The mushroom season in Malaysary usually begins at the end of April, when average daily temperatures reach +10 degrees and above. But this year the warmth came much earlier, so the mushroom season has already opened.
The southern part of the ridge is rocky, unlike the northern
Two main signs indicate that the mushroom season has begun in Malaysary. First, Central Asian or, as they are also called, steppe turtles came out of hibernation en masse. The second sign is that Ferula Dzungarian (herbaceous plant), or carrot plant, is blooming. Now the carrot plant is tall and there are a lot of turtles. Therefore, you can go for mushrooms. The harvest season has just begun and will last until about mid-May.
Ferula jungarica, which we call carrot grass. When this grass grows, it's time to go mushroom hunting
What is a white steppe mushroom? Many will be surprised, but it has nothing to do with champignons. The real name is steppe or royal oyster mushroom. The white steppe mushroom is quite large - the length of the leg is from 3 to 7 cm, the cap has a diameter of 5–12 cm, sometimes reaching 20 cm. Unlike many other mushrooms growing in Kazakhstan, the royal oyster mushroom is very rarely wormy.
Steppe oyster mushroom or white steppe mushroom is the object of mushroom hunting
Steppe oyster mushroom is definitely an edible mushroom; in other words, it can be eaten in any form, including raw.
Characteristics of single-barrel mushrooms
Despite the fact that single-barrel fruits have distinct characteristic features, they can be confused with inedible and even poisonous fruits, so you should be extremely careful when collecting them.
Appearance and photo
The fruit has a wide (from 4 to 30 cm) flat-convex cap with a curled edge. Old individuals can be distinguished by the funnel-shaped shape and smooth skin of the cap. Due to the shape of the cap, inexperienced mushroom pickers may confuse a single barrel with a chanterelle. The color changes from gray (or white) to yellow during the life of the fetus.
The leg is smaller than the cap, has a shape narrowed towards the base and is white or brown in color. The age of the fetus can also be assessed by the very cobwebby, cotton wool-like interior of the stem. Because it is too small, it is often not visible and may give the impression that the mushroom is growing without it at all.
Morphology
The single barrel has rare but fairly wide plates. Its flesh is white and quite dense. Old fruits lose the elasticity of the pulp and it becomes loose. The fruits have a pleasant, faint mushroom smell. The single-barrel mushroom is often called the most delicious mushroom from the Oyster mushroom family. The spores need grass to develop, which explains where the fungi spread.
Place of distribution in Crimea
Mushroom pickers advise going for a rich harvest to the valleys near Mount Demerdzhi, the Bakhchisarai forests, and the steppes near the Donuzlav and Sasyk estuaries. In addition to the Crimean region, single barrels can be found in the Lower Volga region.
Single-barrel oyster mushrooms differ from other varieties of the oyster mushroom family in their rather specific place of growth - they love the grassy cover of the steppe. While all other mushrooms usually grow under trees, single-barrel mushrooms can be found in open, damp areas. During periods of severe drought, you don’t have to look for them, because, despite their steppe habitat, they really love water.
Eating
Single barrels can be eaten and even more so - they are quite valuable for cooking. Mushroom pickers believe that these fruits are the most delicious among all members of the family and therefore are very popular. In addition, this variety contains a large amount of useful substances.
Can be used for drying, pickling, and preparing a variety of dishes. Please note that old mushrooms can only have caps. The legs become rougher with age, sometimes you even have to clean the joints between the knives and the caps.
Collection rules and conditions
Single barrels bear fruit almost all year round, from April until November. In especially warm years, fruits can grow even in early March, so when going into the forest you can almost always find them.
Note!
The best harvest time is during periods of heavy fog or heavy rain, and single barrels do not grow during drought. Another feature that will help with the search for these mushrooms is that at the height of the season they can be found near pastures, farms, near roads, ravines, and reservoirs.
Difference from false, inedible mushrooms
Most often in collection areas you can find false mushrooms, pale toadstools and fly agaric mushrooms. Mushroom pickers advise not to put the entire harvest in one basket and not to rush to collect everything you find in the clearing, because inedible mushrooms grow apart from others.
You can distinguish an edible fruit by the way it grows: unlike many other edible and poisonous mushrooms, the one-barrel mushroom grows in groups and quite often the stems of the fruit are either as close to each other as possible, or even grow together and it seems that the fruit has several caps at once. This is the surest sign of this delicious fruit.
Advice from experienced mushroom pickers on collecting edible fruits
You may be interested in: How do edible talkers differ from false mushrooms? How many days after rain do mushrooms grow? Bitter mushroom: photo and detailed description
Avid mushroom pickers willingly share their experience of mushroom picking, giving less knowledgeable fans the following recommendations:
- if there is any doubt about the edibility of a mushroom, it is better to leave such a fruit in the forest;
- You should go looking for mushrooms in well-known mushroom places so as not to return with an empty basket;
- even noble mushrooms can be poisonous if they grow near busy highways and industrial sites;
- breaking out and twisting the fruits can cause damage to the mycelium, and it will stop bearing fruit - it is better to use a knife;
- they go shopping for mushrooms with baskets, because in plastic bags the fruits wrinkle and lose their attractiveness;
- some species (for example, caesarean mushroom) are listed in the Red Book of Crimea - they cannot be touched.
Mushrooms are no joke! To avoid troubles, it is better to carry out your first trips with experienced mushroom pickers.
Useful properties and restrictions on use
Single barrels are valuable not only for their taste, but also for their high content of nutrients. In terms of the amount of vitamins and amino acids, representatives of this variety are close to meat and dairy products. The only vegetables that contain more protein than single-sided vegetables are legumes.
This is interesting!
Another feature that distinguishes single-barrel mushrooms from other mushrooms is that they do not accumulate harmful substances, but, on the contrary, promote their removal from the body; the fruits also have anti-inflammatory properties and help maintain normal insulin levels.
Eating fruits can also help cope with the following diseases and conditions:
- decreased immunity;
- atherosclerosis;
- high cholesterol levels.
Single barrels contain a huge amount of vitamins (especially group B), antioxidants, and beneficial acids. Their effectiveness in the treatment of anemia has been proven, and can be used to influence the symptoms of liver, kidney, and eye diseases.
The mushroom has a unique tonic. Some athletes use single barrels to get a dose of energy before competitions, as a natural alternative to doping drugs. Like other mushrooms, single-barrel mushrooms are not included in the diet of children, pregnant and lactating women, and patients with gastrointestinal pathologies.
Growing at home and in the country
Steppe mushroom has been grown at home for quite some time. It can be planted in an apartment, on a stump, in a substrate or in beds. The main advantage of this mushroom is that the mycelium grows quickly, does not require special care and has high yields.
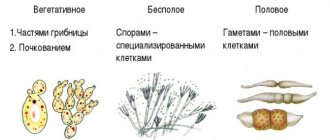
How does the steppe oyster mushroom reproduce?
Steppe oyster mushroom reproduces in three ways:
- Vegetative. The process involves mycelium, which is located under the soil. Mycelium threads have the ability to separate from the total mass, while continuing to grow independently, increasing their system of threads.
- Asexual. The main component is a spore with flagella. In windy weather they disperse over long distances. The spore penetrates deep into the earth and begins to grow actively, but only if the climatic environment allows it. In this way, a new mycelium is formed. For young oyster mushrooms to grow, the two spores need to be close to each other.
- Sexual. The reproduction period is the formation of secondary mycelium, when the primary threads form pairs. In this way, additional mycelium is formed in the soil, from which young mushrooms will appear.
Conditions for growing white steppe mushroom
The most common way to grow steppe mushroom at home is to use a log that should not be rotten.
Other requirements:
- ideal log circumference – 15-30 cm, length – 30-50 cm;
- temperature regime – +10-27ºС;
- the best time for planting is from mid-spring to mid-autumn;
- humidity is about 90%; after the first rudiments of the fungus appear, this figure should be reduced to 80%.
Planting process and care
The technology for growing steppe mushroom at home using logs is as follows:
- Make several holes in the log. Their size should not exceed 1 cm. To speed up the process, it is better to use an electric drill.
- Place several strands of mycelium into each hole formed. Carry out the procedure wearing gloves.
- Pour wax into the holes or seal them with wooden plugs.
- Place the logs in the open air.
Water the entire log every other day. This is necessary to maintain vital humidity levels.
The log will grow overgrown within 2-3 months. If the planting procedure was carried out correctly, then after a few weeks you will see a white coating on the stump.
Eringi can be cultivated using substrate in bags. To do this, purchase ready-made mycelium in the form of grains. Place in containers with sawdust or straw and create the right temperature conditions.
Recipes and cooking features
The most common and easiest way to cook single barrels is to marinate. To do this, you will need to rinse well and clean the fruits from soil, sand, and grass residues. After this, you should boil the water - the mushrooms should be added only after boiling. On average, they need to be cooked for no longer than 30-40 minutes, stirring occasionally and skimming off the foam. The marinade recipe for steppe mushrooms is very simple.
To prepare, you will need the following ingredients (per 1 liter of water):
- 3 teaspoons vinegar;
- 2 tablespoons each of crystalline sugar and salt;
- a pair of bay leaves;
- pepper and cloves to taste.
As soon as you see that the fruits have settled to the bottom of the pan, you can remove them from the heat and put them in jars, immediately pouring them with the pre-prepared marinade. Then roll up the cans and place them upside down, wrap them up.
Pickled oyster mushrooms
You can also prepare very tasty hot sandwiches, which are suitable for a gourmet breakfast, as an addition to soup, and as a snack on the holiday table. To prepare the dish, you need to take:
- slices of white bread or toast;
- a small amount of vegetable oil for frying.
Filling:
- smoked bacon;
- onion;
- mushrooms (about 200 g);
- hard, melting cheese (100-150 g is enough);
- sour cream and spices (salt, pepper, etc.) to taste.
Hot sandwiches with oyster mushrooms
Chop all the ingredients for the filling and fry them over medium heat until cooked. At the end of frying, add a little sour cream to make the appetizer tender. All that remains is to cut the bread and put the filling on it, tightly sprinkling everything with grated cheese.
Next, place the sandwiches in the preheated oven and leave there until the cheese melts. The appetizer is served hot; for aesthetics, you can garnish it with a few sprigs of parsley or other herbs to taste.
Poisonous and inedible species of white steppe mushroom
The white steppe mushroom is often mistaken for the lilac-legged row and leucopaxillus petalis, edible mushrooms that grow with it at the same time. Poisonous and inedible mushrooms similar to it have not been described.
Lepista personata
The diameter of the cap is 5-12.5 cm, the shape is flat-convex, the color is whitish with a purple tint. The edge is slightly tomentose, turned up, fleshy. The pulp is grayish-violet, fleshy. The leg is dense, widened at the base, 4.5-9.5 cm in height and 1.8-2.5 cm in diameter, light purple or bluish in color.
The mushroom grows in deciduous forests, shrubs, meadows and pastures in Russia, Central Asia, Europe, Japan, China, Australia, North and South America. The season begins at the end of March and continues until the beginning of summer, repeating in October-November.
The species is an edible mushroom, pleasant to the taste; it is dried and pickled.
Description of the mushroom place
Mushrooms in Crimea can be found on Ai-Petrinskaya Yayla. The forests in Luchistoye in the area of Mount Demerdzhi produce a rich harvest.
Quiet hunting in the Bakhchisarai forests will be successful. In the East, mushroom places are located in Feodosia. Crimean mushroom pickers harvest in the steppe zone in the area of the Donuzlav and Sasyk estuaries. To get the mice, they go to the village of Kolchugino and to the area of the astrophysical observatory. For boletus they go to the villages of Zelenogorskoye and Stroganovka.
Hunting for saffron milk caps is carried out near the village of Rybachye, and for chanterelles in the village of Mramornye.
Appearance time
Edible mushrooms of Crimea are collected all year round. Everything here depends on weather conditions. Mushroom pickers go hunting after a rainstorm, 3 days later, when clear, warm weather sets in. During this period of time, mycorrhiza develops. Spores located on tree roots and upper layers of soil quickly produce mycelium threads and spread to neighboring areas.
Favorable temperature for the development of mycelium is 18-20℃. If you go for forest products in cold weather, you will be left without a catch.
How to store?
Before storing the mushroom, it must be cleaned. There are several ways to store steppe oyster mushroom at home:
- In plastic containers. Both fresh and boiled mushrooms can be placed in such a container. Storage space - refrigerator or freezer.
- Dried. An inexpensive and most effective method to preserve the taste and beneficial properties of the mushroom. You can dry it in the oven or in the fresh air, but not in direct sunlight.
- In the form of pickles. Mushrooms are salted hot and cold. In the first case, they should be boiled, placed in jars, sealed with lids and stored in a place where the temperature does not exceed +8ºС. When cold-salting oyster mushrooms, rinse, soak for a week in salt water, then proceed with the procedure of rolling and storing.
- Marinating . You will need a saucepan and jars. For preparation, you can use mushrooms boiled in salted water or fresh ones, which are initially boiled in a marinade and rolled in it.
Steppe mushroom does not need to be soaked before storage. It will pick up a lot of excess moisture and lose its taste.
Steppe oyster mushroom is a mushroom that is not similar to its counterparts from the oyster mushroom family. It has a pleasant taste and unobtrusive smell. Grows in many countries of the world. It has no poisonous counterparts, but some people need to use the mushroom with caution.
0
0
Copy link
Where do champignons grow?
Mostly all varieties of the described fungi belong to the category of saprophytes. They prefer to grow in well-manured soil, soil rich in organic matter. They can often be found in meadow and forest humus, steppe zones, anthills, on tree bark, and in dense spruce forests.
Depending on the preferred substrate, all champignons can be divided into five main groups:
- forest , which grow only in the forest;
- soil saprotrophs growing in open, plant-free areas;
- desert or halophytes , found in desert areas;
- herbophiles , which grow exclusively in grass;
- mushrooms that grow in open grass glades or forests.
Most of the described varieties grow in the forest-steppes and steppes of Europe and Asia, the prairies of America, and the meadows of Australia and Africa.