City dwellers rarely encounter mushrooms. Therefore, they don’t even realize that this is a large population. According to some sources, it has more than 100,000 subspecies. And some microbiologists claim that if you sort mushrooms also by area of growth, as well as by individual subgroups, then you can generally count about one and a half million species.
Mushrooms are widespread, they can be found in Russia, and in more southern and northern regions. Mushrooms have a lot of features that the average person doesn’t even know about. Let's find out in detail about the kingdom of mushrooms.
The structure and reproduction of mushrooms
A mushroom is not only what appears to our eyes in the form of a cap, stem and dense pulp. A significant part is still rooted in the ground.
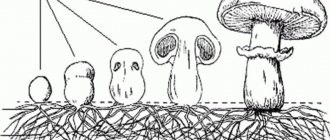
The fruiting body actually consists of two components. Most often it is a fleshy cap that sits on a thin stalk.
From Latin - Fungi.
The fungus sits tightly in the substrate, an environment where it can receive the necessary nutrients for growth and development. We all know that mushrooms have a mycelium and that it should not be damaged. However, mycelium is a complex concept. The cobweb, which is a kind of root and is located in the ground, is mycelium. Threads that can extend almost several meters from the place of growth of the fungus are called hyphae.
The fruiting body grows due to the fact that the hyphae located in the ground begin to compact and gather into dense boxes. The boxes grow and enlarge, causing the mushroom to rise and grow.
Mushrooms have what is called a spore layer. It is most often found at the bottom of the cap. There are three types of spore layers in total.
- One of the most common is the lamellar spore layer. We are used to seeing it in chanterelles and russula. It is characterized by the fact that the spores are securely hidden in the plates, and begin to fall out only when the time comes.
- The next layer is tubular. The spores are contained inside tubes, which become thinner and open over time, and the spore powder spreads around.
- And finally, the rarest type is the intrafruit spore layer. This means that the powder is formed directly inside the fruiting body. A similar phenomenon can be observed directly in raincoats.
In addition to their basic structure, fungi can also form so-called rhizomorphs and mycelial strands. These are very important components on which certain functions lie. For example, rhizomorphs and cords are parallel hyphae that are connected to each other. They can reach several meters in length.
Sometimes the mycelium can be modified under the influence of certain factors and forms sclerotia, that is, a dense weave that forms mycelium. It is interesting to follow the procedure for propagating mushrooms, since it is non-trivial, and for the most part is not similar to the method of propagating plants. Mushrooms immediately have three ways to leave offspring. They reproduce vegetatively, sexually and asexually. Let's look at each type in more detail.
Vegetative
This type of reproduction occurs as a result of the separation of parts of the mycelium. A small piece is separated, this all happens naturally and begins to exist separately from the general mycelium on its own. If the soil is fertile and weather conditions allow, the small spore quickly germinates and forms a new mycelium in a new place.
Asexual
Asexual reproduction is one of the most common in fungi. It is carried out through spores or spore powder. Disputes are presented in different forms. In some places it is a very fine powder, in others they look like small dots with flagella, some even have several.
Spores without flagella are called aplanospores. Most often they are located on hyphae. Spores with flagella are somewhat less common and are called sporangia. They are also located on the hyphae of the zoosporangium.
Unfortunately, if a fungus uses spore propagation, then the probability of the formation of a new mycelium is negligible. The fact is that mushrooms release a huge amount of spores simply into the air, or the spores settle on the leaves of other plants, moss or grass without the opportunity to take root in fertile soil.
Spores are often carried by the wind, and rarely any of them can take root on the ground.
In order for a new mycelium to appear as a result of this method, the spores must clearly fall on the ground, where there is special soil that is suitable for their composition. In addition, the presence of favorable external conditions is important.
In addition, for asexual reproduction and growth of the fruiting body, it is necessary that two spores, each of a different sex, take root in the ground next to each other.
Sexual
And finally, the third and most interesting option is the sexual reproduction of mushrooms. As a result of spore reproduction, we obtain primary mycelium, this is a kind of mycelium embryo. But the second mycelium will form after the two primary mycelium merge. This process is sexual reproduction. This is only possible if favorable conditions for growth and development exist around the mushrooms.
The secondary mycelium is already gaining strength and growing into a fruiting body, which we call mushrooms.
Mycelium cells gradually develop and contain all the necessary genetic information. This means that as the mushroom grows, it takes on the quality of its ancestors.
Signs of the Mushroom Kingdom
The uniqueness of the mushroom kingdom lies in the fact that its representatives combine some characteristic features from the other two kingdoms. Each mushroom has a little of the plant and the animal at the same time, but at the same time has its own properties.
Mushrooms have a lot in common with botanical representatives:
- Immobility;
- growth mostly at the top;
- presence of a cell wall;
- oxygen consumption;
- propagation by vegetative method, with the exception of some representatives.
There are also enough similarities with animals:
- Despite the fact that mushrooms breathe oxygen like plants, they do not contain chlorophyll, i.e. they are heterotrophic;
- from the previous paragraph it follows that they feed on existing organic substances;
- the presence of chitin in the cell walls of fungi makes them similar to some insects, crustaceans and other animals.
Among the unique features are the following:
- the process of feeding mushrooms is impossible without mycelium - a system similar to the root, but different from standard plant roots;
- fungi, which carry out the feeding process in the form of symbiosis, significantly help host plants to resist external negative factors, i.e. can contribute to the survival of the plant in difficult natural conditions;
- many fruitful mushrooms require a large amount of moisture for active growth and reproduction, so they grow most actively in the rainy seasons;
- a nutritious ecosystem can continue to exist even if fruiting bodies are removed from it, in the place of which new ones quickly grow.
History of the origin of mushrooms
How did mushrooms appear on our planet? What foreshadowed that they would be so abundantly distributed throughout the world?
Scientists from all over the globe believe that immediately after the first life arose on our planet, development occurred in several directions at once. Today we call them the “superkingdom of mushrooms.”
The kingdom of plants and animals developed, and the kingdom of mushrooms also developed. By the way, some scientists fundamentally disagree that mushrooms are plants. For many, they are closer to animals than to their green counterparts. This is proven by slime molds, which are fungi, but these organisms live their own special lives and have a multicellular structure.
The oldest fossil mushrooms that scientists have found date back 900 million years. Scientists believe that these were not the most ancient representatives, however, today this age is relevant.
It is believed that fungi originally evolved from algae, with which they indeed still have many very similar bases. Botanists suggest that algae and fungi are similar due to the fact that they evolved from the same ancestors. These are organisms from the category of flagellates.
More than 300 million years ago, the Carboniferous period occurred on earth. It is from this moment that scientists begin to maintain an informed and evidence-based chronicle of the life of fungi. The found representatives of the species were distinguished by their significant diversity. Scientists conducted several experiments, including molecular ones, studying ancient fungi, the so-called “eukaryotes”.
It was revealed that these representatives were unicellular, but with the makings of future development.
The next stage was the Archean and Proterozoic era. At this point, the earth was dominated by a significantly aquatic environment. The climate has seriously warmed and glaciers have begun to melt. This means that the water level has risen significantly. As a result, the proportion of oxygen also increased. Taken together, all these factors have come together to create very favorable conditions for the growth and development of many plants, including fungi.
It is at this stage that fungi begin to experience so-called sexual reproduction and officially cease to be single-celled. The Paleozoic era became even more favorable for the life and development of fungi, as the temperature increased and the climate became temperate and humid. The land began to gradually split into several continents, resulting in a diversity of species.
The next period is Devonian. At this moment, the climate changed, which means that the conditions for the existence of mushrooms became significantly different from the previous ones. It became somewhat colder, so the mushrooms improved their resistance. They were able to hibernate, and a hard shell also appeared.
Today's mushrooms came to us from an era when dinosaurs no longer reigned on earth. However, the first mammals appeared.
Mushrooms continue to improve and change. We cannot trace this process from start to finish, but we are sure that in hundreds of years many new species will appear, and those that currently exist will be improved.
Organisms of the kingdom of fungi
The categorization of fungi within the kingdom is quite varied. Modern scientists can name at least 100 thousand mushrooms that currently exist, but they also believe that there are additional species that have not yet been fully studied. Together, known and unknown mushrooms can number more than 250 thousand varieties.
However, there are general criteria by which all mushrooms can be divided into subspecies. The main one is the division into unicellular and multicellular, each of which belongs to eukaryotes, because. The cells of all fungi have a complete nucleus.
Unable to create organic matter within themselves, mushrooms feed from the external environment. From there they “extract” the necessary minerals and water. Absorption occurs over the entire surface of the fungal body, but there is a clear division-typology formulated based on the form of the feeding process:
- Saprophytes. They ensure, like bacteria, the decomposition of one substance and the appearance of another. The most famous and actively used person in this group is penicillium, which “promotes” rotting processes by appearing on fruits and vegetables;
- Parasites. They feed through the development of their hyphae in the bodies of other living organisms, which they make their “hosts” by consuming the necessary substances from them for a long time;
- Symbionts. They carry out a useful and mutually beneficial “neighborhood” with various plants, creating mycorrhizae and lichens. They are points of exchange of useful substances: the mushroom receives the necessary organic matter, while giving away water and minerals.
History of mushroom picking in Rus'
Russia is very rich in mushrooms. Numerous forests, fields, and even in cities you can find a huge number of representatives of this kingdom.
According to statistics, it is believed that more than 5 million tons of mushrooms ripen and grow in Russian forests every year, and that’s only edible ones. Of course, most of these indicators occur in Siberian forests. However, the central zone of Russia does not lag behind in terms of indicators. It is in central Russia that the most mushrooms are collected. Here the favorite chanterelles, porcini mushrooms, milk mushrooms, russula and so on predominate.
It is believed that about 10 kg of mushrooms per person per year, including children.
Russians have loved mushroom picking since ancient times. Both now and then it was believed that this is a very valuable, healthy and nutritious product that can decorate any dish. In addition, it can benefit the body.
Interesting Facts
Most often, it was women and children who went mushroom hunting, took small baskets with them and picked the fruiting bodies. Mushrooms could be dried and stored for several months in advance, in case the peasants were expecting a cold winter. When Christianity came to Rus', that is, in 1988, mushrooms began to fully replace meat in the diet during Lent.
In case of crop failure, mushrooms also saved the lives of many people. For example, during the Patriotic War of 1812, Russian soldiers who marched through the forests against the French ate mushrooms, which helped prolong their life and endurance.
Mushrooms were loved not only by peasants, but also by rich wealthy people who sent forced people on the so-called quiet hunt. Over time, fields and territories were plowed up, forests were cut down, and because of this, the mushroom population decreased greatly.
Gradually, other species began to appear that were adapted to life in such anthropogenic conditions. Among them are boletuses, moss mushrooms, honey mushrooms, boletus, nigella and greenfinch. In the 19th century, it was the Russian porcini mushroom that was actively collected, which is valued even in Europe. This is what is put on the table of patriarchs and kings.
In addition, the first truffle farm was opened in Russia, which, unfortunately, was lost during the October Revolution.
When the power of the emperor fell and was replaced by the Union, mushroom picking again gained popularity. People need food, the years are mostly hungry, so they actively collect mushrooms.
During this period, a huge number of poisonings were recorded, as people did not understand the difference between edible and inedible mushrooms. Only peasants who lived in past centuries possessed such knowledge.
Through trial, error and serious poisoning, it was revealed which mushrooms can be eaten and which ones are best avoided.
The first directory of mushrooms was compiled in the 17th century by a German botanist temporarily living in St. Petersburg. It was he who made his first notes about the time of collection and the harmfulness of mushrooms, which were then distributed in the homes of wealthy people. Naturally, after the revolution no such publications survived.
Gradually, collecting mushrooms ceases to be a necessity and a way of surviving during cold periods. It takes on more the character of tourism, pastime, and quiet hunting.
It becomes a real event for people to go out of town to pick mushrooms. This procedure was combined with picnics and barbecues.
These features have been preserved to this day.
In Soviet times, young people were involved in mushroom picking, because not everyone was sent to harvest potatoes.
In the 21st century, we collect more than 500 species of the most common mushrooms. There are about 100 mass species.
Mushrooms are divided not only into forest ones, but also into field ones.
A huge number of recipes have appeared, thanks to which you can prepare delicious dishes. All this is thanks to the knowledge of our ancestors, who once left us a wonderful legacy in the form of mushrooms.
Important! At school we are taught that mushrooms cannot be pulled out of the ground. In this way we damage the mycelium, which means that the mushroom will never grow in this place again.
The ancient Slavs also knew about this from somewhere. Therefore, when “picking mushrooms” they only went with a sharpened stick or with a kind of stone knife, which they used to cut off the mushroom, preventing it from dying.
Characteristics of the kingdom of mushrooms
Scientists have approximately established that mushrooms appeared no less than about 500 million years ago, even before the emergence of dinosaurs. In the scientific community, there are still debates and discussions around the mushroom kingdom, and theories are put forward about future scientific discoveries. All this is due to the fact that mushrooms have characteristics that are characteristic of both the plant and animal kingdoms, as well as their own individual characteristics.
In terms of the type of nutrition, all mushrooms are similar to plants; they are also connected with flora by the inability to move. Like a plant, a fungus is forced to remain in one place throughout its life cycle. In this case, fungi reproduce using a complex vegetative system called mycelium, which is a complex network of intertwined threads. It is this characteristic feature that distinguishes the fungal kingdom as a separate section of biology.
Fungi, like all organisms, are made up of cells. Each cell contains water, which is located in the cytoplasm. It also contains enzymes, amino acids, carbohydrates and lipids. In addition to this list, the cytoplasm contains special formations - mitochondria, lysosomes and vacuoles. The latter are designed to accumulate reserves of nutrients - glycogen, lipids, etc. Another distinguishing difference between fungi and plants is that there is no starch in the cells of fungi. Hornbeams are also distinguished from plants by the presence in the cell nucleus of chromosomes that contain DNA.
Chemical composition of mushrooms
The chemical composition is of interest not only to scientists, but also to ordinary people. Some people are very concerned about their health and want to have information about what they eat. Other people dream of losing weight, so they are forced to count calories and also know about the ratios of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
What about the chemical composition of mushrooms?
As for the beneficial substances that mushrooms contain in abundance, we can say that they are contained even in conditionally poisonous ones. It is believed that they contain about 10% dry matter, and the remaining 90% is just water.
Mushrooms are mostly a protein product, which makes up approximately 65% of the total substances.
Mushrooms also contain carbohydrates and some fat. These representatives of the forest kingdom are very rich in vitamins A and C; some also contain a high content of vitamins B, D and nicotinic acid.
Unfortunately, as a result of heat treatment, most of the beneficial vitamins and minerals are destroyed, so in order to experience the positive effects of mushrooms, you need to eat enough of them.
Important! It is believed that the most common types of vitamins contain much more than in the same beef liver.
As for minerals, in fact, there are not very many of them. Mainly iron, copper, chromium, sulfur, copper and sodium are present.
Also, some fruiting bodies may also contain silver.
Many people are also interested in nutritional value. However, everything here is individual and depends on the calorie content of the individual species. It is believed that mushrooms have a nutritional value of 9 to 35 kilocalories per 100 g of fresh food. This means that mushrooms are quickly becoming a popular food on which nutritionists develop their programs.
The most high-calorie mushroom is boletus. There are 300 kilocalories per 100 g of this product.
Nutritionists say that in terms of its chemical composition, a mushroom is nothing more than meat mixed with vegetables. That is why it is also called “forest bread”.
However, mushrooms are a valuable supplier of amino acids, so they should not be excluded from your diet.
The fruiting body also contains high lipids.
Humans need polyunsaturated acids, which are mostly found in the most popular types of mushrooms. They make up approximately 60% of the total mass of lipids. All these properties make it possible to influence human health, ensuring rapid normal tissue development. They also prevent cholesterol from settling. The ratio of fats, proteins and carbohydrates also varies depending on the subspecies.
Even more information on Wikipedia.
Mushroom nutrition
Saprophytic fungi feed on dead organic matter, and parasites can live on plants, animals and humans. There are also transitional forms of fungi (tinder fungi, etc.), which spend part of their life activity as saprophytes, and the other part as parasites. Saprophytic mushrooms live on fallen leaves, wood and humus.
Many species of the kingdom of Fungi live in cohabitation (symbiosis) with algae and higher plants. The mutually beneficial cohabitation of fungal mycelium with the roots of higher plants forms mycorrhiza (for example, boletus with birch, boletus with aspen).
Many higher plants (trees, durum wheat, etc.) cannot grow normally without mycorrhiza. Fungi receive oxygen, root secretions, and compounds that do not contain nitrogen from higher plants. Fungi “help” higher plants absorb hard-to-reach substances from humus, activating the activity of enzymes in higher plants, promote carbohydrate metabolism, fix free nitrogen, which is used in a number of compounds by higher plants, provide them with growth substances, vitamins, etc.
The role of mushrooms in our life
Mushrooms play an important role in people's lives.
They are used in various areas of our lives, from cooking to medicine.
In addition, mushrooms are natural cleansers. They decompose into peculiar organic compounds. This allows you to saturate the soil with nutrients and make it fertile. Also, mushrooms interact effectively with numerous plants. They establish a kind of symbiosis, which is called mycorrhiza. As a result, both plants and fungi can absorb phosphorus and water faster.
As for its importance for human life, the mushroom, firstly, is a very healthy product, saturated with a huge amount of vitamins. It not only allows you to diversify your food, but also has a healing effect.
By the way, about the healing effect. It is because of this that the mushroom is most often used in medicine, as a component of drugs.
And if we turn to the experience of our ancient ancestors, then in Rus' many diseases were treated with decoctions or tinctures of mushrooms. And by the way, it’s very effective.
Today, the mushrooms that we see on supermarket shelves are not forest dwellers. These are species that are specially grown in equipped premises under specially created conditions. And most often these are oyster mushrooms and champignons, the most popular mushrooms that can be grown independently.
Scientists continue to interfere with the mechanism of development and growth of mushrooms, trying to make them more useful and nutritious.
Mold
Everyone has at least once seen the mold that covers bread that has been sitting for a long time or spoiled fruit. Mold is also a mushroom, but, unlike the familiar chanterelles and honey mushrooms, it belongs to the lower fungi. Mold mycelium consists of a single cell with many nuclei. Mold is classified into black, white, grey, pink, blue and green. Some of its species, for example, green, are eaten by people.
Lower fungi also pose a danger to paper. If books or documents are stored in a damp and poorly ventilated place, the cellulose and glue decompose and mold is to blame.
Yeast is also a fungus. If you pour warm water over them, you can see movement and growth through a microscope.
Classification of mushrooms
Mushrooms have a huge number of classifications. However, we are interested in the degree of edibility, since the first thing we pay attention to is edible mushrooms, which is what we look for on the so-called “quiet hunt”.
Mushrooms are a very nutritious product due to their high protein content.
But, unfortunately, as a result of protein synthesis in mushrooms, certain metabolic processes begin that kill the beneficial properties of amino acids. And they can cause serious poisoning in humans. This means that we come across not only edible, but also conditionally edible and, unfortunately, inedible mushrooms.
However, a number of toxic compounds can be eliminated simply by appropriate heat treatment.
Some mushrooms contain a higher content of toxins, while others, on the contrary, contain less of them.
For example, modern scientists distinguish such categories of mushrooms.
Edible
These are the subspecies that can be eaten without fear of consequences. It is believed that the cooking time for these mushrooms is 30 minutes. This applies to cooking, frying, and putting it in the oven. Such absolutely safe mushrooms include the following names:
- white;
- boletus;
- boletus;
- Champignon.
On the topic - types of edibles.
Conditionally edible
The next common subspecies are conditionally edible mushrooms. These mushrooms can also be eaten. However, in case of improper preparation or lack of heat treatment at all, poisoning can be provoked, but not severe. A special feature is the fact that these forest representatives need to be exposed to heat treatment for a longer time. It is believed that the ideal cooking time is at least 40 minutes, and these mushrooms must first be soaked in water for 10 hours.
Before frying, it is also recommended to boil the mushrooms to avoid negative consequences. These representatives include:
- black milk mushroom;
- cobweb;
- talkers;
- valui;
- pigs.
Poisonous mushrooms
And finally, poisonous mushrooms. These are the representatives that are not recommended to be eaten in principle. Unfortunately, if you eat it, you can get seriously poisoned, which will lead to serious disorders of the body and illness, in some cases even the death of a person. Such mushrooms are most often very noticeable in the forest and have a bright and original appearance. Just remember the fly agaric or the white toadstool.
Very often, poisonous mushrooms are disguised as edible ones, so before you add such species to your basket, you need to have a good understanding of who is in front of you.
Poisonous mushrooms in Central Russia include:
- pale grebe;
- satanic mushroom;
- fly agarics of various subspecies.
Important! Surprisingly, some scientists classify the fly agaric as a conditionally edible mushroom, which we are accustomed to consider poisonous and dangerous. Indeed, it contains toxins, however, they are quickly destroyed at temperatures above 80 degrees, taking into account the processing time of more than 1 hour. However, many doctors still do not recommend eating fly agaric, even pre-processed ones. The poison cannot always be neutralized, so the risk still remains.
CLASSIFICATION
Fungi are classified according to the type of spores (they are formed sexually or asexually) and the structure of specialized spore-bearing structures. The hierarchical rank of fungal taxa is indicated by standard endings recommended for these organisms by international rules of botanical nomenclature.
The highest-ranking taxa within the kingdom of fungi - divisions (they are equivalent to "phyla" in animals) - should have the ending -mycota, and subdivisions (second in the hierarchy) -mycotina. Next in descending order are classes (-mycetes), orders (-ales) and families (-aceae). There are no standardized endings for genera and species epithets.
There are still disagreements among mycologists regarding the details of the classification of fungi, and the same groups can unite, split, or change their hierarchical rank among different authors. However, now it is generally accepted not to classify slime molds and a number of other “problematic” forms as “true mushrooms” (division Eumycota), and among the former, five subdivisions are usually distinguished: Mastigomycotina, Zygomycotina, Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina and Deuteromycotina.
Total number of mushrooms on earth
At the very beginning of the article, we talked about how many mushrooms there are on the globe. However, this information should be specified in order to have a general idea of the scale of growth.
Mushrooms are rightfully considered one of the largest groups of living organisms. Today they support all existing ecosystems; the disappearance of mushrooms will inevitably lead to tragedy.
According to modern scientists, today there are more than 250,000 officially registered species of mushrooms on earth. This also applies to the regions of the Far North, Russia, and other continents. Also, fungi also mean microorganisms, which are also named accordingly.
However, if each type of mushroom is divided into subspecies, for example, fly agaric can be red, variegated, gray, pink, and so on, then we will count more than one and a half million species. Agree, it’s big.
Scientists expect that new modified bred species will appear in the next century. They will appear both as a result of the developments of scientists, and may also become a direct consequence of changes in environmental conditions.
Due to severe air pollution, as well as a decrease in nutrients in the soil, the mushrooms will begin to change, resulting in their new manifestations.
Zygomycotina.
These are terrestrial fungi, the asexual reproduction of which occurs with the formation of immobile spores (aplanospores), and the sexual reproduction occurs through the fusion of “genital organs” growing on the mycelium, called gametangia. Aplanospores mature in sac-like structures - sporangia and, in a number of species, are forcefully thrown out of them into the air. During sexual reproduction, the fusion and mixing of the contents of the gametangia lead to the formation of a thick-walled zygospore, which germinates after a more or less long period of dormancy. The most famous genus in this department is Mucor
and related mushrooms, abundantly present in the soil, on manure and on other organic residues, often growing in the form of a fluffy coating on raw bread and rotting fruits.
The structure of sporangia and the method of development of zygospores vary widely and serve as the basis for the identification of various taxa. Many representatives of this subdivision are heterothallomic, i.e. The sexual process and the formation of zygospores are possible in them only when they meet individuals of the same species belonging to different “sexual types” (they are designated + or -). Their “intersexual” relationships are coordinated by special hormonal substances released into the environment. The presence of two sexual types is reflected in the name of the subdivision, derived from the Greek. zygERRORm –
“pair”.
Application in medicine
The use of mushrooms in medicine is the norm rather than the exception. They are directly part of traditional medicine, and are also one of the new effective subdivisions of pharmacology.
The history of the use of mushrooms in medicine dates back to ancient times. Then people made decoctions and tinctures, applied mushrooms to open wounds, and made extracts from them.
According to scientists, this method first showed itself in Japan and China, then spread to other countries.
Today, mushrooms are widely distributed in leading medical fields.
- They are actively used to obtain antibiotics suitable for eliminating infectious diseases.
- Also, mushrooms are widely used in oncology.
- These organisms contain polysaccharides that have a strong immunomodulatory effect.
- They improve metabolism, block angiogenesis and systematically destroy cancer cells.
Many mushrooms today are still used as dietary supplements, components and extracts. The properties of some individual species are still being studied, as they are not yet clear to scientists.
One of the most popular and important areas of mushroom research is the possibility of using mushrooms as anti-cancer agents.
In China, for example, there are entire branches of medicine that help fight cancer thanks to representatives of the mushroom kingdom.
general characteristics
The kingdom fungi are unicellular and multicellular organisms. Currently, taxonomists have counted more than 100 thousand species of fungi.
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms that do not have chlorophyll. They occupy an intermediate position between animals and plants, as they are characterized by a number of properties that bring them closer to animals and plants.
Common signs of fungi and animals:
- The cell membrane contains chitin;
- they accumulate glycogen rather than starch as a reserve product;
- as a result of the exchange, urea is formed;
- absence of chloroplasts and photosynthetic pigments;
General characteristics of mushrooms and plants:
- Unlimited growth;
- absorptive nutrition, i.e. not swallowing food, but absorption;
- the presence of a pronounced cell wall;
- reproduction by spores;
- immobility;
- ability to synthesize vitamins.
Use for hallucinogenic purposes
Surprisingly, some mushrooms have not only poisonous, but also hallucinogenic effects. Just remember the toadstool, fly agaric, stropharia and a number of other subspecies. The hallucinogenic effect allows a person to escape from reality, experience euphoria and ambiguous feelings.
However, if some people experience the hallucinogenic properties of mushrooms as a result of ignorance, that is, due to the collection of certain specific species, which then manifested themselves in a negative way, then others, on the contrary, independently look for representatives of the forest kingdom that will allow them to obtain a similar effect. Today, certain types of mushrooms are sold on the black market with the goal of giving people this same euphoria and hallucinogenic effect. And the cost of these mushrooms, for a minute, reaches several tens of thousands of rubles. per 100 grams.
What feelings does a person experience when under the influence of the hallucinogenic effect of mushrooms?
First, he begins to lose touch with reality. Does not perceive external sounds, images, then the perception, on the contrary, intensifies. For example, one of the people who experienced the hallucinogenic effect of the fly agaric says that for some time he did not hear anything around him, it was as if he was in a vacuum. And then I started hearing a very loud, consistent sound. It echoed throughout the room. The sound was so piercing that the man became scared. Afterwards, it turned out that small children were just running around him.
The hallucinogenic effect can cause you to experience strange images and sounds that do not exist in reality. Therefore, unfortunately, in such a state a person can do a lot of negative things.
Avoid the hallucinogenic effect, carefully check your basket that you have collected or purchased. And also, under no circumstances should you purchase mushrooms in order to experience their hallucinogenic effect on yourself.
Common poisonous mushrooms.
The most dangerous mushrooms belong to the genus Amanita
, which is characterized by white spores and a swollen or cupped stalk base.
The most famous among them is the red fly agaric ( A. muscaria
) with a yellow or orange cap covered with white spots on top.
The pallid grebe ( A. phalloides
) is distinguished by its greenish-white color and is commonly found in open woodlands.
The young fruiting body of representatives of this genus is almost spherical, and later develops an almost flat lamellar cap with a diameter of up to 13 cm on a stalk up to 15 cm high, immersed from below in a membranous vagina. Some species of Amanita
are edible, but it is not worth the risk, because an error in identification can lead to tragic consequences.
Oddly enough, most often people are poisoned not by fly agarics and toadstools, but by mildly poisonous mushrooms. Clitocybe illudens) deserves special attention
), named for its ability to luminesce.
This is an orange-yellow lamellar mushroom with an almost flat cap with a diameter of up to 15 cm. White-spore umbrella mushrooms (genus Lepiota
) are also dangerous.
Most species of this genus, in particular the variegated or large umbrella ( L. procera
), are edible, but there is an exception -
L. morgani
. This is a very large mushroom with a cap up to 25 cm in diameter. It is quite similar to the closely related large umbrella, but differs from it in the spores that turn slightly green with age.
The nature of the toxins found in poisonous mushrooms is different, and the time after which symptoms of poisoning with them appear is also different. Amanita muscaria contains the alkaloid muscarine, which has a strong effect on the nervous system. Symptoms of poisoning take from a few minutes to two to three hours to develop. Stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, loss of consciousness and coma, and sometimes convulsions are possible. In cases of toadstool poisoning, similar symptoms occur within a few hours. Later, liver failure, high blood pressure and a drop in body temperature are observed. After a few days, death occurs in 50% of cases.
Diseases due to mushrooms
Unfortunately, scientists have discovered that mushrooms can not only be used in the medical field as medicine, but can also cause various types of diseases.
What are we talking about here?
In addition to standard champignons, chanterelles and others, mushrooms also include mold.
Fungal spores come into contact with us everywhere. And, unfortunately, if they get on the skin, especially in open wounds, they can quickly cause infections, which then, if undetected for a long time, spread to other organs.
Let's remember candida strains. They settle not only on surfaces and mucous membranes, but can also settle in the intestines. They cause local infections, which are most often grouped in the mouth and vagina, and sometimes can affect internal organs.
Patients with AIDS also experience the development of severe fungal infections, which further aggravates the condition. The same thing can happen in cancer patients.
If a person has a compromised immune system, he is susceptible to various infections, which are caused by fungi.
Such diseases are aspergillosis and mucormycosis. However, fortunately, such diseases are not very common in Russia. They are mainly found in North America and Africa.
The danger of fungal infections comes down to the fact that they develop very slowly, and people often cannot diagnose them in themselves in the early stages of development. And when he realizes that something wrong is happening to the body, it is already too late.
In addition to the diseases listed here, mushrooms provoke:
- leukemia;
- lung diseases;
- Hodgkin's disease;
- lymphoma;
- renal failure;
- diabetes.
Mushrooms surround us everywhere. They grow in forests, fields, sometimes we see them near our house, on football fields, in damp rooms, and so on. Some types of mushrooms are safe for humans, while others, on the contrary, are best avoided. But be that as it may, it is necessary to know all the nuances of the growth, development, danger and medicinal properties of mushrooms in order to use this knowledge to your advantage. No one knows in what situations you will encounter mushrooms and what information you will need about them. We have collected general information that will not only expand your horizons, but will also certainly be useful in your life.
Common edible mushrooms.
The fruit body of the well-known field champignon ( Agaricus campestris
) consists of a cap on a central stem (stump). From below, the cap bears many vertical plates radiating radially from the center. On both sides of each of them, disputes develop - it is estimated that more than a billion for one champignon. Once ripe, they are carried by the wind and germinate in favorable conditions. This species is characterized by a grayish cap, pink plates that turn brown when ripe, and a membranous ring (remnant of the spathe) on the stalk; Even a non-specialist can easily recognize it from the picture.
After champignon, probably the most delicious among naturally occurring mushrooms (as we will call fruiting bodies for simplicity) are dung beetles, or ink mushrooms (genus Coprinus
), so called because when ripe their cap becomes soft and oozes an inky-colored liquid.
Their spores are black. Once you see it, you will not confuse these mushrooms with any others. The most common species of this genus are the white or shaggy dung beetles ( C. comatus
), flickering (
C. micaceus
) and gray (
C. atramentarius
).
Among the white-spore mushrooms, the oyster mushroom ( Pleurotus ostreatus)
) and a related species
P. sapidus
: their stem is shifted to the edge of the cap, and the fruiting bodies grow in dense, stepped clusters on dead tree stumps.
The white-spored chanterelle ( Cantharellus cibarius
) with a light yellow cap is also quite edible, but it can be confused with the closely related species
C. aurantiacus
, which can be slightly poisonous.
Tubular basidiomycetes include representatives of the families Polyporaceae and Boletaceae. The underside of their cap is covered, as it were, with a layer of porous sponge made of tightly packed narrow vertical tubes, on the inner walls of which spores form. However, the first ones, the so-called polypores, the leg is often absent or invisible, and the fruiting bodies of the latter are “ordinary”, like those of a champignon. Some boletaceae are considered delicacies, others are more or less poisonous, so the hobbyist should be careful.
Polypores grow on trunks and stumps. They are usually too tough and woody to cook, but there are known exceptions. For example, the edible liverwort ( Fistulina hepatica
), so called because of its external resemblance to a piece of liver, is easy to identify.
It almost always grows on old chestnut stumps, less often oak, often reaching a diameter of 15–20 cm. The sulfur-yellow tinder fungus ( Polyporus sulphureus
) is also a large mushroom that is easy to identify by color.
Representatives of another family of basidiomycetes - puffballs (Lycoperdaceae) - have spherical fruit bodies of various sizes: sometimes tiny, the size of a pea, and sometimes huge - up to 45 cm in diameter. There are no poisonous ones among them, but many are considered tasty. Goblet puffball ( Lycoperdon cyathiforme
) often grows in abundance in lawns, giant bighead (
Calvatia gigantea
) is much less common. These mushrooms should be harvested while their fruiting bodies are young, white, and resemble cheese when cut. When ripe, they turn into a dry sac filled with yellow, purple or olive spores.
Representatives of basidiomycetes from the family of horned mushrooms (Clavariaceae) are easy to recognize because their fruiting bodies are similar in appearance to corals. None of them are poisonous, but some species are too tough to eat.
Morels (genus Morchella
) usually appear in May, and are so unique in appearance that they cannot be confused with any poisonous mushrooms. These representatives of marsupial fungi resemble with their fruiting bodies a small sponge on a white stalk.
Marsupial mushrooms also include truffles, highly valued by gourmets (genus Tuber
). They are black, tuberous, grow underground, and have to be dug up. Truffles have a distinctive smell, so dogs and pigs are specially trained to search for them. These mushrooms are found throughout North America, but they are brought to the United States for sale from Europe, mainly from France, where their collection and canning are on an industrial basis.
Nutrition
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms. They absorb minerals from the environment, but organic ones must be obtained in finished form. Depending on the need for substances, one or another type of fungi populates a certain type of substrate. They are not able to assimilate large particles of food, so they absorb exclusively liquid substances through the entire surface of the body, for which the huge surface area of the mycelium turns out to be extremely beneficial. Fungi can also feed by parasitizing animals and decomposing dead organic matter.
They are characterized by external digestion, when enzymes are first released into the environment containing food substances, breaking down polymers outside the body into easily digestible monomers, which are then absorbed into the cytoplasm. Some species are capable of secreting all the main types of digestive enzymes - proteases that break down proteins, lipases, carbohydrates that break down fats and polysaccharides, as a result of which they are able to settle on almost any substrate. Other species secrete only certain classes of enzymes and can only live in a substrate containing the corresponding substances.
Based on their nutritional characteristics, there are two main groups of mushrooms:
- Saprotrophs - which include most cap and mold fungi, as well as yeast. Their peculiarity is that an individual representative of this group can form mycelium in a day with a total hyphae length of more than a kilometer. Such a rapid growth rate and the filamentous structure of the mycelium determines a special type of relationship between such fungi and the environment, which is not typical for other groups of eukaryotic organisms. An extensive system of branching hyphae allows them to be in close contact with the substrate. Almost all mycelial cells are separated from the substrate only by a thin cell wall. The digestive enzymes they secrete very quickly act on the substrate material and contribute to its partial digestion outside the mycelium cells. This semi-digested material is then absorbed by the entire cell surface.
- Symbionts – functioning in close connection with other living organisms, primarily various plants. This relationship can be either mutually beneficial or downright parasitic. Often fungi form a mutually beneficial symbiotic association with tree roots - mycorrhiza.
Reproduction
Fungi reproduce asexually and sexually.
- Asexual reproduction is carried out by parts of the mycelium or individual cells, giving rise to a new mycelium. Yeasts reproduce by budding. It can also be carried out through endo- and exogenous spores. Endogenous spores are formed inside specialized cells - sporangia. Exogenous spores, or conidia, appear openly at the ends of special mycelial outgrowths called conidiophores. Once in favorable conditions, the spore germinates and a new mycelium is formed from it.
- Sexual reproduction is especially diverse. In some varieties, the sexual process occurs by the fusion of the contents of two cells at the ends of the hyphae. In marsupial fungi, there is a fusion of the contents of the antheridium and the female organ of sexual reproduction - the archegonium, which is not differentiated into gametes, and in basidiomycetes - the fusion of the contents of two vegetative cells, in which outgrowths or anastomoses are often formed between them.
The Kingdom of Mushrooms is one of the cornerstone elements of the cycle of life on our green planet, and its role in the overall harmony of the world cannot be overestimated. For humanity, its generous gifts are a source of endless culinary riots, and help in the fight against numerous diseases and troubles. We are waiting for the revelation of many more strange secrets of this huge mysterious space - the Kingdom of Fungi.