Honey mushrooms are considered one of the most popular types of mushrooms among lovers of “silent hunting” for a number of reasons. Firstly, the taste is excellent, they are good both on their own and as part of a variety of dishes and are suitable for almost any purpose. Secondly, they can be collected most of the year, since there are many varieties that appear at different periods. Thirdly, mushrooms grow in large colonies, so collecting a basket is much easier than when searching for other species.
Dear readers! For you, we have created communities on social networks in which useful articles and interesting ideas are published several times a day! Subscribe and receive useful content in a convenient format!
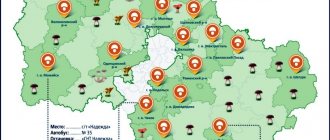
When does the honey mushroom season begin in the Moscow region and where to look for them?
With the end of summer, many mushroom pickers are wondering whether autumn honey mushrooms have arrived in the Moscow region and where it is better to go to reap a rich harvest.
Reference! The picking season in this region begins as early as August, but if the autumn weather is warm, mushrooms can be found in October.
To know when to go into the forest for mushrooms, you need to study the description of honey mushrooms, their main types and growth characteristics:
- Fruiting bodies grow in large groups on stumps or fallen trees. As a rule, they are found in the same place from year to year.
- Several edible species grow in the Moscow region: summer, winter, meadow and autumn. The last one is considered the most popular.
- They go on a “quiet hunt” after warm rain. It is this weather that promotes the active growth of fruiting bodies.
It is noteworthy that autumn species can grow not only on fallen trees, but also on living trees, while winter species are found only on old stumps.
Growing conditions
Honey mushrooms grow in families on fallen trees or dilapidated stumps. To harvest a good harvest, it is also important to determine the weather conditions that are necessary for the growth of mushrooms. One of the main aspects is temperature. It should be in the range of 15-26℃ heat. If this figure is exceeded, the growth of representatives of this kingdom of living nature will slow down, and during drought they will dry out and rot.
In addition, air humidity is also important for honey mushroom growth. Together with the required temperature, it creates ideal conditions for a rich harvest of mushrooms: they will bear fruit after every rain.
But there must also be good air circulation in the layers of soil through which the honey mushroom mycelium passes.
In case of severe drying out of the earth, its flooding and freezing, the growth and development of roots stops, but their viability is preserved.
The lifespan of honey mushrooms is 11 days. Extreme heat or cold is detrimental to the growth of mushrooms. In addition, they become weak due to the presence of worms and insects.
Are there honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in the Yaroslavl direction?
The Yaroslavl direction of the railway is considered one of the best regions of the Moscow region for collecting forest mushrooms.
There are several places worth visiting here:
- Near the Pravda railway station there are many forests rich in mushrooms, and among them there are not only honey mushrooms, but also the more valuable porcini mushrooms.
- Russulas and chanterelles are often found in the direction of the village of Nazarovo.
- You can find a lot of boletus and boletus if you move from the Pravda station to the village of Stepankovo.
But the forests near the Pushkino station are considered the best for picking mushrooms. This is an ecologically clean region where not only honey mushrooms are found, but also saffron milk caps, boletus and boletuses.
Growth conditions again
These mushrooms prefer fallen trees and rotten stumps. For the colony to bear fruit, stable air exchange is necessary in the places where the mycelium has formed. Ideal conditions are semi-decomposed wood.
Spring and winter honey mushrooms begin to develop from +3-5°C, but the optimal conditions for them are + 7-15°C. During frosts and droughts, growth stops; daytime and nighttime changes have a negative impact. The colony grows rapidly after heavy rains and temperatures rising to 15-24°C. But it is best to collect honey mushrooms not in the rain, but 2 days after. Then the mushroom bodies are more fleshy. Winter mushrooms need +7°C to develop. When it freezes, they become covered with an ice crust, but after thawing they do not die, but continue to grow.
Interesting!
The lifespan of honey mushrooms is 10-11 days. The development of the leg stops on day 5-6, and the cap grows all this time. That is why its edges begin to break off, it bends towards the ground, breaks off - it is difficult for the base to hold the overgrown fruiting body. Its condition is affected by insects - with high humidity they actively reproduce. You will attack a large family, but there is nothing to collect.
Where else can you find honey mushrooms in the Moscow region?
Finding autumn mushrooms in the Moscow region is not difficult, because the climate of the region promotes the active growth of mushrooms, and the numerous forests surrounding the capital allow for a rich harvest.
Reference! Forest areas near the villages of Golygino, Novovoronino, Vysokovo and Morozovo are popular among mushroom pickers, but there are a lot of people here during the season.
The most “mushroom” places in the region are:
- The forests around the Gremyachiy waterfall are warm and humid. This environment is ideal for the growth of fruiting bodies.
- The second most popular route is the forest areas near the 43 km platform. Here you can walk along the trails, moving along the Vyaz River. The route is long, but the harvest is very plentiful.
- In the forests next to the Skhodnya River near the Podrezkovo station there are also a lot of mushrooms, and not only honey mushrooms are found, but also saffron milk caps, butter mushrooms and boletus mushrooms.
Experienced mushroom pickers also advise visiting mixed forests near the village of Elino, next to the Firsanovka station.
How to distinguish edible mushrooms from false ones
Honey mushrooms are one of the popular varieties of mushrooms. This is not surprising, since often a lot of them grow within one area. There are many subspecies in one family, including edible and poisonous specimens. They have many similar characteristics, so it is not difficult to confuse them. But there are still specific criteria to distinguish them. Edible honey mushrooms in the Moscow region can be collected if you pay attention to:
- Fruiting body. Real mushrooms have a pronounced membranous rim.
- Edible ones smell like mushrooms, while poisonous specimens have an unpleasant odor.
- The caps of real mushrooms are colored in light brown shades, while the inedible mushrooms have bright colors.
- The caps of young edible honey mushrooms have a scaly structure, while those of poisonous mushrooms have a smooth structure.
Attention! Honey mushrooms come in spring, summer, autumn and winter. But only the last variety does not have poisonous counterparts.
In addition to all of the above, there are plates under the cap of all types. Only in edible species they are colored in cream shades, while in poisonous ones they are yellowish, greenish and even black. To understand what false mushrooms look like, you can look at the photo.
It’s not enough to know when mushrooms will grow in the Moscow region in 2022. It is important to study the growth map of honey mushrooms in advance and learn to identify edible varieties from poisonous ones.
When will honey mushrooms appear in the Kolomna district of the Moscow region?
Kolomna district of the Moscow region is another promising region in terms of mushroom picking. Mixed forests predominate here, in which almost all varieties of forest mushrooms are found.
The best routes in this region are the forests near the village of Kolodkino, Provodnik and Borisovskoye. The village of Uzunovo in the Serebryano-Prudsky district is also popular.
Here you can find not only autumn varieties of mushrooms, but also winter mushrooms in large quantities.
The difference between poisonous mushrooms and edible ones
Poisonous mushrooms can be found in the forests near Moscow: gray-yellow honey fungus, dark red false honey fungus, fringed galerina, spindle-footed money. Eating such toadstools causes poisoning, accompanied by fever, profuse sweating, abdominal pain, stomach problems, and loss of consciousness. They differ from ordinary mushrooms:
- nasty smell;
- green, yellow or blackish lines under the cap;
- bright yellow smooth cap; absence of tubercles and skirt (encircling ring) on the leg.
Honey mushrooms parasitize trees: oak, birch, acacia and hazel. They are noticed on trunks with a white coating or under old stumps.
Advice ! It is not recommended to collect anything near roads, businesses, within the city and in parks.
A healthy mushroom has a round cap, a thin elastic stem, beige lines under the cap, 10-15 cm high. The tree where the mushrooms grow, the soil and the weather are reflected in its shade. The palette ranges from yellow to brown. Over the years, the cap becomes flat, dull, and the plates darken, so edible mushrooms have a dull light brown color. Honey mushrooms in the forest live in groups, and there are 1-2 poisonous mushrooms. Some of them are edible: talker, winter mushroom and others. Among the winter mushrooms there are no false ones.
Other areas
You can choose other areas for “silent hunting”. For example, along the Gorky direction, mushroom places are found near the Fryazevo station. The walk to the forest here is about 2 km, but near the villages of Golenishchevo, Marfino, Dulepovo and Vvedenskoye you can collect not only honey mushrooms, but also boletus, boletus and boletus.
Reference! There are also many mushroom places in the Paveletsky direction. For example, next to the White Pillars station there is the village of Shebantsevo. There are a lot of saffron milk caps and butter mushrooms in the local forests.
Not far from the villages of Uvarovo and Yusupovo there are extensive forests. They are quite wet due to the Severka River flowing nearby, so there are a lot of boletuses and boletuses here.
Not far from the capital, summer and autumn honey mushrooms are found along the Kyiv, Leningrad and Belorussian directions. Along Kazansky you can get to the Gzhel station and pick up a full basket of summer mushrooms. Autumn ones are found mainly near the Shevlyagino and Kuzyaevo stations.
The Moscow region is a region where you can harvest a rich harvest of wild mushrooms at almost any time of the year. The capital is surrounded by forests, and weather conditions contribute to the growth of honey mushrooms, boletus and boletus in almost all railway directions.
When will honey mushrooms start to appear in the Moscow region in 2022?
It is impossible to give an exact date for the appearance of mushrooms in a particular season, since a lot depends on the weather conditions in the region. The summer and autumn varieties are the most collected because they taste good and grow consistently in the same places for many years. Usually the season begins in the second half of August, and peak indicators occur from mid to late September; during this period there are especially many mushrooms and almost all mushroom pickers return with full baskets.
It is necessary to take into account the weather; summer mushrooms begin to grow actively when the daytime temperature does not rise above 23 degrees. High humidity (not lower than 80%) and heavy rain the day before are also required. After rainfall, it takes about a week before large numbers of mushrooms grow.
As for autumn, the optimal temperature for them is an average daily temperature of 12 degrees. In this case, humidity indicators should be similar as for other types. Honey mushrooms grow in so-called layers, each of which lasts about 2-3 weeks. About 3 autumns usually pass, so there is always a chance to pick up mushrooms if you couldn’t find anything on your first trip. It is worth monitoring precipitation and temperature; with the help of these simple indicators you can quite accurately predict when honey mushrooms will begin to bloom.
By the way!
Sellers near the highway and in markets and advertisements on the Internet will be an excellent hint. When honey mushrooms start growing, you can immediately see them on sale.
Winter varieties begin to grow during periods of cold weather and are available until spring; they can be collected from October. During the thaw, mushrooms grow, so if the winter is mild, you can collect them continuously for several months.
Why are honey mushrooms useful?
By the way, if for trees autumn honey mushrooms are unconditional enemies, then for humans they are friends. They contain a lot of vitamins and microelements, they have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, drugs made from them help with nervous and cardiovascular diseases... However, there is a small problem. As Vishnevsky explained to KP, “fungal cells are covered with a membrane that is similar to insect chitin, it is called chitosan. We do not have enzymes in our bodies that can destroy it. But during the grinding process, the cell walls are damaged, and all the nutrients that were previously sitting there as if in a prison immediately become available to us.” Therefore, in order to extract all their beneficial properties from honey mushrooms, it is advisable to grind them properly - to make a puree soup from them, for example. But, of course, few people have heard of such recipes.
Honey mushrooms contain valuable microelements. Photo: Denis KORSAKOV
The Chinese, however, have adapted to preparing tinctures from honey mushrooms, which are used as a tonic in folk medicine. And from the powder of dried fruiting bodies, tablets are made that are used to treat neurasthenia and convulsions.
Undercooked mushrooms can cause allergic digestive disorders. Photo: Denis KORSAKOV
On the other hand, honey mushrooms can cause gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders in some people. It's more of an individual reaction. Whether you have it can only be determined experimentally. If you notice it, from now on, before cooking, boil honey mushrooms for 10 minutes and drain the broth - all problems will disappear. (By the way, for the same reason, honey mushrooms are only suitable for hot pickling, and not for dry or cold - they are salted after preliminary boiling and draining the broth).
Can honey mushrooms prevent cancer?
But an even more medicinal mushroom is considered to be the winter honey fungus , which is also called Flammulina velvetypodia. It belongs to a completely different genus than autumn honey mushrooms. And its peak fruiting comes later - at the end of October. Its uniqueness is that it can grow all winter, until February, under the snow: it is believed that it developed this ability evolutionarily so as not to compete with other honey mushrooms. In the same way, it successfully eludes mushroom pickers: few people go into the forest with a basket in November-December. The secret is that he has learned to produce a substance similar in effect to antifreeze - it helps him cope with the cold.
Winter honey fungus can bear fruit during winter thaws. Photo: commons.wikimedia.org
This is a very tasty, almost gourmet mushroom. In Japan, it has long been bred artificially (fortunately, it is unpretentious). The enoki mushroom , which is so loved in Japanese cuisine, is the same winter honey fungus that grows in our forests, although it is strikingly different in appearance. Enoki has a long, thin, snow-white stalk with a tiny cap at the end, and these mushrooms grow in dense clumps. It's all about the technique that the Japanese have long used: mushrooms are grown in the dark (hence the color) and in an atmosphere saturated with carbon dioxide (this affects the shape of the stem).
Enoki in Japan is grown all year round on an industrial scale. Photo: commons.wikimedia.org
Well, the medicinal power of winter honey mushroom is evidenced by the fact that in areas of Japan where it is actively cultivated and constantly eaten, the incidence of cancer is one hundred times less than in areas where it is not popular.
Description of mushrooms
Before going to the forest, you need to know what honey mushrooms look like so as not to confuse them with a poisonous variety. The most typical mushrooms for the Moscow region have a thin stem, up to 10-12 cm in height, a convex cap of a slightly yellowish or brown color with a light spot in the center. As they grow older, the cap flattens, the spot becomes smaller, and sometimes disappears completely.
Edible honey mushrooms in the Moscow region are represented by several types:
- Spring and summer species prefer rotting deciduous trunks or rotten stumps. The colonies are the most numerous. The cap is small, up to 5 cm in diameter, the flesh is slightly watery, the smell is of freshly cut trees, with which the mushrooms form a symbiosis. Other names: talker, linden mushroom.
- Meadow grass, meadow grass or non-rotting grass is small, with a smooth cap of creamy or creamy color and uneven edges, up to 3 cm in diameter. The flesh is pale yellow, the aroma is almond, the taste is bitter. It is most often mistaken for a poisonous mushroom. It is found in open areas, pastures, forest edges, the sides of dirt roads, and at the edges of ravines. Forms rows or circles.
- Autumn honey mushrooms are the most numerous. They fit the description of classic mushrooms of this species. One by one they almost never come across. They look “noble” - a honey-brown or reddish cap, darker in the center, begins to flatten only on the 7-9th day of life, the cap reaches 10 cm in diameter. The pulp is light, milky or creamy white, dense, the smell is pleasant, like fresh sawdust. Can be found in forests, in forest parks.
- The correct name for the winter honey fungus is Flammulina velvetypodia. Forms numerous colonies, prefers old trees, rotting trunks on the edges or near streams. The caps are yellowish, pale orange, brownish - the edges are light. The pulp is creamy, with a refined delicate aroma.
Honey mushrooms grow in foxes, in parks, and you can find a colony in your own garden plot. In this case, you should cut it very carefully to preserve the mycelium. Then the colony will be restored every year and there will be no need to waste time on long trips.
Honey mushrooms are false
The edible summer honey fungus has several doubles, one of them is the false honey fungus. This mushroom's cap color is approximately the same as that of the summer honey fungus, but the color of the plates changes and becomes gray. It is from the gray plates that the name of the mushroom comes. False honey fungus never grows on deciduous trees. It is worth noting that this mushroom is considered conditionally edible, but it must be boiled before eating.
But the other double, the sulfur-yellow false honey fungus, is not suitable for food. Although this mushroom does not contain poisons, it is inedible. The pulp of the mushroom smells unpleasant and has a very bitter taste. Because of such strong bitterness, sulfur-yellow false honey fungus can ruin the entire dish like a gall mushroom. The main distinctive features of the sulfur-yellow false honey fungus:
- No ring on the leg;
- The plates are yellow-green, gray, olive-black;
- The color of the caps is too bright, practically screaming about the inedibility of the mushroom.
Useful tips
In addition to the standard recommendations described above, it is recommended not to forget about the time of year. One kilogram is enough to use as an ingredient for lunch or dinner. But for screwing on lids, it is more correct to choose the peak season, which falls from August to October. September is the “golden mean” and the best choice for collecting fruits, both honey mushrooms and boletus, boletus and saffron milk caps.
You should dress in closed clothing to avoid additional health problems:
- mosquito or gadfly bite;
- tick penetration;
- snake attacks.
It is better to postpone the trip for weekdays. From Wednesday to Friday is the most suitable and fruitful time. After harvesting over the weekend, the mushrooms will grow and gain the required height and weight.
Due to the fragility of the fruits, it is recommended to use only buckets and wicker baskets for collection. Bags and deformable containers will only damage the appearance by breaking the caps and legs.
Kinds
Honey mushrooms in the Moscow region belong to 10 species out of 40 known throughout the world and which grow on the territory of the Russian Federation. Among them there are several especially popular and beloved by Muscovites.
Edible species
Almost all types in the Moscow region are suitable for various culinary uses. Edible and commonly found ones include:
- meadows;
- honey mushrooms of the Assumption;
- honey mushrooms hemp;
- winter honey mushrooms;
- woody mushrooms.
“In the Moscow region it is easier to find honey mushrooms than to process them later,” say the locals. After rains, the woody species appears in large groups on healthy trees. They are easy to knock down with a stick to which a knife is tied.
A rare species for other regions, winter honey fungus is found with the onset of winter under the snow, on a cushion of old leaves, on old stumps that have absorbed moisture and retained the necessary warmth. Their spherical caps are large, up to 15 cm in diameter. Light plates are located infrequently. The length of the leg is up to 9-10 cm. It is velvety to the touch, pleasant and dry in young people, hard and tough in old ones. The pulp contains a lot of moisture, which evaporates during the cooking process and the volume of the finished winter harvest decreases sharply.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
The season for collecting winter honey mushrooms or Flammulina velvety-footed is in autumn-spring. In winter, you can safely collect frozen mushrooms of this species, because... after thawing, they restore their structure. Due to the presence of a small amount of unstable toxins in the pulp, flammulin must first be boiled for 20 minutes and only then cooked. These are mushrooms that are not for everyone - when boiled they become slippery.
In Korea and Japan, industrial cultivation of winter mushrooms has been established on a substrate of chopped wheat straw or on moistened wood. However, self-breeding of this species stops the need to maintain a certain temperature regime.
By the way. A substance was discovered in the fruiting bodies of winter mushrooms, which got its name according to the genus of the fungus - flammulin. It has the ability to prevent the formation of sarcoma.
Edible Assumption mushrooms received their name from the Christian holiday of the same name, the Dormition of the Holy Mother of God. These days the mass collection of these mushrooms begins. With a warm autumn it lasts until November. The difference between Uspensky honey mushrooms is their yellowish or brown leg, which grows up to 10 cm in length. There is a noticeable convexity on the surface of the cap; underneath it has frequently located plates. A thin “skirt” is visible on the leg, which becomes thinner over time and breaks into several parts.
Several varieties of honey mushrooms grow in the forests
Meadows are often found in gardens and country estates, in May, in the first grass, in open, illuminated spaces in summer, in ditches on roadsides and pastures closer to autumn. This mushroom belongs to the Negniuchkov family. The size of the cap of marasmius (the second name for meadow grass) is up to 5 cm. Its surface is smooth and dry. A tubercle is visible in the central part. The edge is thin and uneven. After rain, the cap becomes covered with a film similar to sticky mucus. The aroma and taste of the pulp is uncharacteristic for honey mushrooms - almond-like, not strong. When broken, the color of the flesh does not change. The plates are sparsely spaced and their color is creamy in dry weather. The leg is in the shape of a cone or cylinder, with a bend at the bottom. The surface is velvety. The harvest time for meadow grass is from May to the end of October.
Inedible and poisonous species
In the Moscow region there are mushrooms that are not edible or poisonous, which are often confused with the edible original. These include:
- false scent;
- death cap.
If such specimens get into food, they can be fatal. Most often, poisoning occurs due to the toadstool, the toxins of which are so poisonous that they can penetrate through the skin into the human blood after simply touching the surface of the cap.
False honey mushrooms are clearly identified by bluish spores and a yellow cap. They do not have scales on their legs that are characteristic of an edible species. Poisoning with them is not fatal, but unpleasant, with vomiting, diarrhea and fever.
How poisonous are false honey mushrooms and what do they look like?
Moreover, the honey fungus is capable of partial modification. Such transformations are the result of changing weather conditions, and also depend on the type of wood on which the fruiting body grows. Experienced mushroom pickers are often already prepared for such “surprises”, so they turn to additional signs. But some beginners, unfortunately, do not always realize how poisonous honey mushrooms are, so they often ignore additional signs, limiting themselves to only superficial knowledge.
In this case, it is highly advisable, even before going for your first harvest, to take a “young fighter course” under the guidance of an experienced mushroom picker. By the way, it is not at all necessary to study the entire group of twins of each species. It is enough to simply deepen your knowledge about one or two species that are most famous in a particular area. If we know what appearance edible types of fruiting bodies have, then we need to determine what poisonous honey mushrooms look like. After all, as already mentioned, false representatives can be very similar to their edible “brothers”.