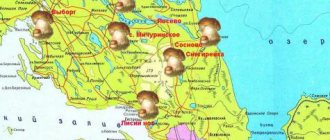
Mushrooms of Kuban 2022 are what interests all fans of “silent hunting”. In this Region, as in many others in Russia, you can find many tasty trophies, but next to them there are also their inedible, dangerous counterparts. In order to return home with buckets full of edible mushrooms, it is important to study all the features of the Kuban region, rich in mountains, forests and plains.
Beautiful, but “crappy mushroom”
This is exactly the case when the title matches the content.
It’s not for nothing that the false valu mushroom or horseradish mushroom is called such an indecent word by the people - not only is it poisonous, but also the flesh is bitter, and the smell it emits is simply disgusting and not at all mushroom-like. But thanks to its “aroma”, it will no longer be possible to gain the trust of a mushroom picker under the guise of russula, which valui is very similar to. False tree grows everywhere, but most often it can be seen at the end of summer on the light edges of coniferous and deciduous forests, under oak, birch or aspen. The cap of a young mushroom is creamy-white, convex, with the edges turned down. With age, its center bends inward and darkens to a yellow-brown color, while the edges remain light. The skin on the cap is nice and smooth, but sticky. The bottom of the cap consists of adherent plates that are gray-white in young valuei and dirty yellow in old specimens. The dense, bitter pulp also has a corresponding color. The leg of the false valuu is quite high, about 9 cm. It is wide at the base, tapers further upward, and is covered with a white coating similar to flour.
Satanic mushroom disguised as boletus
The massive stem and dense flesh of the satanic mushroom make it look like a porcini mushroom, but eating such a beauty is fraught with severe poisoning.
Satanic bolete, as this species is also called, tastes quite good: there is no smell, no bitterness characteristic of poisonous mushrooms. Externally, the satanic mushroom is quite beautiful: the dirty white cap is fleshy, with a spongy yellow bottom that turns red over time. The shape of the leg is similar to a real edible boletus, just as massive, in the shape of a barrel. Under the cap, the stem becomes thinner and turns yellow, the rest is orange-red. The flesh is very dense, white, only pinkish at the very base of the stem. Young mushrooms have a pleasant smell, but older specimens give off a disgusting smell of spoiled vegetables.
Mushrooms autumn and winter 2022 in Kuban
Recipe for mushroom cutlets
The beginning of active mushroom fruiting always occurred in the autumn. It is not surprising that most mushroom pickers, who are not accustomed to a small harvest, try to go hunting in September, when the number of edible species allows them to collect an assortment of useful things, rich in vitamins, macro- and microelements. Low-calorie fruits can be used in different ways, depending on the degree of edibility. Some are suitable only for frying and dietary soups, others are ideal for preparing preparations for the winter. Pates, fried and marinated mushrooms under lids, allow you to extend mushroom pleasure into the winter, when germination is reduced to almost zero. The only exception to the rule is the winter honey mushroom, which prefers low temperatures. Germination is activated from mid-December and continues at temperatures from 0 to 5 degrees Celsius, both in coniferous and deciduous forests on tree trunks. In rare cases, fruiting can be seen at the base on the roots.
Collection time and features of use of mushrooms
Types of plants: list (grade 3). types of indoor plants: list, photos
In terms of the diversity of mushroom species, the Krasnodar Territory can be compared with the Far East, but the peculiarities of soil and climatic conditions allow the collection of fruiting bodies for quite a long time.
Thousands of lovers of quiet hunting travel through suburban forest belts on weekends. Depending on the species characteristics, mushroom picking can begin as early as May, and the last harvest can be harvested before the onset of significant autumn cooling. Of course, main collection dates are approximate and may vary slightly depending on weather conditions each year.
| Species name | Category | Terms of main collection | Use of fruiting bodies |
| White mushrooms | First | Between May and September | Universal |
| Grabovik | Second | Between July and September | Cooking, frying, stewing, drying |
| Yellow hedgehog | Fourth | Between July and November | Boiling, stewing and frying |
| Oiler grainy | Second | Between April and November | Boiling, frying, stewing, drying, pickling |
| The fox is real | First | Between May and November | Boiling, frying, stewing, marinating |
| Oak milk mushroom | Second | Between June and October | Pickling |
| Green moss | Third | Between May and October | Boiling, frying, stewing, drying, pickling |
| Garlic | Fourth | Between July and September | Cooking, frying, stewing, drying |
According to experienced mushroom pickers, the most favorable mushroom places in the Krasnodar Territory are oak forests near the Ubinka River, as well as the Crimean, Seversky, Apsheronsky and Tuapse regions, Goryachiy Klyuch and the outskirts of the city of Gelendzhik. A significant number of milk mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, boletuses, white mushrooms, moss mushrooms, trumpet mushrooms and white mushrooms grow near Barabinsk. Here, regardless of skill, there is always the opportunity to collect a rich harvest of tasty and healthy mushrooms.
Collection rules
Mushroom pickers need to preserve the mycelium so that honey mushrooms can grow again. Following the basic rules for collecting fruiting bodies will help with this:
- The fruiting bodies are cut, not pulled out. You can unscrew it if you want to avoid contact of the mushroom with the metal. This method is preferable.
- Immediately clean the cap of debris and place it in a basket on its side or with the cap down.
- Young specimens are selected.
- Mushrooms are looked for in old forests, especially in plantings older than 30 years.
- It is recommended to collect in a basket, not in buckets. This will keep the mushrooms fresh longer.
Important! Honey mushrooms do not grow on the ground, but only on wood.
Mushrooms of the Krasnodar Territory and Adygea
An excellent variety for lovers of large-fruited sweet tomatoes
The Krasnodar region is distinguished by its amazing flora and fauna, and the mushrooms in this region are extremely diverse. Myceliums in this region are not subject to severe droughts, but live in a temperate climate from the beginning of spring until the onset of frost. In the forests of the Krasnodar Territory and Adygea you can find both edible mushrooms, such as oyster mushrooms, hornbeams, round bighead, common champignons, and inedible ones, for example, pale toadstool, false mushrooms, poisonous entoloma, thin-legged pig. The mushroom season begins in April. For many mushrooms you don’t even need to go to the forest. For example, a type of mushroom such as entoloma can grow in gardens under a peach or apricot tree.
p, blockquote 1,0,0,0,0 —>
Description of mushrooms listed in the Red Book of the region
Kuban is a region where not only edible fruits grow, which can be collected without fear or restrictions. Here you can also find specimens listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation. This:
- Summer truffle. Quite a rare and therefore valuable variety of mushrooms. It has a pleasant nutty taste and exquisite aroma.
- The float is crumbling. A rather rare species of fly agaric, which forms mycorrhiza exclusively with alder. It has miniature sizes (its cap rarely grows more than 3 cm in diameter). The flesh is thin-fleshed, and its color is pale ocher-beige or grayish.
- Cobweb is bluish or bluish-blue. Refers to edible mushroom species. But since it is an extremely rare crop, it is prohibited to collect it in the forests of the Kuban, as well as in other regions of Russia. The fruit got its name for its unusually beautiful appearance and bluish-lilac color.
Compatibility with other drugs
The product can be combined in one container with most pesticides, thus reducing the number of treatments and saving time. The exception is Bordeaux mixture, which is incompatible with Epin due to its alkaline nature.
Epin is not combined with Zircon and other immune stimulants, but alternated.
It is useful to mix the drug with fertilizers. Any complex compositions are suitable, including microbiological ones (such as Baikal M). The growth regulator stimulates metabolic processes inside the plant and increases the absorption of fertilizer.
The drug is combined with insecticides and fungicides:
- Aktellikom,
- Decis,
- Intavir,
- Ridomil Goldom,
- Fufanon.
Storage rules, price and analogues
The product should be stored at a temperature range of -5+25 degrees, isolated from medications and food. The place must be protected from access by animals and children. The price of a 50 ml bottle is 288 rubles, 1 ml ampoules are 13 rubles.
The analogue of the active substance is ComCat (Germany). This is an extract from wild plants containing natural phytohormones. Epin is replaced with other growth stimulants, for example, Agat-25 K, Ribav-Extra, Narcissus, Prorostok, Atlet, Corvitol.
Synthetic hormones successfully help indoor flowers. Use Epin-extra to care for your home greenhouse - the plants will respond with lush green mass and abundant, long-lasting flowering.
5/5 (1 vote)
Active tourism in the South of Russia
based on the book by Kovalenko E.I., N.N., A.E.
To make more complete use of reserves of edible mushrooms, it is necessary to know the timing of the formation of fruiting bodies of each type. The table shows the results of many years of author's research in the Krasnodar region
. The table shows that different types of mushrooms form fruiting bodies at different times, which is explained by their biological characteristics. However, the periods of formation of fruiting bodies depend, as already indicated, mainly on two important environmental factors - temperature and humidity of the soil or other substrate. From April to December, the soil temperature in different areas of our region is favorable for most edible and poisonous mushrooms. In July and August, often in June, soil moisture is low and mushroom fruiting stops. Thus, in summer, the determining factor for mushroom fruiting is soil moisture. When there is precipitation in July and August, mushrooms also bear fruit. Consequently, the timing of the formation of fruiting bodies depends on weather conditions and does not coincide in different years.
It is known that the seasonal development of higher plants depends on the same environmental factors - heat and moisture. Such seasonal phenomena in flowering plants as the swelling of vegetative buds, their deployment, the formation of leaves, budding (swelling of flower buds), the beginning of flowering, mass flowering, the end of flowering, fruit ripening, autumn yellowing of leaves, the beginning and end of leaf fall and many others are called phenological phenomena. They are studied by a branch of science - phenology. Various phenological phenomena coincide with the beginning of the formation of fruiting bodies of different types of mushrooms, for example, with the beginning of the shedding of pollen from male pine cones, the fruiting of the granular oiler begins, with the end of leaf fall in the poplar - the fruiting of the poplar row (poplar mushroom), etc.
Phenological phenomena indicating the beginning of the formation of fruiting bodies of a fungus are called phenosignals. It is very convenient to know these hair dryer alarms. The cherry blossoms are fading - get ready to collect grainy oil cans in 10 days; and if the lily of the valley blooms, then immediately rush for an oil can; in full bloom, the fragrant white acacia is fragrant - in 10 days you will be lucky enough to collect the first fruiting bodies of the porcini mushroom; If the Isabella grapes have already bloomed, then the first beauties are waiting for you - porcini mushrooms. Watch the pheno-alarms, write them down, they will give you a command in subsequent years - it’s time to pick mushrooms. Have an exciting holiday!
When will honey mushrooms start in Kuban?
To harvest a good harvest of mushrooms, it is not enough to know where they grow. We still need to navigate the deadlines. Summer ones are harvested from the second half of August until October. The more southern part of the Krasnodar Territory begins harvesting in June. When autumn comes in Kuban, honey mushrooms should be looked for from the beginning of September until frost. In more southern regions, the “silent hunting” season begins in August. Mass fruiting occurs in September. Winter ones are not at all difficult to find. They stand out well against the snowy background. Mushroom pickers note that winter honey fungus is slightly inferior in taste to its summer-autumn counterparts. But you can collect fruiting bodies in December, January and February. If the temperature drops below 0 °C, the mushrooms stop growing. As soon as warming occurs, they appear again.
Important! The best collection time is early morning. Collected honey mushrooms are well preserved.
Distribution area and mushroom places
In areas with a humid subtropical climate, in particular in the Krasnodar Territory, edible and very tasty birch bark mushrooms grow on fallen trees
It is important to note that among the tree species of mushrooms there are practically no poisonous ones, which greatly simplifies the collection. Edible goats and flywheels most often grow in conifers.
Oak, hornbeam-oak, pine, fir-beech, beech-fir forests and clearings are rich in porcini mushroom, which can grow either singly or in small groups.
In the foothill zones, hornbeam has become widespread, which prefers clayey soils and grows both singly and in fairly large groups. Harvesting a large harvest of yellow hedgehog will not be difficult in deciduous and mixed forests, as well as coniferous forests, regardless of the type of soil.
Granular oiler mostly grows in foothill and mountain zones and is most often found in pine and mixed forests with fairly moist soil. There you can also find oak milk mushrooms, which grow in very large groups. Almost everywhere on wood, often rotten, grows a delicious and very popular garlic mushroom.
Forum 2022 today, what are they discussing?
They mainly discuss the main types of trophies, those mushrooms that grow here in abundance. Mushroom pickers are also interested in what terrain is best to “hunt”.
First of all, the climate of the region is taken into account; here it is mild; the closer to the sea, the more pronounced the features of the subtropical climate are manifested. When searching for trophies, it is advisable to focus on:
- glades of coniferous forests;
- deciduous plantings;
- ravines near lakes and along rivers.
Silent hunt
The natural conditions in Kuban are such that absolutely everything grows here - from wheat to berries. Mushrooms were no exception. This is explained by the fact that Kuban’s location covers several climatic zones at once.
Different parts of the Kuban relief are distinguished by their diversity. Deciduous forests here can be abruptly replaced by coniferous ones, black soil is replaced by clay and sandy soils, which turn into rocky mountains. There is even a saying that if you stick a simple stick into the soil of Kuban, it will easily sprout. And this is actually practically true. The unique climate and fertile lands enable a huge variety of plants to develop in the rich soils of the Kuban.
But along with edible mushrooms, inedible ones also grow well. Therefore, harvesting must be taken seriously. During the mushroom season in the Krasnodar Territory, you can harvest without going into the forest. Here they can even grow in a personal plot under apricots or other fruit trees.
When going on a quiet hunt, you need to take a sharp knife, a wicker basket and a stick with you in order to conveniently move apart the foliage. It is not advisable to use plastic bags, buckets and backpacks to collect nature's gifts. In them, the crop can be damaged, and the mushrooms do not breathe there at all, which can adversely affect the taste of the product.
There is only one rule when hunting quietly. It says that if you are in doubt about mushrooms, you should not touch them. Also, when collecting, you need to know that they grow in families, that is, myceliums. And if one of them is found, his relatives are hiding nearby. They should be cut off with a sharp knife along with the stem.
There is one more point you need to pay attention to. Inedible mushrooms often have a pleasant smell
Therefore, the mushroom picker’s rule applies here again - skip an unfamiliar species.
How to find out if honey mushrooms have appeared in Kuban
There are mushroom years and non-mushroom years. This is the name of the season in which there is almost no rain and humidity. You need to start collecting honey mushrooms in the Kuban when warm, rainy weather sets in. Moist soil is the ideal condition for mycelium germination. After a good rain, after 5-6 days you need to go on a “quiet hunt”.
Important! Frozen fruit bodies cannot be collected; they release harmful substances.
A good reference point for a mushroom picker will be a fallen tree or a stump covered with moss.
Mushrooms of Adegea and Kuban spring-summer 2021
The mushroom season begins in early spring. At this time, honey mushrooms bear fruit well, which can retain their taste even during frost. They don't care about sub-zero temperatures.
In May, those mushroom pickers who are most interested in going hunting:
- Champignon;
- Morels;
- Rows.
In the summer, all these trophies continue to sprout in the forests. There are not as many of them during this period as at the end of spring, but they are still present.
If mushroom pickers go looking for new growth in the summer season, they will find:
- Ezhovikov;
- Grabovikov;
- Green Mossworts;
- Oyster mushrooms.
Such species are preferably collected for pickling or salting.
In general, spring and summer in Kuban are ideal seasons for quiet hunting.
Champignons Morels Rows Hedgehog in the forest Hornbeam Green moss mushroom Oyster mushrooms
Specific data
Many moss mushrooms, morels, honey mushrooms, and fawns can be found in pine forests.
If you go in search of Milk mushrooms, Oyster mushrooms, Boletus mushrooms, Russula mushrooms and Dubovikov, then you need to head to deciduous forests.
If your goal is to collect mushrooms in mycosis with a tree, then you need to go to mixed forests. As for Chanterelles, they, as an unpretentious type of mushroom, germinate in different plantings.
You can even find them in plantings and groves. Delicious Morels are often found in plantings along with Chanterelles.
Important!
In connection with the increasing number of cases of mushroom poisoning (in 2022, the most such cases were observed in Gelendzhik, in Goryachy Klyuch, as well as in the Mostovsky region), experts are drawing attention to the need to study the mushroom map of edible trophies of the Kuban in parallel with the study of the map of inedible counterparts. Toxicologists remind that among 4,000 all types of mushrooms, only 400 are edible, therefore, if a mushroom picker doubts that the trophy in front of him is suitable for consumption, it is better not to put it in buckets and baskets.
Summer mushrooms of the Krasnodar region
Summer is a period of real forest riot of mushrooms in Kuban. It would be quite difficult to list all the species that can decorate a mushroom picker’s basket in the middle of the summer season, because it would result in a whole scientific work. Therefore, I will limit myself to the most common and massively growing species that form the basis of commercial mushroom collection.
Common boletus
Common boletus
It begins to bear fruit here at the end of May, and its season ends in late autumn. A typical boletus mushroom, tubular, the cap is hemispherical or cushion-shaped, the stem is scaly, smooth or widening at the base, with flesh bluish along the edge. A pleasant feature of these mushrooms in the Krasnodar region is that watery specimens characteristic of the middle zone are almost never found here. In Kuban, almost all boletus mushrooms are dense and elastic. True, the worms also eat them very actively and it can be difficult to find an intact specimen.
Boletus
Boletus
Around the same time, aspen boletuses, red and yellow-brown varieties, appear in forests and pendants. These are dense tubular mushrooms with a stem covered in black scales, a dense convex cap of yellow, brownish, red or brick colors. Easily distinguished by the intensely blue flesh when broken.
In the Kuban, these mushrooms grow especially abundantly on the border of the forest-steppe and subtropical zones, in particular in Krasnaya Polyana. Large populations were also seen in the Belorechensk area. In the Krasnodar Territory you can find truly gigantic specimens of boletus mushrooms; the personal record of the author of this article is a mushroom that fell slightly short of 3.5 kilograms. And without a single worm, as is typical for boletus.
Camelina Pine, here more often called “delicious camelina”
A small lamellar mushroom of red, reddish, sometimes with a greenish tint, with a convex or funnel-shaped cap. In the Krasnodar Territory, this delicious mushroom has taken a liking to the foothills and slopes of low mountains, where it is found very abundantly. Very large harvests are collected by local residents in the area of the village with the unpronounceable name Arkhz, and large populations also grow near the village of Chibiy.
Pine mushroom
Real milk mushroom
Real milk mushroom
A large, massive mushroom with a flat depressed or funnel-shaped cap, white or yellowish in color, abundantly releasing caustic milky juice when broken. The real “mushroom gold” of Russia. Unlike more eastern populations, in the Krasnodar Territory this noble mushroom is found mainly in mountainous areas, most often in the vicinity of hornbeams. In the flat parts of the region it can only be found where loamy soils predominate.
White truffle
White truffle
This mushroom is worth mentioning separately, since in our country the Krasnodar Territory is perhaps the only region whose climate is favorable for the growth of this rare and capricious mushroom. In any case, it is regularly found only in Kuban. Externally, the mushroom resembles a rather untidy gray or brown potato of irregular shape.
The fruiting body is completely immersed in the soil, so picking these mushrooms is a separate form of art. In the Krasnodar Territory, it is most often seen in mountainous areas or foothills, in particular, in the vicinity of Apsheronsk. Grows strictly on calcareous soils.
Autumn honey fungus
Autumn honey fungus
Saprotrophic mushroom, grows on weakened or dead wood, small, with a convex or outstretched cap, covered with scales and a characteristic ring on the stalk. It grows in groups; in the Kuban there are often standing trees covered with honey mushrooms from the soil to a height of 3 meters. Here it is more often called “true honey fungus”, since in the Krasnodar region the active growth of this fungus begins much earlier than, for example, in central Russia.
Mushroom pickers begin to collect it from the beginning of June, then the honey fungus produces several “layers” and continues to bear fruit until the end of November. So it can be safely classified as both summer and autumn mushrooms of the region. Here, honey mushrooms are chosen by the mountainous regions of the forest-steppe and subtropical zones, but they are also found on the plains, although not so abundantly.
Description of mushrooms listed in the Red Book of the region
For mushrooms. the best mushroom places in Crimea: where to pick mushrooms in Crimea mushroom season in Crimea
Kuban is a region where not only edible fruits grow, which can be collected without fear or restrictions. Here you can also find specimens listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation. This:
- Summer truffle. Quite a rare and therefore valuable variety of mushrooms. It has a pleasant nutty taste and exquisite aroma.
- The float is crumbling. A rather rare species of fly agaric, which forms mycorrhiza exclusively with alder. It has miniature sizes (its cap rarely grows more than 3 cm in diameter). The flesh is thin-fleshed, and its color is pale ocher-beige or grayish.
- Cobweb is bluish or bluish-blue. Refers to edible mushroom species. But since it is an extremely rare crop, it is prohibited to collect it in the forests of the Kuban, as well as in other regions of Russia. The fruit got its name for its unusually beautiful appearance and bluish-lilac color.
Spring mushrooms
Oyster mushroom
Among local residents, the name “birch bark” is more common. A fungus that parasitizes the wood of deciduous trees. It has peculiar “ear”-shaped caps and a very short or missing stem. Grows in large clumps. In the Krasnodar Territory, it begins to bear fruit from the beginning of May until winter, and guests from other regions of the country are often amazed at the size of the oyster mushroom “families” and its fertility.
Golovach is round
One of the earliest mushrooms in the region, it begins to bear fruit in mid-April. Quite a large mushroom, strongly reminiscent of an ordinary raincoat. It differs in that it has a false stalk, which is part of the general fruiting body. Almost simultaneously with it, the giant bighead, distinguished by its larger size, and the spiny raincoat, a typical spherical raincoat, decorated with small soft spines, appear. All three species are edible only when young.
Gray dung beetle
A low, gray mushroom with an ovoid and later bell-shaped cap, covered with small scales. Unlike other regions, where this type of mushroom mainly accompanies human habitation and agricultural buildings, in the Kuban this mushroom can be found almost everywhere, with the exception of areas with clay soils. This is explained by the rich composition of the soil layer. It begins to bear fruit very early, from the beginning of April.
Common champignon
A fleshy lamellar mushroom with aromatic flesh, a grayish scaly cap, a dense ringed stalk and a pink or brown lamellar layer. In the Krasnodar Territory, its fruiting begins in mid-April, much earlier than other regions. It grows here surprisingly abundantly, sometimes covering entire clearings with its fruiting bodies. I personally, in the vicinity of Apsheronsk, collected three buckets of champignons in 15 minutes at one small forest edge. And this despite the fact that I chose only specimens no larger than 5 centimeters.
Somewhat later, around the beginning of May, another type of champignon appears, field champignons. It is easily distinguished by its anise-scented pulp and white cap with small yellowish spots. In Kuban they grow as abundantly as the common champignon, preferring open space. Very often they can be found on agricultural lands, especially those that are fallow.
Podvishen
A mushroom that resembles a large white or grayish chanterelle with a mealy odor. In the Khadyzhensk region, individual specimens of these mushrooms have been found since mid-April; by the end of the month, cherry blossoms are already bearing fruit abundantly throughout the region.
Porcini
A powerful tubular mushroom with a cylindrical or club-shaped stalk, a convex or pillow-shaped cap and skin color ranging from almost white to brown, depending on the place of growth and climatic conditions. Yes, don’t be surprised - in Kuban it is classified as a spring mushroom. Or, rather, to all-season, since the first specimens appear already in May, and the last finds of porcini mushroom occur even at the end of November. The porcini mushroom is found especially abundantly in the foothills, in open forests.
Moss fly green
A typical representative of moss mushrooms with a velvety cap and yellow flesh that quickly turns blue when damaged. In general, almost all types of moss mushrooms are represented in the Krasnodar Territory, but the green variety appears here first, in mid-April or early May. Its brother, fissured moss, begins to grow a little later, from mid-May.
Dangerous types of mushrooms in the Krasnodar region
What types of mushrooms are there? lamellar tubular tubular mushrooms are called mushrooms in which the underside of the cap, resembling a sponge, consists of small, usually
Some poisonous mushrooms are identical to edible ones. Only certain external signs allow them to be identified. But an experienced mushroom picker will always be able to accurately determine whether a particular mushroom is worth eating or whether it is better to refuse to eat it.
The most famous poisonous mushrooms are fly agarics and toadstools. The first type has a characteristic coloring of the cap. It is reddish in color with white patches. The leg of fly agarics is quite thin, usually white.
The pale grebe gets its name from its pale gray coloration with a slight greenish tint. The hat is dome-shaped, the edges of the upper part are uneven, sometimes wavy. The stalk is usually thin, tapering at the top. The most characteristic external feature is a thin translucent ring that the mushroom has under the cap. Many poisonous species have this element, which allows them to be distinguished from edible ones.
Another poisonous mushroom that is best avoided is called satanic mushroom. It has a cushion-shaped cap that is pale gray in color. Its lower edge is reddish. The leg of this species is very brittle. It is usually colored yellow-red. The flesh of the satanic mushroom is white, but turns blue and red when cut.
Conditionally edible mushroom or dangerous poison?
Svinushka is very common in the Krasnodar region. Until the 80s of the last century, it was considered conditionally edible. It was eaten after long-term processing: it was soaked in water for 72 hours and boiled for 30-60 minutes. Today this mushroom is recognized as poisonous. It contains a dangerous toxin that can destroy red blood cells and cause acute kidney failure, which can even result in death.
The pig has several names: barn, pig, dunka. This is a mushroom with a yellow-brown round cap with concave edges; it grows in large groups in places with high humidity. The straight small leg has the same shade as the upper part. The pulp is fleshy, lacking a pronounced taste and aroma.
Post Views: 713
Warfarin and acetaminophen
The INR is also increased by prednisolone, which is another commonly seen cause of increased INR in patients receiving warfarin.
Awareness of the possibility of a transient increase in INR during a short course of prednisolone may help avoid unnecessary changes in the selected warfarin dose.
A slight increase in INR over a short period of time may be acceptable; however, caution should be exercised in these cases, especially if the patient is also taking other drugs that increase the INR (eg, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole).
Description
Rue fragrant grows up to one meter and is characterized by an erect stem. This is a subshrub intermediate between herbaceous plants and shrubs, which has a woody lower part of the shoots. The leaves are round in shape and contain a large number of secretory glands from which essential oils are extracted. Small, yellow flowers appear in summer. Flowers, depending on their location, can be five-membered (peak) or four-membered (lateral), collected in semi-umbrella inflorescences at the top of the stem. After flowering, a box with very small seeds appears.
What mushrooms to collect in Adygea
These are russula, aspen boletuses, boletus mushrooms, deer horns, milk mushrooms and white milk mushrooms, milk mushrooms and many others. Champignons also grow in Adyghe forests.
Already in mid-spring, you can see the first morels in the aspen forests. Their discovery causes great delight and they look like little wizened old forest creatures or fairy-tale gnomes sticking their curious heads to the surface.
The king of mushrooms, the boletus, appears twice per season: at the end of spring and at the beginning of summer.
Often in mountain forests you can find mushrooms growing on the trunks of fallen or still living trees. But you shouldn’t collect them, since most parasitic mushrooms are not eaten, they are at least not tasty, and at most dangerous.
As everyone has long known, the mushrooms that we eat have a cap and a body. The shape of both caps and legs can be very different. But every type of mushroom today has poisonous counterparts - this is how they try to resist the animals and people who love to feast on them. Therefore, you should only pick the mushroom that you are absolutely sure of.
What mushrooms to look for?
You can go for the first finds already at the beginning of autumn, when the heat gives way to moderate temperatures. Cool air, frequent precipitation and warm sun that has not yet cooled down have a good effect on the germination of mycelium of such species as:
- hedgehogs;
- moss mushrooms;
- rows;
- russula;
- noble boletus;
- hornbeam pickers;
- oyster mushroom
You can reap a good harvest in other months of the year. For example, in the spring you can hunt morels, in the summer you can collect chanterelles and honey mushrooms, and in the fall you can enjoy any tasty mushrooms that are classified as “edible.”
Helpful information!
Unfortunately, the modern world, despite its progressive development, forgets folk recipes and secrets of beloved grandmothers, passed on from one generation to another. So by 2022, despite the large population of mushrooms, both beginners and experienced mushroom pickers are unlikely to be able to name more than 350 species of edible mushrooms and +3000 thousand inedible ones. What can we say about the distinctive features... therefore, in order not to harm your body and the health of your loved ones, you should avoid unknown breeds. The same applies to forest products growing near highways, cemeteries, garbage dumps and factories. Mushrooms, like a sponge, absorb all carcinogens and poisons. There have been cases when, upon contact with a toadstool, edible gifts were saturated with substances that poison the human body.
Rules for using rue
Many doctors are categorically against using fragrant rue for medicinal purposes, despite its healing properties. This is due to the same toxic qualities of the plant. If the dosage is incorrect, the substances contained in rue will not only not solve the health problem, but will also aggravate it.
The plant is poisonous - you need to be careful even with normal contact with it
Before using raw materials as a medicine, you need to know how to prepare it correctly, while maintaining all the healing properties
It is important to remember about the toxicity of the plant and prepare gloves in advance. Harvesting is usually done during the flowering period.
The tops should be cut off, washed under running water and dried in fresh air without exposure to direct sunlight. It is best to store in a tightly closed container in a dark, dry place.
Warning! The shelf life of the dried plant is no more than one year, provided all storage rules are followed.