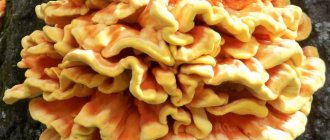
Description of appearance
Sulphur-yellow false honey fungus - these honey mushrooms are inedible, like edible varieties, and are found in large families on stumps and rotten wood.
hat
False honey fungus is sulfur-yellow.
Small in size, on average reaching from 2 to 7 cm in diameter. Initially hemispherical, bell-shaped, then it becomes flatter. The color is light yellow, with brownish or grayish tints. The central part is painted in darker colors, sometimes red-brown.
Pulp
It is also light yellow in color and does not change color when cut or broken. At the same time, it gives a specific unpleasant aroma.
Under the cap there are plates, they come very often, thin, initially also have grayish-yellowish tints, but darken with age. At first they become greenish, then olive and almost black.
Honey fungus is sulfur-yellow.
Leg
Quite large, grows up to 10 cm in height, but no more than 0.5 cm in diameter. It has a regular cylindrical shape, without thickening.
Straight, fibrous, quite soft, hollow inside. It is painted in the same way as the cap - in light yellow colors.
Spore powder
Painted in rich brown shades.
Growing area
Sulfur-yellow false honey mushrooms grow in large groups. Rotting and dead trees, as well as various trunks and stumps, are chosen as a place. They can even grow in the roots of trees. Most often found in coniferous and deciduous forests, as well as in mountainous areas. The largest number of these poisonous mushrooms is found in the northern regions of the middle zone.
The period of mushroom growth begins in late spring and ends in mid-autumn.
Similar species
Autumn honey fungus.
First of all, this species is similar to edible autumn honey mushrooms.
To distinguish them, you need to pay attention to several signs:
- The blades of edible species are not colored green.
- You can notice a small ring on the leg of the false honey fungus.
- Its cap is often olive-colored with gray shades.
However, young false twins may not have these characteristics, and in old mushrooms the rings almost completely disappear. Therefore, it is also worth smelling the mushrooms and looking at them carefully. If even slight doubts arise, you should definitely not take the mushroom.
Virulence
The sulfur-yellow false foam contains aldehydes and ketones. They have a toxic effect on the stomach and intestines. Other organs also suffer when these poisons enter the human blood. Serious negative consequences from taking this mushroom are observed in children and elderly people with chronic diseases. Death is rare, but the recovery process is very long.
The first sign of poisoning is the development of acute gastroenteritis. Symptoms of this disease include: diarrhea, acute abdominal pain, vomiting and nausea, and less commonly, fever. At the first symptoms, you must urgently call an ambulance.
Doubles
If you confuse an edible mushroom with a sulfur-yellow false fungus, you can be seriously poisoned. The ordinary edible honey fungus is very similar to the false honey fungus. The main difference between them is the color of the plates: edible honey mushrooms are endowed with white or cream plates, without green or other shades.
p, blockquote 10,0,0,1,0 —>
The sulfur-yellow pseudo-foam also has a number of similarities with the sulfur-yellow pseudo-foam. The second mushroom is edible. Young sulphurous pseudofoams have a convex cap that becomes flat.
—>
The color of the cap is predominantly brown or red-brown. However, there are also yellow caps. The plates of young mushrooms are white, while in mature species they acquire a bluish tint. However, they do not have any green color. Many edible sulfur-plastic pseudofoams remain in the forest because they are easily confused with the sulfur-yellow poisonous honeyfoams.
—>
Interesting Facts
Despite the fact that consumption of the mushroom, as a rule, does not lead to death, after 2-6 hours severe nausea, vomiting occurs, and the person may even lose consciousness.
The poisonous mushroom, sulfur-yellow honey fungus, is easily confused with the edible varieties of honey mushrooms. In order not to put your health at risk, it is advisable to learn to distinguish between these types.
Beneficial features
Honey mushrooms are recognized as tasty, aromatic mushrooms and, being productive and affordable, are readily collected by mushroom pickers. The fruiting bodies contain easily digestible proteins, including valuable amino acids.
At the same time, they have a low calorie content - only 18–20 kcal per 100 g of finished product and can be successfully used as a source of valuable nutrients when losing weight.
Honey mushrooms are rich in microelements useful for the hematopoietic system - zinc and copper; just 100 g of these mushrooms will satisfy the daily need for these elements. They contain B vitamins, especially a lot of thiamine, and ascorbic acid, which have a positive effect on the immune system and nervous system.
The anti-cancer substance flammulin, which has an inhibitory effect on the development of sarcoma, was discovered in winter mushrooms. In the tissues of honey fungus, researchers found antibacterial compounds that slow down the development of Staphylococcus aureus and other virulent microorganisms.
Contraindications for use
Honey mushrooms of various types are grown on an industrial scale on wood waste or straw, considered a healthy food product, and in some countries a delicacy. And yet, consumption is associated with risks for people suffering from inflammatory processes of the stomach and pancreas.
Contraindications for use are diseases of the liver and gallbladder, including its resection. Improperly prepared, undercooked mushroom dishes without sufficient heat treatment can cause digestive upset and allergic reactions. Mushroom products should not be included in the diet of children under three years of age, pregnant or lactating women.
A variety of honey mushrooms, growing compactly near stumps and among lush meadow grass, are healthy, nutritious and tasty. They are suitable for preparations, first and second courses, and contain valuable antibacterial substances, vitamins and minerals. A knowledgeable mushroom picker will not ignore these small fragrant mushrooms, and there will always be a place for them in the basket, next to the noble boletuses and bright saffron milk caps.
Is it possible to eat honey mushrooms?
Of all the mushrooms listed in this article, only sulfur-yellow fungus is truly dangerous. Eating it is guaranteed to lead to poisoning, although the risk to life in general is not very great.
As for all other false honey mushrooms, complete safety and edibility have been proven only in relation to the sulphurous or poppy honey mushroom. All other doubles of the real honey mushroom are in the conditional “gray zone”.
For example, the red brick false honey fungus has a pronounced bitter taste, which is why in most countries of the world, including Russia, this mushroom is simply classified as inedible. At the same time, this mushroom is eaten in Italy, the USA and Japan. Obviously, with prolonged heat treatment, the weak toxins that brick-red honey fungus contains evaporate or disintegrate. However, is it worth the risk for a mushroom with very dubious taste? This is a rhetorical question.
A similar story occurs in the case of Candolla's false honey fungus, also known as Candolla's psatirella. For a long time, in official mycology, the mushroom was classified as inedible or even toxic. Today this statement is highly doubted. Many experts and experienced mushroom pickers say that the mushroom is quite safe if it is thoroughly boiled. However, due to the fact that the condole false honey fungus has questionable taste and is generally difficult to distinguish from related species, it is not recommended to collect it and eat it.
Finally, watery honey fungus also does not represent any sane culinary value, and therefore from this point of view is not interesting to mushroom pickers. At the same time, there is no clear information regarding whether this mushroom is edible in principle, or whether its consumption poses any undesirable consequences.
Thus, a completely safe mushroom, which can be eaten along with real autumn and summer honey mushrooms, in this list is only poppy or sulphurous honey fungus. We recommend ignoring all other mushrooms from the “false honey mushrooms” category and not collecting them.
False honey mushroom and honey mushroom: main differences
Although only one species is truly dangerous, the species is an evolutionarily established set of individuals characterized by a single ... mushrooms that fall under the category of false honey mushrooms should never be risked. Only after learning to distinguish between false honey fungus and honey mushrooms can you safely go on a “quiet hunt”. Otherwise, you are putting your health and life at unnecessary risk.
Since several individual species are called false honey mushrooms, remembering the distinctive features of each of them will not be easy at first. Especially if you have to study them not in the forest using a living example, but on the Internet using a verbal description and not always expressive photos. For this reason, it is better to focus on the distinctive features of the honey mushrooms themselves.
The first rule that any mushroom picker must follow: never take a mushroom if you are not sure about it. This means, no matter how beautiful and seductive a mushroom may look, if you have doubts about its species, it is better to pass by.
The main distinguishing feature of a real honey mushroom is the so-called “skirt” on the leg - a membranous ring, which is the remnant of the blanket that protected the mushroom in the first days of its life. The absence of a cover on the stem means that in front of you is any kind of mushroom (possibly edible), but definitely not honey fungus.
Next, you should evaluate the overall color scheme of the mushroom. Good edible honey mushrooms are painted in a faded light brown color, while false ones have a brighter and even variegated color. However, this does not always happen. For example, the gray-yellow honey fungus is also quite dull and not very bright, but it can be recognized by the yellow color of the fruiting body, which is not typical for honey mushrooms.
Take a closer look at the surface of the cap. In honey mushrooms it is completely covered with small scales, while false honey mushrooms, on the contrary, have a very even and smooth surface. True, honey mushrooms’ scales also disappear with age, but it’s still not worth losing your vigilance because of this.
Another distinctive feature of real honey mushrooms is the color of the plates under the cap. They should be the same color as the entire mushroom (that is, light brown), or a little lighter. If the plates are yellow, greenish, gray or olive-black, you should not take such a mushroom.
Finally, you can determine whether this is really a honey fungus, or its “evil twin,” by smell and taste. Real mushroom has a pleasant aroma - classic mushroom. But many false honey mushrooms have a not very pleasant earthy odor.
As for taste, you need to be extremely careful here. Experienced mushroom pickers sometimes decide to try a raw mushroom by touching it with the tip of their tongue, and then immediately spitting generously and rinsing their mouth with water. If such a test shows even a hint of bitterness, you should not put the mushroom in a bucket. However, we do not recommend that you use this method, since it is extremely risky for beginners. However, if among the mushrooms on your plate that you thought were completely edible, you come across at least one bitter one, you should throw away the entire portion and immediately consult a doctor.