The Krasnodar region is distinguished by an abundance of mushrooms, and a wide variety of them. The myceliums here are not subject to drought, which means they produce a large harvest. They can be collected from the very beginning of spring until the very first frosts, which occur here in November. In the Krasnodar region you can find oyster mushrooms, hornbeams, honey mushrooms, champignons and others. However, we should not forget that their poisonous or inedible counterparts also grow here.
Some types of mushrooms even grow in gardens, of which there are many. In this case, you don’t even need to go out into the wild, but just drive a few kilometers from the city.
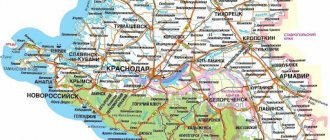
Map of the Krasnodar region.
Mushroom map of the Krasnodar region (Kuban)
The peak of the season depends on the summer: if it was first hot and then rainy, there will be a lot of mushrooms in the forests. Autumn brings rain, after which many people flee to the forests. But mushroom pickers are in no hurry to collect: the first to emerge “into the light” are the poisonous doubles. Mushrooms are most often collected in the Krasnodar region. There are many foothill forests, ravines and fertile meadows. They are most often sent to the following places:
- Absheronsky and Tuapse districts: chanterelles are collected here. Oyster mushrooms and some russula also grow here.
- In the Mostovsky district in the vicinity of Psebay: places are rich in honey mushrooms; they are collected from July until the first ten days of December. Chanterelles are less common (near the village of Zelenchukskaya). Here you can also find rarer specimens of yellow hedgehog.
- the villages of Kaluzhskaya and Smolenskaya: white and boletus are often found not far from them.
- Goryachy Klyuch, Arkhyz region (between Lake Kardyvach and Krasnaya Polyana): honey mushrooms bear fruit well in this area. They are collected at any time of the year (except for the snowy months of winter).
- the villages of Dakhovskaya and Smolenskaya, the villages of Shabanovka and Fanagoriyskoye: milk mushrooms grow abundantly.
- Goryacheklyuchevskaya and Absheronsk districts: here, as well as near the coasts of Gelendzhik, Sochi, Tuapse, boletus and aspen boletuses are searched for in the mountain forests.
- the mouth of the Ubinka River: the oak forests growing here are rich in oak trees.
The Crimean and Seversky regions are also considered favorable. Honey mushrooms are “hunted” in the vicinity of Krasnaya Polyana and in the territory of Goryachiy Klyuch. They get to their destinations using railways and minibuses. It is better to travel to remote areas by car.
Blunt leaf pistachio
The tree, whose height reaches 10 m, has a beautiful and dense crown of an ash-green hue. By autumn, the foliage turns red, decorating the area in which the pistachio grows. The main feature of this tree is the unusual aroma of resin during the ovary period of the first leaves before shedding the crown.
Pistachio begins to bloom in May, and the first fruits are formed in July or August. Nuts appear 8 years after planting. This amazing tree can reach an age of 1000 years. By the age of 125 its height reaches 5 m.
In the Vodopadnaya Glit region, a pistachio-juniper woodland was discovered, in which up to 70 plants grow, ranging in age from several years to centuries. In other regions, pistachio trees are found in smaller quantities.
Mushroom places in the Krasnodar region
These are the Absheron and Tuapse regions. Oyster mushrooms, different types of chanterelles, russula and other edible species grow in large quantities here. Porcini mushrooms can be found almost throughout the region, especially in forests:
- oak;
- birch;
- pine;
- fir
Many of them are found in the following areas and villages, the vicinity of the villages:
- Saratovskaya;
- Kaluga;
- Smolenskaya.
One of the most commonly found mushrooms in these areas is honey mushrooms. They always grow in large colonies and collecting them is not difficult. Boletus mushrooms can be easily found in the foothills - Goryacheklyuchevskaya, Apsheronsky districts, as well as near the sea - the vicinity of the cities of Gelendzhik, Tuapse and Sochi.
According to local experienced mushroom pickers, the most favorable mushroom places in the Krasnodar Territory are oak forests near the Ubinka River, as well as the Crimean, Seversky, Apsheronsky and Tuapse regions, Goryachiy Klyuch and the outskirts of the city of Gelendzhik. A significant number of milk mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, boletuses, white mushrooms, moss mushrooms, trumpet mushrooms and white mushrooms grow near Tuapse. Here, regardless of skill, there is always the opportunity to collect a rich harvest of tasty and healthy mushrooms.
Little tricks of the Kuban mushroom picker
Do you explore the forests of your regions in search of mushrooms?
Of course! I'm going to
The geographical features and climate of Kuban leave their mark on such a seemingly common task as picking mushrooms.
I will list a few tips based on local specifics:
- When going mushroom hunting, choose shoes that will be comfortable for walking not only on the forest floor, but also on rocks. Many types of mushrooms will lure you quite high into the mountains, and moving there in the usual rubber boots with smooth soles will be extremely uncomfortable.
- For the same reason, it is best to use buckets rather than baskets as containers for mushrooms. It is very easy for a person unaccustomed to moving in the mountains to fall here. We can say that you will certainly fall on your first trip. An ordinary basket will most likely not withstand such a test.
- Kuban has a fairly humid climate with high summer temperatures. Therefore, containers for mushrooms must be well ventilated. It is best to make a sufficient number of holes in plastic buckets with a drill for free access of air.
For “mushroom tourism” the Belorechensky, Apsheronsky districts and the surroundings of Goryachiy Klyuch are best suited. These are the richest mushroom crops and fairly easily traversed areas.
When to collect porcini mushrooms in the Krasnodar region
The fruiting season of porcini mushrooms in the Krasnodar region begins in mid-June and lasts until October. And if weather conditions are favorable for growth already in May, then its collection begins much earlier than usual. Even an experienced mushroom picker dreams of finding such a noble mushroom. After all, the size of its cap can reach up to 20 cm in diameter, with a thickness of up to 7 cm. The smell of the porcini mushroom is very pleasant, and it also looks very beautiful and stately. It is considered universal in cooking and is suitable for any processing process.
The white mushroom grows both in small groups and single specimens. Therefore, if you find one such delicacy, look around and look for its relatives. In the Krasnodar region, porcini mushrooms are harvested when constant warmth and light, soft rains begin, thanks to which the average humidity reaches approximately 50%. The oak forests near the Ubinka River are also considered the most mushroom places.
Kuban is a unique region with complex terrain and a variety of climatic conditions, characteristic of several climatic zones. Thus, the mushrooms of the Krasnodar region include many known and previously unknown species, including those dangerous to human life and health. This circumstance allows us to recommend collecting exclusively well-known and guaranteed edible species.
The flora of our planet is incredibly diverse. There are more than one and a half million species of mushrooms alone. However, only a small part of them, called macromycetes, have large bodies. It is these types of mushrooms, visible to humans, that are the object of “silent hunting”. Favorable climatic conditions determine the presence on the territory of the Krasnodar Territory of almost all species of mushrooms growing in the Russian Federation. But not all of them are popular among mushroom pickers. Let's turn to the most recognized, outwardly recognizable and valued species by gourmets. So, more about which ones grow in the Krasnodar region:
The culinary value rating is “average”. Can be used as food boiled, fried, pickled and salted. Suitable as an ingredient for any dishes.
The distribution area is mountain and foothill territories of the Krasnodar Territory (Arkhyz, Kamyshanovaya Polyana, Ilsky village, the vicinity of the Laba River). Favorite places of growth are forest glades, replete with fallen trunks of trees of various species, stumps, and rhizomes of living trees extending outward.
Silent hunt
The natural conditions in Kuban are such that absolutely everything grows here - from wheat to berries. Mushrooms were no exception. This is explained by the fact that Kuban’s location covers several climatic zones at once.
Different parts of the Kuban relief are distinguished by their diversity. Deciduous forests here can be abruptly replaced by coniferous ones, black soil is replaced by clay and sandy soils, which turn into rocky mountains. There is even a saying that if you stick a simple stick into the soil of Kuban, it will easily sprout. And this is actually practically true. The unique climate and fertile lands enable a huge variety of plants to develop in the rich soils of the Kuban.
But along with edible mushrooms, inedible ones also grow well. Therefore, harvesting must be taken seriously. During the mushroom season in the Krasnodar Territory, you can harvest without going into the forest. Here they can even grow in a personal plot under apricots or other fruit trees.
When going on a quiet hunt, you need to take a sharp knife, a wicker basket and a stick with you in order to conveniently move apart the foliage. It is not advisable to use plastic bags, buckets and backpacks to collect nature's gifts. In them, the crop can be damaged, and the mushrooms do not breathe there at all, which can adversely affect the taste of the product.
There is only one rule when hunting quietly. It says that if you are in doubt about mushrooms, you should not touch them. Also, when collecting, you need to know that they grow in families, that is, myceliums. And if one of them is found, his relatives are hiding nearby. They should be cut off with a sharp knife along with the stem.
There is one more point you need to pay attention to. Inedible mushrooms often have a pleasant smell
Therefore, the mushroom picker’s rule applies here again - skip an unfamiliar species.
Poisonous mushrooms of the Krasnodar region
In principle, learning to distinguish poisonous mushrooms from edible ones is not so difficult. In Kuban, there are mainly three types of very poisonous mushrooms, but in total, over 10 varieties of poisonous mushrooms can be found in our region. And, first of all, this is the pale toadstool, poisonous entoloma (very similar to champignon and russula), false honey fungus, etc., but you can also be poisoned by the usual edible mushrooms if you eat overripe, rotten, wormy, or long-stored mushrooms .
Honey mushrooms that are too young, the structure or color of which is not yet clearly defined, can also be hazardous to health. Edible mushrooms under unfavorable environmental conditions accumulate toxic substances, acquiring toxic properties. This is observed near industrial facilities, highways, livestock farms, with the release of toxic substances into the atmosphere, water, and soil pollution. But in any case, if the mushroom is not familiar to you, then leave it in the forest without touching it.
The most poisonous mushrooms in Kuban are:
- Pale toadstool is the most terrible poisonous mushroom. This mushroom is the most difficult to distinguish from russula or champignon. And the poison content in it is very high. To get a lethal dose, it is enough to eat 30 g. Moreover, the poison from the toadstool cannot be removed either by heat treatment, drying, or freezing.
- Fly agaric - it can be identified by its red or burgundy caps and bright white spots. Toxins act primarily on the nervous system. Fatal poisoning can occur even from small doses.
- Entoloma - this mushroom can often be found next to trees such as oak, birch, beech, hornbeam, and willow. It is usually white, gray or yellow in color and feels like silk. For severe poisoning, it is enough to eat only one small piece, but death occurs after eating several mushrooms.
Honey mushrooms in Kuban
It is important for all mushroom pickers in Kuban to know where they grow. This will help you go mushroom hunting in the right direction in the fall of 2022, when honey mushrooms in the Kuban begin to bear fruit. The main distribution area is considered to be the foothills and mountain areas of the Kuban - the vicinity of Laba, Kamyshanovaya Polyana, Arkhyz. Most mushrooms are found in forest clearings where there are fallen tree trunks or stumps. Autumn species can be found in pine forests. In any case, they prefer moist, damp plantings. The most mushroom places in Kuban where you should go for honey mushrooms: Summer and autumn mushrooms grow in the Arkhyz area (Goryachiy Klyuch), between Krasnaya Polyana and Lake Kardyvach. The Seversky district, Krymsky, Apsheronsky, Belorechensky, and the outskirts of Barabinsk are considered productive.
Large growths are found in the Kuban in the Afips valley, near Tuapse and near Gelendzhik. When will mushrooms begin to appear in the Kuban? To harvest a good harvest of mushrooms, it is not enough to know where they grow. We still need to navigate the deadlines. Summer ones are harvested from the second half of August until October. The more southern part of the Krasnodar Territory begins harvesting in June. When autumn comes in Kuban, honey mushrooms should be looked for from the beginning of September until frost. In more southern regions, the “silent hunting” season begins in August. Mass fruiting occurs in September. Winter ones are not at all difficult to find. They stand out well against the snowy background. Mushroom pickers note that winter honey fungus is slightly inferior in taste to its summer-autumn counterparts.
Honey mushrooms in Kuban.
But you can collect fruiting bodies in December, January and February. If the temperature drops below 0 °C, the mushrooms stop growing. As soon as warming occurs, they appear again. Collection rules Mushroom pickers need to preserve the mycelium so that honey mushrooms can grow again. Following the basic rules for collecting fruiting bodies will help with this: Fruiting bodies are cut, not pulled out. You can unscrew it if you want to avoid contact of the mushroom with the metal. This method is preferable. Immediately clean the cap of debris and place it in a basket on its side or with the cap down. Young specimens are selected. Mushrooms are looked for in old forests, especially in plantings older than 30 years. It is recommended to collect in a basket, not in buckets.
This will keep the mushrooms fresh longer. Read also: Where to add dried barberry How to find out if honey mushrooms have appeared in the Kuban There are mushroom years and non-mushroom years. This is the name of the season in which there is almost no rain and humidity. You need to start collecting honey mushrooms in the Kuban when warm, rainy weather sets in. Moist soil is the ideal condition for mycelium germination. After a good rain, after 5-6 days you need to go on a “quiet hunt”. A good reference point for a mushroom picker will be a fallen tree or a stump covered with moss.
Real chanterelle in the Krasnodar region
The cap is 3-9 cm in diameter, up to 1.3 cm thick, convex, depressed in the middle, periodically funnel-shaped. The edge is bent down, wavy, solid, thin. The mushroom is yellow-egg-colored. The surface is dry, smooth, matte, bare, the pulp does not separate from the skin. Fresh taste, pleasant mushroom smell. It is almost never affected by larvae. Hymenophore in the form of branched veins running down the mushroom stalk. The veins that replace the plates are narrow, thick in places, in the form of folds, very sparse, and are not separated from the pulp.
The leg is curved or straight, thinner in the lower part, passes upward into a cap, one-color, solid, eccentric or central, dry, smooth, matte, bare. So where are mushrooms of this species collected in the Krasnodar region? Everywhere! Mountain and foothill belts are suitable for this (the area of the villages of Smolenskaya, Kaluzhskaya, Kamyshanova Polyana, Goryachiy Klyuch, between Lake Kardyvach and Krasnaya Polyana, in the area of Arkhyz, Psebay, not far from the village of Zelenchukskaya), in hornbeam-oak, mixed and coniferous forests ( Caucasian fir, aspen, beech, hazel, maple, hawthorn), on all kinds of soil, mainly with a cover of moss.
Material on the topic: Chanterelle mushroom: where and how to collect it correctly
Oak milk mushroom
An edible mushroom, but requiring special processing before cooking because it contains bitter juice. It has light flesh with a pleasant aroma. The cap is concave in the middle, the color is reddish-orange. The diameter of the cap reaches about 6 cm. The height of the stem is up to 7 cm, and is predominantly light in color. Where and when does it grow? The mushroom grows in deciduous forests in the middle zone and south. Prefers clay soil. It begins to bear fruit from mid-summer until the end of September. They are combing the forests in the west of the Kaliningrad region in search of mushrooms.
The most popular destinations are Kumachevo, Kruglovo, and the Baltic Spit. In the southwest, milk mushrooms are found in Ushakovo, Ladushkinsky Forest, and Devil's Bridge. Varieties. The oak milk mushroom has several varieties in this region: Pepper milk milk. The cap is predominantly creamy white, with occasional reddish spots. The surface in the center of the cap is slightly velvety. A distinctive feature of the mushroom is its spicy peppery taste and aroma, reminiscent of rye bread. Aspen mushroom. It is considered conditionally edible due to the content of milky juice. Grows in warm temperate zones. Grows in groups. Ripens underground. Doubles. Due to inexperience, oak milk mushrooms can be confused with large milkweed or pink milkweed.
Oak milk mushroom.
Yellow hedgehog
The mushroom is also called Hydnum or Dentium notched. The hedgehog has a smooth yellow cap, 3-6 cm in diameter. A yellow-white leg, up to 8 cm high, expands from below. The flesh of the mushroom is light, brittle, and has a fruity smell. Old mushrooms are a little bitter. Where and when does it grow? The mushroom grows in groups near tree trunks in mixed forests. The fruits are harvested from mid-August to the end of November.
Yellow hedgehog.
Violet lacquer
Violet lacquer is a small and beautiful mushroom, which sometimes scares away with its non-standard colors. The violet-lilac color is a distinctive feature of the mushroom. It is dominated by a perfectly round cap, about 5 cm in diameter. The cap is located on a high, thin stem. Virtually odorless. Grows in forests, in damp lowlands on a moss substrate. Mushrooms are collected from the beginning of June until the end of November. Varieties. A variety of the mushroom is the pink lacquer, characterized by a varied cap shape: from convex-depressed in youth to funnel-shaped in old age. The diameter of the cap is 2-6 cm. It has no special smell or taste.
Doubles: purple lacquer is similar to a poisonous mushroom - pure mycena, which often grows in the neighborhood. The main difference between mycena is its rare smell and the presence of white or grayish plates.
Violet lacquer.
boletus
Young mushrooms have a white cap, and with age it becomes dark brown. Mushrooms grow both singly and in small groups. The boletus cap resembles a hemisphere, forming a cushion shape with age. Predominantly white, dense pulp, slightly darkening when cut. The diameter of the cap is up to 18 cm. The length of the cylindrical gray or white leg is up to 15 cm. On the surface of the leg there are dark gray scales located longitudinally. Where and when does it grow? Boletus trees grow in any light deciduous and mixed forests where there are birch trees. Mushroom pickers go to the forest when the bird cherry blossoms. Harvest until mid-autumn. It is better to look for fruits in open glades and forest edges.
Boletus mushroom.
Mushroom pickers collect boletus mushrooms in the Shipovsky forest, near Polessk, near the villages of Kosmodemyansky, Bolshoye Selo, in Sovetskoe forestry. Varieties. There are a huge number of varieties, but in this region the following types of boletus predominate:
- Ordinary. The cap has a reddish or brown color. The stem of the mushroom is dense, massive, covered with gray scales.
- Bolotny. Found on heavily moist soils. The hat is painted in light gray or light brown tones. The mushroom has loose flesh.
- Harsh. The mushroom cap is grayish, brownish and sometimes has a purple tint. The cylindrical stem is creamy at the bottom and white closer to the cap.
- Multicolored. The mushroom cap can be orange, pinkish or light brown. When it rains, the cap becomes slimy. Multi-colored boletuses have white legs, sometimes covered with gray scales.
The boletus's counterpart is a gall mushroom with a pockmarked, gray leg and a white-gray cap. False boletus is very bitter.
Material on the topic: Boletus mushrooms
Morel
Morels can be found in mixed and deciduous forests; they grow on the edges, clearings, and in mossy ditches. Also found in parks and gardens. They grow in groups. Mushroom pickers look for them in places where there have been forest fires. Mushrooms are collected already in early March, after the snow melts. Varieties. There are such varieties of morels in this area: Common. The hat is brown with large cells. Mushrooms are found on forest edges and grassy lawns. The fruits are harvested as early as May, and the season lasts until mid-June. Conical. A special feature of such mushrooms is the bell-shaped conical shape of the cap with shallow wrinkles. Rarely found near birch, willow or aspen. Doubles. Edible morels can be confused with false morels, which are dominated by a dark olive cap and have an unpleasant smell, attracting insects.
Morel mushroom.
Oyster mushroom
Among local residents, the name “birch bark” is more common. A fungus that parasitizes the wood of deciduous trees. It has peculiar “ear”-shaped caps and a very short or missing stem. Grows in large clumps. In the Krasnodar Territory, it begins to bear fruit from the beginning of May until winter, and guests from other regions of the country are often amazed at the size of the oyster mushroom “families” and its fertility.
How oyster mushrooms grow.
Golovach is round
One of the earliest mushrooms in the region, it begins to bear fruit in mid-April. Quite a large mushroom, strongly reminiscent of an ordinary raincoat. It differs in that it has a false stalk, which is part of the general fruiting body. Almost simultaneously with it, the giant bighead, distinguished by its larger size, and the spiny raincoat, a typical spherical raincoat, decorated with small soft spines, appear. All three species are edible only when young.
Gray dung beetle
A low, gray mushroom with an ovoid and later bell-shaped cap, covered with small scales. Unlike other regions, where this type of mushroom mainly accompanies human habitation and agricultural buildings, in the Kuban this mushroom can be found almost everywhere, with the exception of areas with clay soils. This is explained by the rich composition of the soil layer. It begins to bear fruit very early, from the beginning of April.
Common champignon
In the Krasnodar Territory, its fruiting begins in mid-April, much earlier than other regions. It grows here surprisingly abundantly, sometimes covering entire clearings with its fruiting bodies. I personally, in the vicinity of Apsheronsk, collected three buckets of champignons in 15 minutes at one small forest edge. And this despite the fact that I chose only specimens no larger than 5 centimeters.
Somewhat later, around the beginning of May, another type of champignon appears, field champignons. It is easily distinguished by its anise-scented pulp and white cap with small yellowish spots. In Kuban they grow as abundantly as the common champignon, preferring open space. Very often they can be found on agricultural lands, especially those that are fallow.
Common champignon.
Podvishen
A mushroom that resembles a large white or grayish chanterelle with a mealy odor. In the Khadyzhensk region, individual specimens of these mushrooms have been found since mid-April; by the end of the month, cherry blossoms are already bearing fruit abundantly throughout the region.
Porcini
A powerful tubular mushroom with a cylindrical or club-shaped stalk, a convex or pillow-shaped cap and skin color ranging from almost white to brown, depending on the place of growth and climatic conditions. Yes, don’t be surprised - in Kuban it is classified as a spring mushroom. Or, rather, to all-season, since the first specimens appear already in May, and the last finds of porcini mushroom occur even at the end of November. The porcini mushroom is found especially abundantly in the foothills, in open forests.
Moss fly green
A typical representative of moss mushrooms with a velvety cap and yellow flesh that quickly turns blue when damaged. In general, almost all types of moss mushrooms are represented in the Krasnodar Territory, but the green variety appears here first, in mid-April or early May. Its brother, fissured moss, begins to grow a little later, from mid-May.
Edible varieties
Mushrooms in Kuban are diverse. Quite rare species grow in this area.
Oyster mushroom
Category 4 mushroom. The taste often depends on the culinary abilities of the cook, but their combination with meat and vegetable dishes has long become a classic.
Thanks to its unpretentious cultivation and abundant fruiting throughout the warm summer and autumn, it is easily cultivated at home.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
When eaten regularly, oyster mushrooms help reduce the level of so-called “bad” cholesterol in human blood, normalize blood pressure and remove radionuclides. The pulp of these mushrooms contains calcium, iodine and iron compounds and other micro and macroelements, vitamins B, C, E, D2, PP. The ability to lower cholesterol levels is due to the presence in the pulp of the mushroom of a special compound - lovastatin, which biochemists call a natural inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis.
For mass production, we chose varieties that naturally grow on oak, willow, alder and the bark of weak, diseased deciduous trees.
- Oyster. The hat is curled downwards, the diameter reaches 5-25 cm. The color scheme is creamy-beige, the smell is subtle mushroom. In the natural environment it grows by the end of May, bears fruit until September, but under favorable conditions - until frost.
- Horn-shaped. A distinctive feature is the cap, curved upward when ripe, fan-shaped or tongue-shaped. The color is uneven, various shades of beige lighten at the edges.
- Oak. The shades of gray characteristic of the cap of this species depend on the wood, humidity and location of growth. The shape is lamellar, semicircular, the edges are wavy or jagged. The size rarely exceeds 15 cm, the surface of young specimens is covered with a white-gray coating, which is simply cleaned off.
Green moss mushrooms
They grow in single individuals on the edges of coniferous forests, sometimes deciduous. They choose well-lit areas and occasionally find themselves among bushes, anthills, and old stumps. They are considered healthy and tasty; the visible above-ground part is suitable for consumption.
- there are olive-brown, gray, yellow or greenish;
- legs length 10-12 cm, circumference up to 15-17 cm;
- Only the area of pressure on the cap turns blue;
- unripe pulp smells like dried fruit, the structure is dense, old pulp becomes more porous and loose.
Before cooking, you need to remove the skin; only young specimens can be eaten raw - if the “age” is unknown, be sure to boil for 10-15 minutes.
Grainy boletus
The name comes from the specific milky-white drops that appear on the inner whitish-yellow surface and stem in wet weather. Their size is 1-2 mm, drying and becoming dense, brownish-brown.
- the pulp of a young oiler is soft, with a nutty and fruity aroma, overripe fibers become coarser and are excessively saturated with moisture;
- the circumference of a smooth cap without a cover is up to 10-12 cm, the color of the cut remains unchanged;
- The skin is easily peeled off, but during rains it becomes covered with sticky mucus.
The fruiting period is short - from early June to July. Collection places are near coniferous trees, the edges of young plantings, sparse forests with sandy, loose calcareous soil. Granular boletus usually grows in groups.
It is recommended to peel the skin before cooking; it turns black after heat treatment.
Entoloma garden
Entoloma tastes like oyster mushrooms
It grows in mixed, broad-leaved forests; often the mycelium grows in gardens under apricots and plums. Collection season is mid-spring and early summer.
- the body is grayish-brown, the smell is mild, mealy;
- the taste is mostly neutral, there is a similarity to oyster mushroom;
- considered conditionally edible, requires mandatory boiling for 15-20 minutes;
- the surface is silky, glossy, later covered with dark brown scales;
- the plates are sparse, with uneven edges of different widths;
- the curved, cylindrical leg often twists.
An unripe specimen is similar to some poisonous mushrooms: crushed entoloma, tin mushroom, spring mushroom. The first symptoms of intoxication appear 30 minutes after consumption, the condition requires emergency hospitalization.
Graboviki
In appearance, the fruiting body of the mushroom is similar to the common boletus. The second (Russian name) is gray obabok. They are collected from early July to November. The maximum size of the spherical caps is 20 cm, the color varies from light walnut to dark brown.
Summer mushrooms of the Krasnodar region
Summer 2022 is a period of real forest riot of mushrooms in this region of Russia. The most common mushrooms are the following types.
Common boletus
It begins to bear fruit here at the end of May, and its season ends in late autumn. A typical boletus mushroom, tubular, the cap is hemispherical or cushion-shaped, the stem is scaly, smooth or widening at the base, with flesh bluish along the edge. A pleasant feature of these mushrooms in the Krasnodar region is that watery specimens characteristic of the middle zone are almost never found here. In Kuban, almost all boletus mushrooms are dense and elastic. True, the worms also eat them very actively and it can be difficult to find an intact specimen.
Boletus
Around the same time, aspen boletuses, red and yellow-brown varieties, appear in forests and pendants. These are dense tubular mushrooms with a stem covered in black scales, a dense convex cap of yellow, brownish, red or brick colors. Easily distinguished by the intensely blue flesh when broken.
In the Kuban, these mushrooms grow especially abundantly on the border of the forest-steppe and subtropical zones, in particular in Krasnaya Polyana. Large populations were also seen in the Belorechensk area. In the Krasnodar Territory you can find truly gigantic specimens of boletus mushrooms; the personal record of the author of this article is a mushroom that fell slightly short of 3.5 kilograms. And without a single worm, as is typical for boletus.
Pine saffron milk cap or “delicious saffron milk cap”
A small lamellar mushroom of red, reddish, sometimes with a greenish tint, with a convex or funnel-shaped cap. In the Krasnodar Territory, this delicious mushroom has taken a liking to the foothills and slopes of low mountains, where it is found very abundantly. Very large harvests are collected by local residents in the area of the village with the unpronounceable name Arkhz, and large populations also grow near the village of Chibiy.
Material on the topic: Mushrooms: where to look and when to collect
Real milk mushroom
A large, massive mushroom with a flat depressed or funnel-shaped cap, white or yellowish in color, abundantly releasing caustic milky juice when broken. The real “mushroom gold” of Russia. Unlike more eastern populations, in the Krasnodar Territory this noble mushroom is found mainly in mountainous areas, most often in the vicinity of hornbeams. In the flat parts of the region it can only be found where loamy soils predominate.
White truffle
This mushroom is worth mentioning separately, since in our country the Krasnodar Territory is perhaps the only region whose climate is favorable for the growth of this rare and capricious mushroom. In any case, it is regularly found only in Kuban. Externally, the mushroom resembles a rather untidy gray or brown potato of irregular shape. The fruiting body is completely immersed in the soil, so picking these mushrooms is a separate form of art. In the Krasnodar Territory, it is most often seen in mountainous areas or foothills, in particular, in the vicinity of Apsheronsk. Grows strictly on calcareous soils.
White truffle.
Autumn honey fungus
Saprotrophic mushroom, grows on weakened or dead wood, small, with a convex or outstretched cap, covered with scales and a characteristic ring on the stalk. It grows in groups; in the Kuban there are often standing trees covered with honey mushrooms from the soil to a height of 3 meters. Here it is more often called “true honey fungus”, since in the Krasnodar region the active growth of this fungus begins much earlier than, for example, in central Russia.
Mushroom pickers begin to collect it from the beginning of June, then the honey fungus produces several “layers” and continues to bear fruit until the end of November. So it can be safely classified as both summer and autumn mushrooms of the region. Here, honey mushrooms are chosen by the mountainous regions of the forest-steppe and subtropical zones, but they are also found on the plains, although not so abundantly.
Etruscan honeysuckle
The semi-evergreen shrub reaches a height of 5 m and is very different from garden representatives. Honeysuckle leaves are very thick and dense, rounded or blunt. The shrub blooms beautifully: peduncles up to 4 cm long envelop the entire crown and appear on the sides. You can see this amazing picture in May and June, but wild honeysuckle bears fruit in September. It can grow in the form of a vine and a bush spread on the ground.
The number of honeysuckle is extremely small: in Lobanovaya Shlya there are up to 9 plants, and near the village of Yuzhnaya Ozerevka - up to 141. Also, over 290 shrubs are registered on the Big Profile, up to 2600 m long.
Mushroom picking in Kuban in summer and autumn
With the onset of mid-June, there are much more mushrooms in mixed forests. Some of them can only be found in summer, others grow almost until the end of autumn. The latter includes the porcini mushroom, traditionally considered a noble species. Every lover of quiet hunting dreams of finding it. The porcini mushroom grown in the Krasnodar region is no different from those collected in other regions. The hat is round and convex. Over time it becomes flatter. Its color is initially light gray, then gradually darkens to brownish brown. The leg is always light. The pulp is white with a pronounced mushroom aroma and fresh taste.
Noble mushrooms grow in large quantities in beech-fir and oak-hornbeam forests, which are rich in Kuban. This type is suitable for any processing and is considered universal in cooking.
Another interesting mushroom, characteristic of Krasnodar and the entire region, is hornbeam. It stands out among other species with its golden-yellow wrinkled cap. The leg of the hornbeam is most often curved. It has a fibrous surface and thickens at the base. The pulp of this species is fleshy and heterogeneous. It darkens when cut.
Hornbeam grows in foothill areas. Most of these mushrooms can be collected in coniferous forests with clay soil. But even in mixed oak forests, hornbeams are found in fairly large groups. Its fruiting period lasts from July to September. No less popular mushrooms in the Krasnodar region are hedgehog mushrooms. They appear in mid-summer in deciduous and mixed forest zones and finish bearing fruit in November before the onset of cold weather.
The thick and uneven cap of the hedgehog has wavy edges and an irregular oval shape. The color of the upper part of this species is pinkish-yellow. The pulp of the fruit body when cut has the same shade. The pinkish cylindrical leg tapers towards the base. Yellow hedgehog grows on any soil. It belongs to category 4, suitable for frying, boiling and stewing.
The Krasnodar Territory is compared with Primorye in terms of the number of different types of mushrooms. Favorable climatic conditions contribute to such diversity. Here you can find almost all the mushrooms that exist in Russia:
- boletus;
- boletus;
- chanterelles;
- saffron milk caps;
- Russula;
- milk mushrooms;
- rows;
- morels;
- honey mushrooms and many others.
But in addition to edible species, in the Kuban you can find a large number of mushrooms that are unsuitable for consumption. They are represented by dozens of items. Inedible mushrooms can be very dangerous, as many of them are toxic. Therefore, you should always collect forest gifts with extreme caution.
Early edible species
The most famous mushrooms that can be eaten are difficult to confuse with fly agaric or toadstool, which pose a danger to humans. Even in the photo, the difference between some safe and poisonous names is so obvious that, having encountered these species in nature, even a beginner can easily figure out which find can be put in the basket and which is better to stay away from.
The Krasnodar region is surprising in that May, which is not considered a mushroom month, can bring great luck to lovers of quiet hunting. Warm spring weather combined with high humidity and suitable soil types create favorable conditions for early germination of spores of some species.
To see what mushrooms grow in Kuban in May, just come to any mixed forest in this region and carefully look at the ground, fallen trees and old stumps. It is here that the first edible mushrooms of the Krasnodar region usually appear.
One of the first to notice is birch bark or oyster mushroom. It grows on the bark of trees in large groups. This is a small mushroom that appears already in May. Its fruiting period lasts all summer and autumn. The humid subtropical climate is perfect for birch bark. The harvest of this species is always rich.
The oyster mushroom has an irregularly rounded cap. Over time, it becomes slightly concave in the center. The edges of the upper part of the mushroom are thin and curved inward. The diameter of the cap reaches 5-15 cm. Its color can be pale pink, gray or brownish. The skin is not separated from the fruiting body, the flesh of which is light and has a pleasant mushroom smell. The photo is not very accurately able to convey the shade of oyster mushroom, but it is difficult to confuse it with dangerous species, since poisonous mushrooms do not grow on trees.
Another May mushroom that can be found in Kuban is called “green moss mushroom”. It got its name from the olive-golden color of its cap. It can reach 15 cm in diameter. Young mushrooms have a convex spherical cap. The leg has a lighter shade. The skin of the fruiting body is dry. The flesh turns slightly blue after cutting.
Starting in April, in the forests of the Krasnodar Territory you can find granular oiler, which bears fruit almost until the onset of cold weather. This mushroom has a convex round cap of orange-brown color. After rain it usually becomes slippery, as if oily. Hence the name. The leg is quite short, with a thin mesh.
All edible mushrooms that grow in spring can be fried, boiled, dried, pickled or salted. Their great advantage is that the period of active fruiting of many poisonous species does not coincide with the time of their appearance. This partially reduces the risk of poisoning. But still, the collection of this natural delicacy must be taken very responsibly, even in May.
Features of growth
In the climate of Kuban and the Black Sea coast, the process of plant vegetation occurs faster. Mushrooms are not far behind them. Therefore, honey mushrooms have acquired a number of features.
Most often they are parasites on more developed plants. Representatives of the group infect more than 200 species of trees and perennial shrubs. Honey mushrooms can even settle on homemade potatoes.
Mushrooms grow in large families; solitary mushrooms are extremely rare. Less often they become saprophytes. This means that mushrooms are able to grow on stumps and dead trees. In this case, they can generate a pearlescent glow at night.