after a dry and hot summer at the beginning of autumn the time of warm and heavy rains comes, then the porcini mushroom will be found in forests covered with moss, where even in hot and dry weather the mycelium developed.
Lighting is also one of the factors affecting the growth of mushrooms. With minor fellings of about 15-25%, the illumination and amount of moisture in the soil increases. The yield of fruiting bodies in such places is higher due to improved growing conditions. If clear cuttings occur, the species composition of fungi changes completely. Soil acidity is of little importance for the development of mycelium. In a slightly acidic environment, fruiting bodies develop better, and some species themselves regulate the acidity of the environment.
Attention!
The beginning, duration and end of fruiting are determined by the biological characteristics of various types of mushrooms and the specific weather during this period and even several previous years.
Where are porcini mushrooms found?
Boletus can grow on any continent except Australia. The porcini mushroom chooses deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests. Boletus can appear on almost all soils, except peaty ones. Sometimes in large colonies.
If in summer there are low average daily temperatures (even if the day is hot) and high humidity, boletus mushrooms can be found in open, well-lit places. Experienced mushroom pickers advise looking for forest gifts around deciduous trees over 50 years old, and coniferous trees over 20–30 years old.
Did you know? “ The plucked mushroom is lost forever
" . This is not only a folk sign, but also the true truth. When the fruiting body is pulled out, it causes serious damage to the mycelium, from which it can even die. The mushrooms are carefully cut off with a sharp tool, and the cut is sprinkled with turf so that next year.
Mushroom growth after precipitation
Water entering the soil encourages the mycelium to actively grow. This process takes from ten hours to 3-5 days. Next, the fruiting body itself grows - the stem and cap. The completion of the life cycle occurs 2 weeks from the moment the top of the cap appears on the surface.
Mushrooms grow quickly after rain, unless there has been a long period of drought before.
Water awakens mycelium
Under the influence of high temperatures for some time, the mycelium is not able to saturate itself with the required amount of moisture. And the soil’s ability to absorb water in dry times deteriorates significantly. This especially applies to areas of land where the soil is open to direct sunlight for a long period of time.
Not every rain can cause mushroom growth.
Short-term precipitation and heavy downpours rarely contribute to the active growth of fruiting bodies. Fungi appear after rain of medium duration, when water gradually enters the soil over a period of time and can accumulate and moisten several layers of soil. The appearance of autumn fogs promotes the development of mycelium, and in spring and summer the same role is successfully performed by falling dew.
Appearance oily
The butterfly mushroom got its name because of the slippery skin covering its cap. It looks like it was painted with oil-based, glossy paint.
Butterflies have many varieties. The color of their cap ranges from yellow to light brown.
Boletus mushrooms are not for everyone. Some mushroom pickers consider them their best mushrooms. But there are forest hunting enthusiasts who do not recognize them at all.
Butterflies are small mushrooms. They are small or medium in size. The largest radius of the cap can reach seven centimeters.
The pulp of the mushrooms is soft, often watery, yellowish-whitish in color. When cut, some types of mushrooms can change color: darken or turn blue. The pulp of the boletus has a fragrant smell of pine forest. Worms love these mushrooms. They also attack young mushrooms, especially in damp, warm weather. A wormy oiler can be distinguished from a good one. It has a flabby appearance.
The legs are cylindrical in shape. Their length varies from three to ten cm, and width from one to three cm.
Butterflies have a covering between the cap and the stem that connects them. When the mushroom grows, it breaks and a border forms on the stem.
What time do boletus mushrooms grow? When to collect boletus mushrooms
The first month of summer arrives - June, rowan, viburnum, and raspberry bloom. It's time for haymaking, and rye is sprouting in the fields. That’s when the first layer of mushrooms appears, which are called “hayfields” or “spikelets”.
Mushroom pickers are in a hurry to the forest - for boletus mushrooms, because the first layer of mushrooms is very short and you need to have time to collect at least a little for frying and cooking.
The first boletuses appear on the edges of the forest, in open clearings. The very name of these mushrooms speaks about their location. Boletus trees grow where there are birch trees: in a birch grove, in mixed forests, even in clearings where there are single trees.
Boletus is suitable for almost any climate. They exist even in the Arctic tundra, of course, in the presence of birches. And even though these trees are stunted, almost creeping
This doesn’t matter to the fungi, the main thing is that there is a root system, from which the mycelium feeds. After all, boletuses live in symbiosis with birch
The boletus has several names: black mushroom, birch mushroom, black mushroom, gray mushroom, obabok, babka. There are also several types of boletus. Depending on its location, the appearance of the mushroom is also different.
Types of boletus
1. The common boletus appears before all the boletus species. Single mushrooms can be found as early as May, which is why this mushroom is also called spikelet.
This mushroom is the largest of the boletus mushrooms. Its cap grows up to twelve centimeters in diameter. The color of the cap ranges from whitish to black-brown. The leg is light, covered with scales, turning slightly pink at the break. This mushroom is found in birch groves.
2. Pink boletus pleases mushroom pickers with its appearance closer to autumn - in August, or even later. It can be found in wet pine-birch forests, on peaty soil, and also along swamps. Often pink birch grows not under the birches themselves, but where the young roots of these trees are located underground.
The cap of this mushroom grows no more than 10 cm in diameter and has all shades of gray, but the stem remains white. Only the black-brown scales on it indicate its relationship with boletus mushrooms.
3. In late autumn, marsh boletus appears in swamps and damp places. He's very small. Its off-white cap is no larger than 5 cm in diameter. It has a long thin stem, the flesh is white and loose. Of all the boletus mushrooms, this is the lowest-grade mushroom. Mushroom pickers do not like it because of its watery pulp.
4. The oxidizing boletus with a yellow-brown cap and the black boletus with a black-brown cap are similar to the pink boletus.
Boletus mushrooms grow very quickly, but this advantage over other mushrooms is also their disadvantage. After all, these mushrooms quickly become wormy. And all because of their loose pulp. Therefore, mushroom pickers, taught by bitter experience, collect only young mushrooms. It has been noticed that even if an adult mushroom by some miracle turns out to be without wormholes, but lies in a basket for two to three hours, a mass of passages in which worms operate inexplicably appears in it.
Boletus mushrooms are most often salted and pickled.
You can use them to prepare soups and main courses, but these mushrooms become very soft during heat treatment, become jelly-like, but do not lose their shape. And the finished mushrooms become very dark. But their condition justifies their excellent taste. And there are enough useful substances in boletus mushrooms.
They contain as much vitamin B1 as in grain products or baker's yeast. Boletus mushrooms contain a lot of vitamin D and PP.
Boletus mushrooms are also dried. True, you need to spend much more time drying boletus mushrooms than drying other mushrooms. Dried mushrooms also turn almost black, which is why they are called black mushrooms. Mushroom powder is made from dry boletus mushrooms, and to improve its taste, it is mixed with porcini mushroom powder.
In terms of nutritional value, boletus belongs to the second category, only the marsh boletus, due to its watery pulp, belongs to the third category.
What mushroom can boletus be confused with?
Sometimes novice mushroom pickers may confuse boletus with an inedible gall mushroom. You cannot be poisoned by such a mushroom, but if at least one gall mushroom gets into a mushroom dish, then such a dish will be spoiled due to its very bitter taste.
The cap of the gall mushroom is similar to both the porcini mushroom and the boletus mushroom. But you can distinguish it from the latter by the pattern on the leg. In the gall mushroom, the leg is covered with a kind of mesh, while in the boletus it is all covered in scales.
But if you still have doubts about the suitability of the mushroom, then such a mushroom is either not put in the basket, or tasted (which is not very pleasant).
When will there be mushrooms 2022?
According to experienced mushroom pickers, it is better to pick mushrooms during the waxing moon phases. In 2022, these are the following days: September (1, 18-30), October (1, 17-31), November (16-29). There are also days for mushroom preparations - September (3-16), October (3-15), November (1-14).
Interesting materials:
Is it possible to plant apple tree seedlings in summer? Is it possible to visit the Trinity St. Sergius Lavra? Is it possible to go nowhere after 9th grade and not go to 10th grade? Is it possible to put 1600 memory on 1333? Is it possible to enroll in a master's program for free after a specialty? Is it possible to congratulate a woman at 40? Is it possible to call the post office and inquire about the letter? Is it possible to celebrate Halloween in Ukraine? Can I represent my interests in court? Can I stop taking antibiotics?
How to look for boletus, where and when is the best time to collect them
However, it is not enough to know in which forest boletus grow. After all, the forest is large, and not under every pine tree you will find this “cute” mushroom. To do this, you need to know where exactly to look for boletus in the forest. The following photo of the butterfly mushroom in the forest shows in what places it likes to grow:
As you can see, the oil can gets along well with coniferous plants. So, in nature, this mushroom interacts well with pine, so experienced mushroom pickers probably know how to look for boletus in the forest. Being in symbiosis with this tree, the boletus does not try to go far, but stays close to the pines. They love sandy soils with lots of pine needles, as well as forest plantations. They are comfortable on spacious forest edges, flooded with sunlight. Since boletus does not tolerate excessive moisture, there is no need to look for them in swampy places. In plantings about 5-8 m high, which have open ground but no bushes or grass, boletus will not grow.
You can see how boletus mushrooms grow in the forest in the photo below:
Although boletus prefer young pines with open glades, they can still be found in mature pine forests. Here their “families” usually live near a forest road or path, where the cover of lichen and moss is disturbed.
So, it is better to collect boletus where coniferous trees grow. Young fir trees, mature pines, majestic cedars, mixed spruce and birch plantings - all this is considered a “paradise” place for them to live. In a word: if there are pine needles under your feet, then the oil can lives here.
It is also very important to know not only where boletus grow in the forest, but also how they grow. It is known that these mushrooms are very friendly and do not tolerate living alone.
They grow in whole families, hiding in the grass and needles. Therefore, when you find one oil can, look around: there will probably be a whole “community” of its relatives nearby.
Where to collect boletus: collection map and locations by region
Where to collect boletus in the Moscow region in 2022? The collection map this year is extensive: boletus is growing in abundance this year in the north and east of the Moscow region. Among the significant mushroom places are the stations Morozki and Fryazino, Tourist and Iksha, Lugovaya, Nekrasovskaya, Semkhoz, Kalistovo and Abramtsevo, Lobnya and Sofrino.
Where to collect boletus in the Moscow region: map of mushroom places for 2020
- Kursk: Chekhov, Serpukhov, Kolkhoznaya, Stolbovaya, Grivno, Lvovskaya;
- Yaroslavl: Pushkino, Abramtsevo, Sofrino, Kalistovo, Ashukinskaya, Semkhoz, Fryazino, etc.;
- Rizhskoye: Nakhabino, Opalikha, Dedovsk, Kholshcheviki, Snegiri, Rumyantsevo;
- Belarusian: Golitsino, Zhavoronki, Khlyupino, Zvenigorod, Petelino, Skorotovo;
- Leningradskoye: Golovkovo, Podrezkovo, Firsanovskaya, Povarovo-1, Alabushevo;
- Savelovskoye: Morozki, Tourist, Lobnya, Lugovaya, Iksha;
- Kazanskoe: Grigorovo, Gzhel, Antsiferovo, Podosinki, Shevlyagino, Sands, pl. 55th and 82nd km;
- Ryazanskoe (in moderation): Konev Bor, Shchurovo, Lukhovitsy, Bronnitsy, Faustovo, Peski, pl. 63rd km;
- Kyiv: Dachnaya, Bekasovo, Rassudovo, Selyatino.
Leningrad region: mushroom places and popular locations where it is important to look with a basket.
Vsevolzhsky district - Agatovo, Toksovo, Kirovsky district - Sinyavino, Lavrovo, Gory village, Priozersky district - Sosnovy Bor, Mallyupelto, Sosnovo and Losevo.
The most mushroom places are rich and not only, according to reviews of mushroom pickers - in the vicinity of St. Petersburg it is Lakhta, the Yuntolovsky Nature Reserve, in the Vyborg region - it is worth going on a quiet hunt near the Saimaa Canal.
In the Lomonosov district there are excellent places near the village of Koporye (along the Tallinn highway), the village. Sverdlovo, Berngardovka - in Vsevolzhskoye, in Tosnenskoye - Nurma, in Volkhovskoye - village. Kolchanovo, in the Luga district - Mshinskaya, in the Podporozhye district - Verkhniye Mandrogi.
And also: mushroom deposits in 2022 - where boletus is collected by region
Where is the best place to pick boletus mushrooms, where to go for boletus mushrooms and how to get there: by train, by car - mushroom places, where to go for boletus mushrooms, and mushroom picker locations.
- In the Voronezh region, the mushroom areas were Somovskoye forestry - to the north of the railway station, to the east (closer to Grafskoye, Orlov, Dubovki), Novousmanskoye and Levoberezhnoe forestries, Semilukskoye.
- In the Lipetsk region it is worth visiting the vicinity of Yelets-Lozovka, visiting the Plekhanovsky forest, the Zadonsky district and Dobrovsky, near Zadonsk (Quiet Don, b.o.), visiting the Yellow Sands, Sentsovsky forest.
- Mushroom places of the Sverdlovsk region: the village of Kashino near the city of Sysert - get from Yekaterinburg by bus from the South Station, near Nevyansk and the village of Kosulino (get there from the North Bus Station, by train or by car), Mount Volchikha - from Yekaterinburg in the direction of Revda, Art. Sports.
- In the Tomsk region: in the Tomsk region - for boletus mushrooms, welcome to the village. Luchanovsky Bor, 86-Kvartal, from Kurlek, in the villages of Zerkaltsevo and Butrino, Shegarsky tract (get there by car, beyond the village of Voronino), the village of Berezkino.
- Mushroom places in Ryazan: Left bank of the Oka - you can go for boletus in the direction of Meshchera - the forests between Polyany, Agro-Pustyn, between Polkovo and Solotchi, near the village. Laskovo, the vicinity of the village of Lopukha (which is between Dubrovichi and Varavsky), in the peat area near Malinovka, Ryabinovka, along the Keletskaya ditch. In Spassky direction: s. Izhevskoye, Fedotevo, forests along the Oka River near the village. Sumbulovo and to the village. Panina (bus stops - Aglomazovo, Vypolzovo, Petrovichi). There are fewer mushroom places on the right bank, but they exist: plantings near the village. Slema and Divovo, near the village. Sushki and Kiritsy (area 270 km), near the Vanchur platform, Ushinsky near Shilovo.
- In the Rostov region: Tarovsky district - pine forests will be met with boletus near Millerovo, st. Veshenskaya, Nizhnekundryuchenskaya, Dubrava, beyond Ust-Donetsk.
- In the Volgograd region: Tsimlyansky massif, Chernyshevsky district, village. Rudnya, Shakinskaya, Kumyzhenskaya Dubrava on the territory of Kalache-on-Don, the vicinity of Lebyazhya Polyana, hut. Ryabovsky and Vityutneva, Trekhostrovskaya villages.
- Tula region: forests near Suvorov, Dubny, near the city of Efremov, in the Chernogorsky, Leninsky, Belevsky and Arsenyevsky districts.
- In the Samara region: Stavropol, Krasnoyarsk part of the Kamyshinsky district, Iskalinsky, Syzransky, Kinnelsky, Buzuluksky bor. Places near Samara: forests near the village. Mechanical plant, Krumoch, village. Shiryaevo, Podgory.
These are the mushroom places and even deposits where boletus grows. Happy quiet hunting!
Features of growth
Mushrooms are living organisms whose growth, in addition to rain, depends on other factors. These include:
- Air temperature. Optimal temperatures range from +10 to +20°C. When the temperature is significantly lower or higher than these numbers, the growth of organisms stops. Sudden temperature changes also negatively affect the development of fungi.
- Air and soil humidity. This factor is individual for each species, but if we take average indicators, then 70% humidity level is most suitable for ripening. If there is insufficient moisture, the growth of mushrooms will slow down, and if there is excessive watering, the spore organisms will begin to rot. Balance is achieved when air humidity matches soil moisture.
- Lighting. If there is insufficient sunlight, the development of the mycelium will slow down, and the mushroom itself will begin to deform.
- The presence of harmful organisms on the mycelium. When the mycelium is affected by larvae, the process of its maturation is disrupted. This leads to the fact that the stem and cap of the spore organism begin to quickly deteriorate and rot.
- The presence of beneficial substances of natural origin. Needles, fallen leaves and other substrates have a positive effect on the formation of mycelium.
Fungi are living organisms whose growth depends on many factors. The illustration for the article is used under the standard license ofazende.com
When to collect?
If we talk about what month boletus is collected, then most often this is done in June, and this period lasts for about two weeks. After this, the described mushrooms completely disappear, and will reappear only in the second half of July. Mass growth begins from mid-August until the first half of September. It is worth noting that this period may differ slightly from when to collect boletus in Siberia.
The mushrooms themselves are not picky; they can grow both in fairly young overgrown pine plantings and between triple pine trees with a bare trunk. In addition, if you correctly determine at what time boletus is collected, you can find them in large quantities on grassy pine edges or in young spruce forests.
When does the butter season begin in Russia?
It all depends on what region we are talking about:
- In the Moscow region, the most favorable time is considered to be the beginning of June. In summer, mushrooms can be collected throughout the summer. The most abundant growth is observed at the end of August.
- In the Leningrad region, boletus also begins to grow from the beginning of June, but due to weather conditions, their most abundant growth occurs only at the end of August - beginning of October.
- In Siberia, the mushroom season is one of the shortest, since nature does not indulge in heat, and frosts come early and suddenly. The most abundant growth occurs in August-October.
- In the Urals the climate is milder than in Siberia. Boletus begins to grow actively at the end of June, but the peak of their distribution in local forests is observed in August, and frosts begin to approach in early October.
Features of mushroom growth after rains
For active growth of the mycelium, moisture is needed, which is taken by the mycelium not only from passing groundwater, but from precipitation falling into the soil.
The process from rain penetration to complete absorption by fungal cells takes from 10 hours to 5 days. After this period, a fruiting body grows from the mycelium.
Life expectancy is up to 2 weeks from the moment the top of the cap appears on the ground surface.
The efficiency of moisture supply is noticeably reduced and the growth period of fruiting bodies increases during prolonged drought and in open, well-lit areas, when rapid evaporation of water occurs in dry air conditions.
Short rain, like heavy rain, does not lead to the active growth of mushrooms. This requires precipitation of medium duration, which evenly moistens the soil, gradually penetrating into the inner layers. Contributing factors are fog in autumn and dew in summer.
A combination of rain and sun is ideal for fruiting, because... An excessively rainy summer and autumn will produce a watery, small harvest.
Development of different species
There are varieties with intensive growth rates and slowly growing ones.
They appear quickly, adding 1-1.5 cm in a few hours or a day:
- from tubular ones - oiler, boletus, boletus;
- from lamellar ones - camelina, russula and champignon.
They are distinguished by the superficial location of the mycelium, which does not grow deeper than 15 cm, therefore a well-warmed and moist mycelium ensures full maturation within a couple of days after the rain.
Grow much more slowly: chanterelle, white, milk mushroom, morel and the like. Their stocky, tightly folded fruiting body does not allow intensive growth and increases up to 3 mm per day. They reach full size 1-1.5 weeks after precipitation.
How long do boletus grow after rain, how long does it take to appear, when to collect
How quickly do boletus grow after it has rained: by time, growth rate
All experienced mushroom pickers are familiar with a very simple rule: if there has been warm rain, you can soon go on a “quiet hunt.” The physiology of mushrooms is such that after the rain has passed, boletus grows very, very quickly, being one of the very fast-growing species in the Russian climate. Next we will consider how many days this species develops in order to achieve optimal size for collection.
How fast do they grow?
The question about the speed of development of forest products is, in its essence, slightly incorrect. The main part, the mycelium, grows regularly and at approximately the same speed. It is not disturbed by atmospheric conditions, even frost.
The aerial part, the fruiting body, is a completely different matter. Its pace depends too much on a variety of conditions: temperature and air humidity, soil content, available amount of moisture, etc. Therefore, if we talk about how much boletus grows over time, it is impossible to give a correct answer.
In the absence of rain, but on sufficiently moist soil, development can last from 7 to 12 days, while compliance with all “wonderful” conditions can lead to the emergence and ripening within 2-3 days.
What determines speed?
The rate of emergence and development not only of butterfly, but also of any other species depends on how beneficially the mycelium feeds and breathes. This is a rather complicated organism that lives, which is average between animals and plants. The physiology of the mycelium is quite complex, and the impact on it of even one seemingly not very important factor can significantly increase or decrease both its growth rate and that of the fungi.
The first factor is well-moistened soil. The second is warm and especially well-warmed by the sun turf, in which the mycelium is located.
Actually, the combination of these moments, and not just the abundance of water, as many people think, leads to the emergence and rapid development of fruiting bodies. If you look at where butter beetles are predominantly found, they actually never appear in dark places.
When do boletus grow, at what time of year?
The period of growth and collection of boletus is quite long and occurs in almost all summer months - June, July, August, and autumn - September and October. The exact time depends on the climatic and weather conditions of the area.
When do the first boletus appear?
It has been noticed that boletus produces crops in waves throughout the season. The first wave occurs in the second half of June, when haymaking time begins. In July, after the rains, boletus will begin to actively grow. This is the second wave when you can go mushroom picking. The most mushroom time is August-September. At this time, trips to the forest for mushrooms are always crowned with success, especially if it has recently rained and the weather is warm.
In what weather do boletus mushrooms grow?
Boletus grows best after rain. On the 2-3rd day after precipitation, you can go on a quiet mushroom hunt. For rapid growth of the mycelium, warmth and sun are also needed. If it rains, but the weather is cool and cloudy, the mushroom will not rush to grow. Autumn specimens are considered the most delicious.
At what temperature do boletus grow?
Butterflies prefer cool weather so that the average daily temperature is no higher than +180C. Fluctuations in night and day temperatures do not affect the growth of mycelium. But if the night temperature drops to -50C, then the mushrooms stop bearing fruit.
Until what time can boletus be collected?
You can collect mushrooms until the end of autumn, when frost sets in. If the soil freezes 2 cm deep, the mushrooms stop reproducing. But if it suddenly became very cold, and the ground did not have time to freeze, and it warmed up again, then they will continue to grow again.
When does the butter season begin in Russia?
In the Moscow region and central Russia, the first boletus appears in early June and delights mushroom pickers with its appearance all summer long. And from the second ten days of August their most abundant growth is observed. At the end of September, their activity subsides, but they can still be collected until the first ten days of October.
In the Leningrad region and northern parts of Russia, boletus also begins to grow in early June. But the most active growth occurs in August-October. In November you can still collect them, but they may be frozen.
Siberia does not spoil its residents with long and hot summers. Even at the end of May there are returning frosts, and already at the beginning of October the first snow falls. The main time for collecting boletus is in August-September, when it is still quite warm and rainy.
In the Urals the climate is slightly milder than Siberian. Therefore, you should go out for collection in June, when boletus is already growing quite actively. The growth of the mycelium continues until the first frost, which usually occurs in the second ten days of October.
Growth time oil
It is better to go for mushroom picking on the second day after the rain, or more precisely, after 12-18 hours. They appear very quickly. They become ready for cooking within a few hours. But for this, in addition to rain and abundantly moistened soil, you also need warm air, as well as good sunlight. All this should be taken into account in order to correctly determine the time to go mushroom picking.
Important! Mushrooms grow quickly, but also spoil quickly. Therefore, you need to collect boletus before the worms attack, which also like to feed on the sweet pulp of these mushrooms.
How long does the butterdish mushroom grow on a good mycelium?
How long does boletus grow after rain?
The mycelium of the boletus is located almost on the surface, i.e. under the top layer of soil - at a depth of 10-15 cm. Therefore, good rain and warm sunny weather are needed. Only under such conditions will the mycelium grow.
Oilseeds are collected in young coniferous forests, as well as in open, well-lit clearings. They grow in large families, which allows you to collect a whole basket in one place. An important role for mushroom picking is played by how much boletus grows after rain.
It is worth noting that boletus on a good mycelium after rain begins to grow the very next day. If a mushroom picker wants to collect strong young boletus, then you should go “hunting” after 12-18 hours.
How long it takes boletus to grow after rain depends on the condition of the soil, lighting, air temperature, etc. On average, 2-3 days are enough to reach full maturity of the mushroom. But do not forget that boletus mushrooms are “fast” mushrooms, which means they will also begin to spoil quickly. The most important thing here is to correctly calculate the moment of going into the forest.
Every mushroom picker knows that the main harvest of boletus occurs in August, September and early October. Therefore, how long boletus mushrooms take to grow depends on two main factors. The first, as already mentioned, is well-moistened soil, and the second is a warm and sufficiently illuminated upper layer of the mycelium.
Many knowledgeable mushroom pickers claim that it takes very little time for an oil can to rise from the ground. So, how long does the butterfly mushroom grow after warm rain? 5-7 hours are enough, and a young, clean, small mushroom appears in the basket. By the way, it is precisely these butters that are highly valued for marinating in jars because they have a beautiful appearance and the appropriate size.
As you can see, in order to correctly determine how much an oil can grows, it is necessary to take into account weather conditions and the characteristics of the local climate. They must be suitable, because even after heavy rainfall, boletus may not appear. Sometimes it happens that there is a lot of moisture, but there is no sunlight and heat. Or the soil is poorly saturated with moisture, and the sun greatly heats the air and the mycelium dries out.