general characteristics
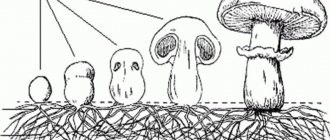
Previously, mushrooms with a lamellar structure were combined into the Agaricaceae family.
Later they were distributed into genera and families, taking into account the main characteristics within the order Agariaceae, or Lamellar. Almost all fruiting bodies of this group are considered annuals, have a fleshy, less often leathery or cartilaginous consistency and a lateral stalk. There are them (fruiting bodies) without stems - sessile. This structural feature is characteristic of some species that develop on wood, for example, oyster mushroom.
To identify families, experts used the following data:
- coloration of spores and hymenophore;
- the presence or absence of private and general covers;
- structure and type of arrangement of the plates in relation to the stem.
Mushrooms are very fragile and break easily. For most, the surface is covered with a film that breaks as it grows. When cut, they secrete milky juice. The color range is varied - in nature there are varieties of red, brown, yellow, lilac and beige.
The plates that form in the lower part of the cap vary in thickness and frequency, but they all form a hymenophore (spore-bearing layer).
- In some they do not reach the edge of the leg and remain as if hanging (free).
- In others, they form a notch and are rounded in the area of the leg.
- In still others, they are firmly attached to the edge of the stem with the entire edge or tooth.
The legs differ in structure - fibrous or hollow. At the same time, they are thin and elegant, with a smooth cylindrical shape.
In some edible species, the main feature is the presence or absence of a vulva, which helps to avoid confusing them with dangerous false counterparts.
In terms of taste, they are not inferior to tubular mushrooms - they are of great value in the cuisine of many countries.
Application
In cooking
Black mushrooms are edible after processing. Before cooking, they are soaked for 2-4 days, changing the water several times, especially the pepper milk. You can also boil mushrooms in several waters and salt them already boiled. These mushrooms make excellent pickles; the flesh of milk mushrooms remains very dense, perfect for salads and snacks in general when sliced. Mushrooms can be put in hodgepodges, made into sandwiches and canapés.
In medicine
Mushrooms are used in dietary nutrition; fresh chernukha juice is used in folk medicine to remove warts and condylomas.
Places and timing of growth
Lamellar mushrooms can be found in different areas - forests, steppes, forest-steppes, park areas, gardens, fields.
They prefer to grow in sandy or sandy loam soil with high humidity and an admixture of deciduous compost, on dead wood. They are characterized by the ability to form mycorrhiza (especially with tree species).
Some species are considered parasites - as they grow, they destroy the trunks of living trees.
Fruiting is long: begins in early March and ends in late autumn. Many specimens are successfully cultivated not only industrially, but also privately.
Distribution by region
Each region has its own popular mushrooms, which are most often found in the forest and end up on the table of mushroom pickers.
Lamellar mushrooms of the Moscow region
The nature of the Moscow region is rich in a large number of mushroom places, which is due to the presence of deciduous tracts, in which the most common are:
- honey mushrooms;
- chanterelles;
- saffron milk caps;
- Russula;
- milk mushrooms;
- Champignon;
- purple and gray rows.
The peak of the harvest occurs in August-September. There are dozens of places in the region where you can organize a “quiet hunt”; popular ones include Ruzsky, Yegoryevsky, Odintsovo, Kolomensky, Meshchersky and Dmitrovsky districts.
Mushrooms of the Leningrad region
The Leningrad region is famous for its coniferous forests, in which you can find:
- chanterelles;
- red and yellow russula;
- bitters;
- black milk mushrooms.
The collection season begins at the end of April, the peak month is August, during which toadstools and fly agarics also actively grow. The villages of Sosnovo and Snegirevka are considered popular fertile places.
Edible varieties
Spruce saffron milk cap
This mushroom has a bright orange cap, of two types - funnel-shaped or flat-concave. The surface is smooth, without hairiness; when broken, the flesh turns green.
The stem is the same color as the cap, the shape is cylindrical, brittle, and becomes hollow with age. The cut areas turn green.
When cut, the fruit body is orange, has a light fruity aroma and has a pleasant taste.
Real saffron milk cap
The hat is orange with dark rings. The surface is smooth, with a sheen; in damp weather it can be sticky.
There are two types of shape: funnel-shaped or prostrate.
The pulp is orange-yellow and turns green when cut. The plates, which are hymenophores, have a reddish or light brown tone.
The leg is cylindrical, the same color as the head, hollow, erect.
Common fox
Each mushroom has its own peculiarity
The spore-bearing layer of the chanterelle consists of folded, thick, sparse and branched pseudoplates, the same color as the cap, which descend along the stalk and blur the boundary between it and the cap. The leg is fused with the cap, thick at the top, narrowed towards the bottom.
Color - orange-yellow. The surface of the upper part is wavy, often irregular in shape, spread out and slightly concave inward.
The pulp is fleshy, dense, thins the faint smell of dried fruit, and tastes sour.
Autumn mushrooms bear fruit from late summer until frost.
Summer honey fungus
The surface of the hat is yellowish-brown, the center is a couple of tones lighter, the shape of the head is spread out.
When cut, the honey fungus is light brown and emits a rich mushroom aroma. The pulp is thin, medium density.
The leg is dark brown, hollow, often curved with a rigid structure. Contains film edging.
Russula
This lamellar species has several varieties with different cap shapes: funnel-shaped, bell-shaped, prostrate, round or hemispherical. The surface is pale pink, some are red or ginger.
In cross section, the fruit body is white, hard and very fragile, with a spongy structure.
The leg is smooth, dense, color from snow-white to light brown, depending on the subspecies.
Russula blue
This mushroom is called so because its large cap is dark blue or light lilac.
The leg is thick and white. The hymenophore of this species of russula is formed by straight, most often forked-branched white plates.
Real milk mushroom
The cap is of two types - flat-convex or funnel-shaped, the edges are pubescent, rolled inward.
Color - white or yellowish. The fruit body is dense, thinning out the light fruity aroma.
The leg is erect, white or pale yellow.
Volnushka pink
The surface of the cap is pink with slight pubescence, it is round in shape with a depression in the center, the edges are turned inward.
The pulp is white or creamy, dense in young mushrooms, with an islandy aftertaste.
The leg is cylindrical, hard, pale pink.
Pluteus deer
The white cap can be convex-spread or bell-shaped. The edges are ribbed and striped. The surface is scaly or silky, the color depending on snow-white to almost black.
When the spores ripen, they give the plates of young mushrooms a pink color, while in older specimens they become flesh-red.
When cut open, the fruit body is soft, white, without any special taste or aroma, or has a faint radish odor. The leg is the same color as the cap.
Champignon
The cap of young specimens is hemispherical or spherical; in adults it becomes prostrate. Color - from light to dark brown.
The hymenophore (plates) are pale pink, becoming brown in older ones. The leg is whitish, erect, smooth, fibrous.
The pulp is dense, white, darkens when processed, thins out the pleasant mealy aroma, and has a good taste. This mushroom is even consumed raw.
Champignons growing in a bunch can be found in places with a high content of organic residues - in pastures, in the steppe and forests. They reproduce well at home, so they are available for sale all year round.
What are black tree mushrooms called?
This species is often called muer. Literally translated, it sounds like “firewood” and “ear.” Sometimes known as black mushroom, tree abalone and Chinese wood mushroom, Chinese muer mushroom. Another definition - the ear of Judas - the fruit received for the external resemblance of the shape of the cap to a human ear.
In mycology, the black mushroom is described as auricularia, or auricularia. This is a collective name that combines several varieties of mushrooms. On the territory of Russia you can find the following types of muer:
- auricularia ear-shaped;
- auricularia densely pilose (hairy);
- auricularia membranous;
- auricularia rosea;
- auricularia tender;
- auricularia cornea.
The ear-shaped variety is considered the most common. Auricularia densely hairy is slightly less common.
Inedible
You need to be able to recognize inedible mushrooms
Among the general variety of lamellar mushrooms, there are poisonous and extremely life-threatening ones.
Having familiarized yourself with their external description and name, you will be able to distinguish edible specimens.
Death cap
This is a particularly dangerous mushroom that can be fatal 7-8 hours after consumption.
You can recognize the pale grebe by the following signs:
- cap with a diameter of 6-13 cm, the surface is glossy, yellowish-olive or whitish-green, with white, thick plates;
- leg 14-15 cm high, white or beige, erect, contains a ring in the form of torn flakes;
- Old specimens are characterized by an unpleasant putrid odor.
fly agaric
Prefers to grow in sunny areas in coniferous and mixed forests. They are not tied to specific woody plants, so they can grow everywhere.
The hat is bright scarlet or rich red-red in color, strewn with white dots. In young fly agarics it is convex, in adults it becomes prostrate and flat.
The leg is tall, thick, white, surrounded by a membranous border. The lower part contains the remains of the spore-bearing sac.
Young specimens emit a pleasant mushroom aroma.
Fiber fiber
Fruits among conifers, birches, aspens, oaks and hornbeams. In terms of toxicity, it is equal to the pale grebe.
At the beginning of growth, the hat is bell-shaped, later it becomes prostrate, covered with numerous cracks along the edge.
The surface color is dirty yellow or olive brown. The leg is erect, cylindrical, brownish or brown in color, and contains a powdery coating.
False honey fungus
It differs from its edible relatives in color. The convex cap is gray-yellow, closer to the center it is fiery red.
The leg does not contain a girdle, is dark yellow, with a smooth transition to a red-gray shade.
In the cross section, inedible honey mushrooms are gray. They are characterized by a bitter taste and an unpleasant specific odor.
Galerina bordered
These mushrooms look like honey mushrooms, so you need to be very careful when picking them.
You can recognize them by the following characteristics:
- the body is very fragile, thin, visible in the sun;
- the cap is brownish-yellow or light chestnut, convex in young specimens, spread out in older specimens with a tubercle in the center;
- edges with white border, turned down;
- the leg is thin, long, ocher-brown in color, and contains a powdery coating.
Entoloma spring
Grows in forest areas, park areas and gardens. The hat is bell-shaped, later becoming cone-spread. The surface is sticky, smooth, brown-gray.
The leg is of medium length, smooth, gray or light brown in color. When broken, the dense flesh thins out the smell of dampness and tastes bitter.
They belong to the group of especially dangerous ones and can cause severe poisoning, even death.
Leopard print row
The caps of the fruiting bodies are convex or prostrate with curled edges. The color is different - dirty white, light silver, gray or gray-brown with a bluish tint.
The leg is dense, covered with a white coating. The lower part has a brownish tint.
When cut, the mushroom is snow-white in color and emits a light mealy aroma.
This row rarely grows alone, mainly in small colonies that form “witch rings”.
Collection rules
Mushrooms called funnel mushrooms are collected as they appear - from July until autumn. It has been noticed that they bear fruit better and more in August. You should look for them in mixed forests or deciduous forests, in open areas. They can also be in the shade, under leaves and moss. Not found in purely coniferous forests.
They grow in groups; if you notice one mushroom, you need to inspect the entire surrounding area. Their color makes them difficult to see.
Mushrooms are cut with a sharp knife, trying not to harm the mycelium. You should not take funnel-shaped funnelweeds along highways, as they accumulate harmful substances.
The funnel mushroom is distinguished by its black color, as well as a funnel-shaped cap with a raised edge and a fragile mushroom body. The black chanterelle has no poisonous counterparts.
Beneficial features
Edible lamellar mushrooms are valued not only for their good taste, but also for their beneficial properties. The pulp contains:
- vitamins of group B, A, E, C, D, PP;
- micro and macroelements - potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, selenium, manganese and sodium;
- amino acids;
- cellulose;
- mushroom protein;
- organic acids;
- lipids (fats) containing lecithin, provitamin D, and some fatty acids (all in combination are important for the human body).
Thanks to such a rich composition, they increase immunity, normalize general condition, prevent the development of cancer, skin aging, and improve the structure of hair and nails.
Other names for black milk mushroom
Common names for black milk mushroom:
- blackie (due to the color of the spots on the hat);
- spruce mushroom (this name appeared as a designation of the place of cultivation - coniferous forests, mixed forests);
- black hollow (associated with a depression on the surface);
- gypsies (also because of the color);
- the mushroom has as many as eight Latin names assigned to it by mycologists and botanists such as Jean Baptiste François Pierre Bulliard, Elias Magnus Fries, Otto Kunze and Samuel Frederick Gray.
Important! The best time to collect is early morning. The sun and dew make the mushroom cap shine, and it is easier to find it in dense grass.
Cooking features
There are many examples of preparing lamellar mushrooms - stewing, salting, pickling, frying, drying and baking.
The most delicious and popular options are presented in the table.
| Name of the dish | Ingredients | Recipe |
| Soup with champignons | young mushrooms (200 g); potatoes (2-3 pcs); onions, carrots (1 pc); pepper, salt (to taste). | Peel the mushrooms, rinse, cut into slices. Fry finely chopped onion in vegetable oil, after 5 minutes add finely grated carrots. When they acquire a golden hue, you can add the sliced mushrooms and simmer until all the moisture has evaporated. Pour 2 liters of water into a saucepan, add chopped potatoes, add salt, at the boiling stage, mix vegetables with mushrooms, salt, pepper, and other spices, cook until the potatoes are fully cooked. Before serving, let the soup sit for 20 minutes, then pour into portioned bowls, sprinkle with herbs and add a spoonful of sour cream. |
| Mushrooms in pots with cheese | mushrooms (250 g); hard cheese (200 g); potatoes (3-4 pcs); onions (2 pcs); salt pepper; sour cream (100 ml); greens (optional). | Peel the mushrooms, rinse, cut into pieces. Chop the onion into half rings. Fry both components in different pans until golden brown. Place diced potatoes on the bottom of the pots, add salt and pepper, place a mixture of mushrooms and onions on top, sprinkle with grated cheese and pour over cream - 1-2 tbsp. l. per container. Place in the oven for 30-40 minutes at a temperature of 180-190°C. |
Taste qualities
If you cook milk mushrooms correctly, it will look like a delicious dish, the like of which cannot be found among homemade preparations. Due to the dense pulp, this product saturates very quickly. Has a subtle mushroom smell. The surface of salted or soaked milk mushrooms is smooth and slimy. It is practically not eaten when fried or raw.
The taste is generally neutral, but it is quite possible to enhance it by adding garlic or other herbs and spices. When salted, it is served drizzled with butter and seasoned with herbs or crushed garlic. It is an excellent cold appetizer.
Did you know? Fungi were the predecessors of trees on Earth. Before the appearance of trees, they were gigantic in size (up to 7 m in height).