Infectious disease specialist
Sinitsyn
Olga Valentinovna
34 years of experience
Highest qualification category of infectious disease doctor
Make an appointment
The vast majority of Russians know that consuming low-quality canned or smoked products can lead to a serious illness - botulism. This is an acute disease of infectious-toxic origin, caused by the pathogen Clostridium botulinum and the toxic product of its vital activity, which is a powerful poison of biological origin. It is botulinum toxin that makes the disease extremely severe and often fatal.
How to distinguish false honey mushrooms from edible ones
Poisoning by false honey mushrooms can be caused by inattentive picking, during which the mushroom picker cannot accurately recognize the type of mushroom. Poisonous and edible mushrooms are very similar to each other, their places of growth often coincide, and the feature of growing on stumps in large groups is also copied.
Despite the great similarity of these mushrooms to each other, there are still certain differences, among which it is necessary to highlight the following:
- skirt;
- color;
- cap texture;
- smell.
Only inedible honey mushrooms have a so-called skirt, located under the cap. They differ in the color of the cap and the plates located on the inside. Poisonous mushrooms have a brighter and more saturated color. Edible honey mushrooms have a light brown cap with creamy plates located under it.
It is possible to distinguish mushrooms by texture only if there are old honey mushrooms, since young ones do not have this feature. Inedible species have scales in the central part of the cap.
A photo and description will help you recognize and distinguish between edible and false honey mushrooms. Poisoning by these mushrooms can be very dangerous for humans, and in some cases even leads to death.
What you need to know about saffron milk caps
Collected in an ecologically clean place and prepared according to all the rules, saffron milk caps have a general strengthening effect.
Due to the presence of the natural antibiotic lactarioviolin in its composition, saffron milk caps are included in the menu of patients with infectious diseases and tuberculosis. Saffron milk caps are rich in vitamins A, B, C, iron, and zinc. A sufficient amount of fiber will support the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Saffron milk caps are a low-calorie product (18 kcal), which is important for people on a diet. But for all their positive qualities, seemingly harmless mushrooms can cause poisoning. This may happen in the following cases:
- the mushrooms were collected along highways, in the area of industrial enterprises or airfields, where the concentration of mercury and lead in the soil is high;
- the mushrooms were overripe, rotten or spoiled;
- the rules for the technology of canning or pickling mushrooms were violated, which led to the accumulation of harmful products in jars (for example, botulism bacillus);
- saffron milk caps were salted or pickled in galvanized containers;
- Instead of saffron milk caps, inedible mushrooms were collected.
Saffron milk caps are difficult to confuse with other mushrooms because of their characteristic bright cap. But such cases still occur. Saffron milk caps can be confused with some species of lacticaria, which are inedible, and with saffron mushrooms, which belong to the conditionally edible mushrooms.
Most often, the amber milky is mistakenly included in the basket. Outwardly, it really resembles a saffron milk cap, and you can distinguish a milkweed by its yellow pulp, a smell reminiscent of chicory, and the juice it produces.
Another false relative of the saffron milk cap is the pink wave. It can be recognized by its fluffy pink hat with drooping edges. Volnushka is not considered a poisonous mushroom, but it can only be eaten after a very long heat treatment.
But let’s return to real saffron milk caps. If the rules for collecting and preparing these mushrooms are not followed, intoxication of the body often occurs.
Types of false mushrooms
Before you determine what the signs and symptoms of false mushroom poisoning are, you need to know what types of these mushrooms exist. In particular, the following types are distinguished:
- sulfur-yellow honey fungus;
- brick-red poisonous honey fungus;
- false foam of Candol.
Sulfur-yellow honey fungus is most similar to edible honey mushrooms. To distinguish them from each other, a very careful examination is required. The cap of a poisonous mushroom has a brighter and more saturated color. It is often reddish or yellowish and smooth. The edible version has a light film between the stem and the cap, which is absent in the false honey fungus.
The plates located on the underside of the cap are also different. Edible mushrooms are white, while poisonous mushrooms are brown. The poisonous mushroom has a bitter taste.
The brick-red poisonous honey fungus has a bright cap, as well as yellow plates located under it. Over time, they begin to change color to brown, dark or even greenish. It has an unpleasant odor and bitter taste.
Candol's false honey fungus has a very large and soft cap that easily breaks when touched. There is a white fringe along the edges of the cap. The bottom of the plates are black, with a grayish or purple tint.
Survey
In order for a doctor to diagnose food poisoning, as a rule, it is enough to carefully interview the parents and examine the child. Sometimes the doctor may additionally prescribe:
- a blood test to see if symptoms are caused by a bacterial or viral infection;
- stool analysis to rule out infection caused by abnormal bacteria;
- If an examination by a surgeon is required, he may also prescribe an additional examination.
Online consultation with pediatrician Olga Nikolaevna Tekutyeva
Registration online
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Causes of poisoning
You can be poisoned not only by poisonous honey mushrooms, but also by edible ones, since this mushroom tends to accumulate heavy metals. This is especially pronounced when they grow in environmentally unfavorable places. Similar conditions are created at a short distance from highways and roads with a large flow of cars. Significant emissions of toxic substances are typical for industrial areas and radioactive zones.
Toxic substances can be released during prolonged or improper storage of mushrooms. In this case, they become a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. For the same reason, it is worth paying attention to the preliminary preparation of the product.
Symptoms
Many people are interested in how long it takes for symptoms to appear in case of false honey mushroom poisoning, so that the presence of a problem can be recognized in a timely manner. Often, the first signs appear 10-60 minutes after eating dishes that contain mushrooms. The symptoms of poisoning with false honey mushrooms are very acute. How long this happens depends largely on the amount of product, as well as the specifics of its preparation.
The primary signs include:
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness and headache;
- severe diarrhea;
- breathing problems;
- loss of consciousness;
- abdominal pain;
- chills, numbness of extremities.
Attacks of nausea and vomiting continue even after food particles are removed from the stomach with liquid, which can cause severe dehydration. A sign of poisoning by false honey mushrooms may also be that there is a lack of coordination, since it seems to a person that everything is revolving around him. Severe diarrhea can lead to dehydration.
In addition, breathing problems are observed, which are expressed in the occurrence of shortness of breath and attacks of suffocation. In this case, the person must be provided with urgent medical care, as this can lead to serious consequences, including death. In some situations, fainting may occur, and in particularly severe cases, coma may occur. Painful sensations in the abdomen can occur even when consuming small amounts of mushrooms.
It is worth noting that symptoms of poisoning with false mushrooms can be observed even if you eat a small amount of a poisonous mushroom. Substances may remain toxic after prolonged cooking, salting or frying.
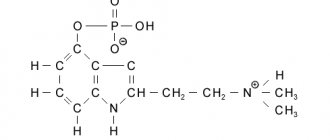
Botulism
Improperly prepared or stored mushrooms, such as canned mushrooms, can cause botulism.
Botulism is a serious and serious disease that develops as a result of an infection entering the body, located mainly in the ground, next to the spores of the mycelium. If the mushroom is poorly washed, peeled, or not sufficiently boiled, an infection can enter the body.
The first signs of botulism appear 12-72 hours after eating mushrooms.
The main symptoms of botulism are:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Visual impairment (everything floats, doubles);
- Convulsions;
- Diarrhea;
- Headache;
- Labored breathing;
- Dry mouth.
Important! At the first signs of botulism, i.e. After eating canned mushrooms, consult a doctor immediately!
Hepatotoxicity of false mushrooms
Symptoms of false honey mushroom poisoning resemble those of ordinary food poisoning. A negative factor is the rapid absorption of toxic substances into the blood and then distribution throughout the body. The biggest danger is that toxins cause liver damage, which cannot cope with toxic substances. As a result, the organ becomes enlarged.
Among the external manifestations, one can distinguish that the skin acquires a somewhat yellowish tint. In especially severe cases, jaundice spreads to the mucous membranes. Among the symptoms of poisoning with false honey mushrooms, one can highlight the presence of painful sensations on the right under the ribs. The initial signs are not strong enough, but if poisonous mushrooms are consumed in large quantities, liver cell necrosis may begin.
First aid for poisoning
Symptoms of poisoning with false honey mushrooms can be very different, which is why it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner for a diagnosis. If a person shows signs of intoxication after consuming honey mushrooms, then it is important to take urgent measures. First aid is to cleanse the body of toxic substances. To do this, you need to do a gastric lavage and take activated charcoal.
To perform gastric lavage, you need to drink several glasses of water and induce a gag reflex. To reduce possible harm from poisons and toxins, you need to flush the intestines with an enema and a laxative.
When poisoned, the patient loses a lot of fluid and may die from dehydration, so the patient is provided with a lot of warm drink. To eliminate weakness, tremors and numbness of the limbs, a person should drink sweet, strong tea and apply a heating pad to his legs and arms.
Treatment of poisoning
If the first symptoms of poisoning occur, first aid measures must be taken in a timely manner. Treatment involves the use of medications that induce vomiting. A medication is also required to help remove poisons and toxins from the body. After eliminating the main signs of intoxication, it is imperative to take medications to restore the affected organs.
It is necessary to follow a special diet for faster recovery during the first 24 hours from the moment the first signs of poisoning appear. You can only consume light soups and broths, lean meats, dairy products, and cereals.
Complications after poisoning
If the victim receives qualified assistance in a timely manner, then within a few days all the signs will disappear. With more serious poisoning, when there is a high concentration of toxins in the liver and blood, the prognosis may not be reassuring enough. Severe poisoning can lead to complications such as:
- disruption of the functioning of internal organs;
- damage to the nervous system;
- deterioration of water-salt balance;
- death of the patient.
The most severe signs of poisoning are observed in the elderly and children under 3 years of age. A weakened immune system can lead to a rapid progression of the disease, which is why mushrooms should not be eaten by people of these age groups. The following factors significantly increase the risk of death from poisoning:
- pregnancy;
- weak immunity;
- rehabilitation period after serious illnesses;
- diseases of the liver, kidneys and heart.
It is important to promptly identify the first signs of the disease and consult a doctor. Correctly carried out medical measures will help eliminate the signs of poisoning without consequences for health.
Prevention
Despite the fact that saffron milk caps do not belong to the group of mushrooms that are dangerous for consumption, certain precautions must be taken.
- Never collect mushrooms along roads, near landfills, or in close proximity to industrial enterprises.
- The amount of accumulated toxins can be reduced by boiling mushrooms in water with the addition of citric acid or vinegar.
- Do not use galvanized utensils for salting and marinating saffron milk caps.
- Do not eat saffron milk caps 12 hours after picking them.
- Before cooking, thoroughly wash and clean the mushrooms from accumulated particles of sand, leaves and soil.
- Never eat pickled mushrooms if the lid of the jar is swollen!
- Pregnant women and nursing mothers should refrain from eating saffron milk caps or at least eat them in limited quantities.
- Harvest only young saffron milk caps for the winter, carefully observing all heat treatment requirements.
- All types of mushrooms (even gourmet ones) are not recommended for feeding children under 7-8 years of age.
- You cannot buy homemade mushrooms at spontaneous markets.
- It is recommended to store pickled mushrooms in a dark place at a temperature of 4-15 C.
How tempting it is to take a walk through the autumn forest, breathe in the fresh air, and even return home with a basket of delicious saffron milk caps! To prevent a delicacy from a forest delicacy from landing you in a hospital bed, you need to be very careful both when collecting saffron milk caps and when processing and preparing them. If you have the slightest doubt about the quality or freshness of mushrooms, you must throw them in the trash without mercy. If poisoning does occur, you should not hesitate to consult a doctor.