The usual time for picking mushrooms in the forest is from July to September. However, there are species that can grow even in winter. There are few such mushrooms, but they are edible or can be used for medicinal purposes, and their collection is quite simple, since in winter it is easier to notice the caps on trees or over white snow. Even if you can’t find such mushrooms, during a walk you can recharge your energy from the fresh forest air and calm your nerves or think about something deep along with the quiet and long sleep of the forest.
What mushrooms are called winter mushrooms
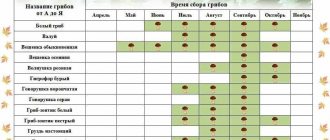
There are species that do not grow all winter, but only at the beginning of the season. For example, tinder fungi, autumn honey mushrooms and rows can be found only during the period of early frosts. Early winter mushrooms are afraid of thaws and lose their nutritional qualities when thawed, so they can be collected only before the first rise in temperature above 0 °C.
Picking mushrooms in winter is quite simple, since it is easier to notice the caps on trees or above white snow. Other types of winter mushrooms do not spoil during warming, but with the arrival of warm temperatures they begin to grow rapidly.
Signs
Edible mushrooms are mushrooms that do not require special processing and can be cooked and eaten immediately. Edible mushrooms do not contain any toxic substances that can harm the body; they are absolutely safe for humans.
The nutritional value of edible mushrooms falls into four categories, from high-grade to low-grade mushrooms.
In order to distinguish edible mushrooms from inedible ones, you need to know some common distinguishing features:
- edible mushrooms do not have a specific pungent odor;
- the color of edible mushrooms is less bright and catchy;
- edible mushrooms usually do not change color after the cap is cut or broken;
- the flesh may darken when cooked or broken;
- In edible mushrooms, the plates are attached to the stem more firmly than in inedible ones.
The video clearly shows how to distinguish edible mushrooms from poisonous ones using the example of the most common mushrooms. It also tells you what to do in case of poisoning:
What are the benefits of picking winter mushrooms?
Picking mushrooms in winter is much easier than in summer. They are much easier to spot in the snow than under summer vegetation and branches. Another problem that automatically disappears in winter is the lack of mosquitoes. Winter mushrooms usually grow on tree trunks, so you don’t have to bend over to pick them up. Many mushroom pickers ski through the forest.
Mushrooms available for collection in winter are located high on trees or on dry stumps
Description
The diameters of the caps of these mushrooms vary from 2 to 10 centimeters. The surface of the cap is smooth to the touch, slightly slimy. The color can be yellow with a brown or orange tint, with a dark center and almost transparent edges. Young mushrooms have a convex cap with rolled edges; as the mushroom matures, it straightens. An interesting feature of flammulina is the dependence of color on the type of tree on which it grows.
The plates can grow to the stem, or they can remain free, the color ranges from white to ocher. Characteristic bridges are visible between the plates. With age, the color of the plates darkens, they become sparser and wider. The spore powder, like most mushrooms, is white. Disputes can take different forms.
The pulp of the winter mushroom is thick, dense, cream-colored, with a soft, pleasant taste and persistent mushroom aroma.
The leg is long but thin. The structure of the leg is dense, elastic, cylindrical in shape. It is painted in different shades of brown.
List of edible mushrooms that grow in winter
Among winter mushrooms there are edible and conditionally edible representatives. Most of them are well known.
Winter honey fungus (Flammulina velutipes)
Winter honey fungus appears at the beginning of winter or at the end of autumn. In some cases, it persists even after the New Year. Young honey mushrooms have a bell-shaped cap; as they grow and develop, it straightens out and becomes flat. The diameter of the cap reaches from 2 cm to 8 cm. It can have a yellow-ocher or rusty-brown color. The plates are white or light ocher. The thin leg has a velvety texture and black color, its length is from 3 cm to 8 cm.
Winter honey fungus is an edible mushroom that appears either at the beginning of winter or at the end of autumn
Winter honey mushrooms grow in bunches among the trees. During thaws, they can be hidden under a layer of snow. It is convenient to look for a yellow cap on white snow.
They usually choose as a place of growth:
- linden;
- willow;
- maple;
- poplar;
- elm.
In rare cases, mushrooms of this species grow on oak, apple and pear trees. They are found on both forest and garden trees. They love the south side, so there are noticeably fewer of them on the north side.
In most cases, winter mushrooms grow on the south side
Before cooking, honey mushrooms need to be boiled, as they contain toxins that need to be eliminated. To remove harmful substances, you need to keep them in boiling water for 20 minutes. In addition to toxic components, winter honey mushrooms contain flammulin, which is used to treat cancer.
In the Far East, winter mushrooms are grown as a mushroom crop. They are used not only for food purposes, but also in pharmaceuticals and traditional medicine.
Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus)
Late oyster mushroom is the most noticeable of all the mushrooms growing in the winter forest. They are often found on sale, so mushroom pickers quickly recognize them by their appearance. Sometimes they can be confused with polypores of the gray or whitish variety, but knowing one feature, this can be easily avoided: polypores always lack a stalk, while oyster mushrooms have a rather pronounced base.
The close-knit growth in groups also gives it a resemblance to the tinder fungus. Oyster mushrooms choose dead or fallen trees as their habitat. As a rule, these are aspen or birch trees. Many mushroom pickers claim that oyster mushrooms like to settle on poplars. It is not so common on other deciduous trees.
Oyster mushroom - the most common winter mushroom
The oyster mushroom has a side stalk with a smooth, expanding transition into the cap. The shape of the mushroom resembles a shell, so it is sometimes called a shell or oyster. Most often the cap is light gray in color, but sometimes bluish, yellowish and brownish representatives are found. The diameter of the cap reaches 10 cm. Due to the special structure of the stem, it is difficult to confuse the oyster mushroom with other varieties.
These mushrooms can be prepared in many ways. Whatever processing option is chosen, they must be boiled and drained before cooking. In cooking, only the caps of oyster mushrooms are usually used, and the hard stems are set aside. However, you can also cook these parts of the mushrooms by boiling them and passing them through a meat grinder or mixer.
Oyster mushrooms can be used to prepare many dishes for different tastes.
According to many people, fried oyster mushrooms have the best taste. Mushrooms straight from the winter forest, picked by hand, turn out to be tastier than store-bought ones or those sold at bazaars.
Late panellus (Panellus serotinus)
Panellus is often confused with oyster mushroom, although it has nothing in common with it. Panellus grows from September to December, as long as there are no severe frosts. For full growth, it requires a temperature of +3 to +8 °C. It is collected from stumps and dry trunks of deciduous trees. Old mushrooms are best left alone as they are too tough to eat. Most often, panellus is consumed fried, but it can also be pickled or pickled. Taste qualities are at a decent level.
Late panellus grows on stumps and dead wood of deciduous trees
Chaga (Inonotus obliquus)
Birch chaga is considered a particularly valuable mushroom prey during the winter season. It has large dimensions and a non-standard appearance, so it is unlikely to be confused with other types of mushrooms. The cap forms a large growth on the tree, the mass of which can be several kilograms. Grows on old birch trees in places where the bark is broken. Chaga grows tightly to the tree trunk, so to remove it you will need a large knife or even a special camping ax.
Birch chaga is a valuable mushroom, the main advantage of which is its pronounced antimicrobial and antiseptic properties.
This mushroom has strong antimicrobial properties. Substances included in the composition of birch chaga:
- strengthen the immune properties of the human body;
- activate the central nervous system;
- have a positive effect on metabolism.
Chaga is used to create medicines in conventional and traditional medicine.
Auricularia auricula-judae
Auricularia grows throughout the year. It is collected during the winter temperature rise and in early spring. This mushroom looks like a growth in the form of a brown cap. They usually settle on dry trees, but sometimes on living ones. As a rule, they choose elderberry and alder as their home, in some cases maple, ash or elm.
Auricularia auriculata grows on dead wood and on the branches of deciduous trees and shrubs
This mushroom has become widespread in Chinese cuisine. There they call it “black tree ear”, despite the fact that it only turns black when it dries. Soups and salads are prepared from it.
The taste of auricularia is not for everyone; not everyone will like the feel of it either.
Late hygrophorus (Hygrophorus hypothejus)
Hygrofor usually grows on the outskirts of a pine forest among young coniferous trees. Life time is from August to December. An unremarkable small mushroom forms a mycorrhizal relationship with the roots of the pine tree it happens to be next to. Very often boletus grows next to hygrophores.
Hygrophorus late grows in mixed forests next to linden and oak trees
The edible mushroom tastes especially good after roasting. It is not marinated and salted so often.
Hypholoma Capnoides
Compared to winter honey mushrooms, this mushroom is quite rare. The cap is brown or yellowish-gray, the plates are white-yellow when young and darken in old age to a grayish-blue tint. The sulphurous honey fungus has a poisonous counterpart - the sulfur-yellow honey mushroom. They differ in smell: the edible variety has a pleasant and delicate aroma, while poisonous mushrooms have a bitter and foul aroma. Gray-plated honey mushrooms cluster on the stumps of coniferous trees and dry standing trunks.
Seroplate false honey fungus - a rare winter mushroom
Inedible and useful gifts of the forest
Fungal vegetation, as we know, is not necessarily food. You can go on a quiet hunt in order to get valuable medicines. For example, the cold period of the year is the right time to collect birch chaga.
However, for those who don’t know, we’ll give you a hint: if the subject of your search is birch chaga, then it’s better to go after it with a good, large cleaver. Or better yet, with an axe. Because this woody growth is dense and weighs several kilograms. You are unlikely to separate the chaga from the trunk with a simple knife - it is easier to chop it off.
It should be noted that the benefits of birch chaga are also recognized by traditional medicine. The plant activates immune processes, strengthens the nervous system, and helps improve metabolism.
Even if a trip to the forest does not bring the desired result, you will definitely saturate your body with crystal clear air and get a lot of pleasant emotions.
Happy quiet hunting!
Source: https://spezrezerv.ru/
- Notify about new comments.
What other mushrooms can be found in late autumn and early winter?
At the end of autumn you can still find ordinary mushrooms, the main growth time of which is summer and early autumn. Sometimes they just linger for a longer period.
Purple row (Lepista nuda)
Not all mushroom pickers are familiar with the purple row, because this species is not well-known. However, it often grows in gardens and parks, where it remains unnoticed throughout its life. When young, the mushroom has a fleshy, convex cap, reaching 14 cm in diameter. By adulthood it becomes flat, and by old age it curves slightly. The edges of the mushroom are slightly curved.
The violet row grows not only in the forest, but also in parks, gardens and in private plots. Not only the mushroom cap, but also the stem with plates has a purple color. As it ages, it may darken and acquire a brown tint. The mushroom plates lighten slightly and expand. The shade of the stem is lighter than the cap. The leg has a massive base and dense consistency in youth, but becomes loose in old age.
The smell of the mushroom pulp depends on where it grows. Sometimes it emits a pronounced mushroom aroma, in some cases it turns out to be mealy or aniseed.
Green rower (Tricholoma equestre)
The cap is medium in size (up to 14 cm) has a brown center and yellow-green edges, while it has a slippery and uneven surface. The leg is usually hidden in the ground or only slightly visible. The pulp has a distinct floury smell.
Green row
Earthy row
Ground grass (Tricholoma terreum)
It has a small gray cap (up to 9 cm), conical in youth and flat in adulthood, and a thin elastic stem. The pulp has a mild mealy aroma and good taste. In Crimea, this is one of the most popular types of mushrooms.
Polish mushroom (Imleria badia)
The Polish mushroom has a white stalk, a convex semicircular brown cap from 3 to 12 cm in diameter, and a light yellow porous layer under the cap. Its other name is “chestnut moss fly”. It is popular and edible, and can be prepared in a huge number of ways.
The Polish mushroom is valued by mushroom pickers for its exceptional taste, aroma and abundance.
Mushrooms love moss and sandstones and can most often be found under coniferous trees.
White mushroom (Boletus edulis)
The porcini mushroom is one of the most famous species among mushroom pickers. Despite the fact that it is difficult to classify it as a winter species, in warm latitudes it can grow until the end of autumn. The boletus has a convex brown cap on a massive white stalk, reaching up to 30 cm in diameter. The caps of different mushrooms differ in terms of the brightness of the shade, which can reach whitish. The mushrooms have crisp white flesh with excellent taste.
Porcini mushrooms can be collected until late autumn
From "House Economics" 1956
At the end, I would like to cite excerpts from the book Home Economics, published in 1956. “For hot salting, for 1 kilogram of mushrooms take 2 tablespoons of salt, 1 bay leaf, 3 peppercorns and cloves, 5 grams of dill, 2 blackcurrant leaves. Pour half a glass of water into the pan (per 1 kilogram of mushrooms), add salt and put on fire. When the water boils, add the mushrooms. During cooking, carefully stir the mushrooms with a paddle so that they do not burn. When the water boils, carefully remove the foam with a slotted spoon, then add pepper, bay leaf, and other seasonings and cook with gentle stirring. ...The cooked mushrooms must be carefully transferred to a wide bowl so that they cool quickly. The cooled mushrooms should be transferred along with the brine into barrels or jars and closed. The brine should be no more than one fifth of the weight of the mushrooms. Mushrooms are ready for consumption in 40-45 days.”
It is recommended to prepare a marinade for mushrooms as follows: “For 1 kilogram of mushrooms you need to take one and a half tablespoons of salt, half a glass of vinegar, 1 bay leaf, 0.1 grams each of pepper, cloves and cinnamon and 2 - 3 grams of dill.”
Particular attention is paid to vinegar: “The quality of marinades largely depends on the type of vinegar. Marinades prepared with grape or table vinegar... with aromatic herbs are especially tasty.
If the vinegar is strong (6 percent), then it must be diluted by half with water, then add salt, sugar, spices (pepper, cinnamon, cloves, nutmeg, coriander, bay leaf, etc.), let it boil, and then cool.” .
And one more useful tip: “To protect against mold, the marinade is poured with a thin layer of vegetable oil. The jars are covered with parchment paper and tied with twine. Marinades should be stored in a cool, dry place.”
A. Anashina. Blog “Moscow Region”, www.podmoskovje.com
Website "Moscow Region", 2012-2019. Copying texts and photographs from the site podmoskоvje.com is prohibited. All rights reserved.
When and how to collect winter mushrooms
Winter types of mushrooms almost always grow on trees with which they form a symbiosis. They can be collected from October to December, before severe frosts set in and massive snowdrifts formed. At this time, the fruiting bodies retain nutrients. Mushrooms are very visible behind bare branches that have lost their leaves, so they are easy to look for.
To remove chaga or tinder fungi from the trunk, you will need a hatchet, since these types of mushrooms grow firmly to the tree. For the rest, a regular kitchen knife will suffice. To extract hygrophorus growing between the roots, no improvised means are required - it can be freely pulled out of the ground without it.
A winter mushroom trip is a great opportunity to take a walk through the forest, admire nature and breathe fresh air. You can quickly prepare a dish from mushrooms collected in the winter forest and feed your family with it.
Have you tried picking mushrooms in winter? What kind of “booty” did they return with? Share your stories in the comments.
Application in medicine
Winter honey fungus is unique in its beneficial properties. These mushrooms contain more protein and amino acids than many berries, vegetables and fruits. Flammulin contains trace elements such as zinc, phosphorus, potassium, manganese, iodine, copper and many others. In this regard, only beef and milk can compete with the winter honey mushroom.
Scientists and doctors have conducted in-depth biochemical studies that have shown a high content of various antioxidants in these mushrooms. Experiments with the discovered substances revealed their ability to fight various malignant and benign neoplasms. In Japan, a special map was even compiled on which you can see the dependence of the occurrence of cancer on the level of enokitake consumption. The more often mushrooms appear in a person’s diet, the lower the risk of tumor development.
Winter honey fungus is characterized by antibacterial and antiviral properties. Thanks to this, mushrooms significantly increase human immunity. The use of flammulina has a restorative and supportive effect on the liver and stomach. The content of substances that lower cholesterol levels in the blood allows the winter mushroom to be used in the manufacture of medications for the prevention and control of atherosclerosis.
This mushroom is also widely used for cosmetic purposes. Based on it, special masks, lotions and creams are prepared that eliminate dryness and flaking of the skin and have a rejuvenating effect.
Attention! Winter honey fungus is one of the few mushrooms that are resistant to severe atmospheric pollution. They can grow in the center of a big city, on the sides of polluted highways
But this in no way means that they can be collected in such places. These mushrooms accumulate a huge amount of harmful and even toxic substances from the surrounding air. Consumption of such mushrooms risks serious poisoning.
Winter honey fungus is similar to a poisonous mushroom - galerina fringed. Since these species bear fruit at different times, the likelihood of confusing them is quite small. But still, it will not be superfluous to remember the main difference between these mushrooms: galerina has a ring on its stem, characteristic of poisonous mushrooms.