Honey mushrooms are among the most popular types of mushrooms that autumn forests are so rich in, and are especially loved by mushroom pickers. These modest gifts of nature have a pleasant taste; they can be used for preparing first and second courses, baking, salting, frying, and pickling. But you should know that, contrary to the already established public opinion, the danger is posed not only by false honey mushrooms containing dangerous toxic substances, but also by completely edible species of these mushrooms.
Real honey mushrooms (pictured) are the most popular and beloved gifts of the autumn forest by mushroom pickers.
Intoxication of the body with substances that make up mushrooms is one of the most dangerous and can lead to death. How not to get poisoned by honey mushrooms, how to distinguish edible mushrooms from poisonous ones, what are the early signs of poisoning and what is the essence of treatment? Let's look at these and other questions in more detail.
Honey fungus - what kind of mushroom
Honey mushrooms is the popular name for a large group of mushrooms belonging to various genera and families. Highlight:
- meadow,
- mucous membranes,
- yellow-red,
- thicklegs and other types of these mushrooms.
They are found mainly in autumn. Honey mushrooms are very popular among mushroom hunters, as they can be prepared in a variety of ways. It is believed that the forest delicacy reveals its taste best if it is marinated or fried.
Main causes of intoxication
In most cases, people are sure that in medical practice only poisoning by false honey mushrooms occurs. This opinion is incorrect. Edible mushrooms can also lead to intoxication if:
- collection took place near highways, chemical plants or simply in contaminated areas,
- even insect-infested specimens are collected,
- requirements for cooking mushrooms are ignored,
- storage standards have not been met or its shelf life has expired.
Honey fungus growing in polluted areas, no matter whether it is meadow or any other, quickly accumulates many toxic substances, such as cadmium, mercury, zinc, lead, cobalt. These mushrooms, in general, are capable of storing a huge amount of poisons without changing their external qualities and taste, which is why their consumption often leads to the development of intoxications.
Doctors recommend that women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as young children, exclude mushrooms from their diet!
You can also be poisoned by pickled or salted honey mushrooms due to botulinum toxin if the mushrooms were poorly washed before cooking or the product’s expiration date has expired.
How to distinguish a false or real honey fungus in front of you
When searching for mushrooms in local forests, as well as purchasing delicious specimens collected from sellers standing in the market and sitting next to the highway, you need to pay close attention to some of the visual characteristics of the mushrooms that appear before you. Let's look at the following table to see what features are characteristic of each category.
Table 1. Signs of false mushrooms
| Honey mushrooms of false category | Honey mushrooms are real | |
| External differences and taste |
|
|
As you can see, there are actually few significant differences. It is very important to pay attention to such little things as dark plates and a skirt, since at the stage when you feel the bitter taste, the harmful poisons of the honey fungus will already be inside your body.
In addition, if you made, for example, fried mushrooms, and it contained not only honey mushrooms, or, say, you used them in soup, it is quite difficult to feel their taste. In addition, when chopped and cooked, it will be extremely difficult to distinguish them from other ingredients, and you may think that you simply overcooked the vegetables in a frying pan.
Symptoms
How long does it take for the first symptoms of mushroom poisoning to appear? In most cases, the first signs begin to bother a person after an hour, but sometimes the latent period lasts up to 12 hours.
Read also: Poisoning of the body with organophosphorus compounds
Toxins, once in the body, are quickly absorbed into the blood and spread throughout the body. Once in vital organs, poisons have a detrimental effect on them. Heavy metals and toxic compounds can have a detrimental effect on the condition of cell membranes, lead to damage to cellular structures and cause disturbances in metabolic processes.
First of all, in case of poisoning, the digestive system is affected, which is manifested by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- attacks of dizziness and headaches,
- nausea,
- discomfort in the abdominal area,
- spasms,
- pain in the stomach and intestines.
As intoxication progresses, the following symptoms appear:
- severe vomiting,
- diarrhea,
- signs of dehydration.
If intoxication is caused by the use of false honey mushrooms, it will be characterized by the following signs:
- hallucinations and delusions,
- dizziness,
- severe shortness of breath,
- severe diarrhea.
Mushroom poisoning, accompanied by neurological symptoms (drowsiness, lethargy, dizziness), is considered life-threatening for the victim. You must immediately call an ambulance!
Symptoms of poisoning
Stage 1:
- flatulence;
- stomach ache;
- heartburn;
- dizziness.
Stage 2 is characterized by an increase in intoxication of the body:
- lethargy;
- tremor of the hands and lower extremities;
- nausea;
- repeated vomiting;
- increased stomach pain;
- spread of pain to the abdomen;
- cold sweat;
- diarrhea;
- decrease in blood sugar levels.
First aid and treatment for poisoning with edible mushrooms
First aid for poisoning with ordinary honey mushrooms begins with inducing vomiting and gastric lavage. Before the procedure begins, the patient is forced to drink a large amount of liquid and then vomited. You can do this in two ways:
- press your fingers on the root zone of the tongue,
- Dilute 1 tablespoon of salt in a glass of water and drink the mixture.
It is recommended to repeat the gastric lavage several times until all mushroom particles are removed from the stomach and the lavage water becomes clean. If the person is unconscious, the procedure is not performed to prevent choking on vomit.
If the patient is poisoned by edible honey fungus, it is also recommended:
- in the absence of diarrhea, give any saline laxative (for example, castor oil),
- provide the victim with plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration,
- force the patient to drink activated carbon (1 tablet for every 10 kg of body weight) or any other sorbent (the amount is calculated in accordance with the instructions).
Patients are prohibited from giving antiemetics, antidiarrheals and painkillers until emergency medical assistance arrives! Calling an ambulance is mandatory. If the symptoms worsen due to honey mushroom poisoning, the patient may need qualified help:
- repeated gastric lavage through a tube,
- accelerated elimination of toxins through infusions of the urinary system and gastrointestinal tract,
- use of hemosorption.
Read also: Spice poisoning in humans
General principles of treatment
Only timely first aid measures can prevent serious consequences.
Is it possible to be poisoned by pickled honey mushrooms that have been salted or undergone any type of heat treatment? And how does the chosen treatment depend on the type of food intoxication?
As mentioned above, despite the fact that the amount of mushrooms eaten, as well as the method of preparing them, have a direct impact on the symptoms and degree of poisoning, in general, characteristic signs appear even if a small portion is consumed. Conservative treatment of mushroom poisoning is selected in accordance with the clinical picture, the degree and form of poisoning, as well as such factors as the number of mushrooms eaten.
However, some procedures occur regardless of the aspects listed above, including:
|
|
|
| Lavage of the stomach and, if necessary, intestines. | Taking medications that cause vomiting. | Complete refusal of food during the first day after the appearance of early signs of poisoning. |
| Taking medications classified as enterosorbents, which is necessary to prevent the penetration of toxins into the blood. | The use of medications in the form of tablets, powders, injection solutions and injections that help remove toxins from the body. | Refusal of heavy, fatty, unhealthy and sweet foods. To restore the body and normalize the condition of internal organs, it is necessary to adhere to a gentle diet for at least two weeks. |
| Preventing dehydration and restoring water and salt balance by drinking plenty of fluids. | The use of medications that normalize and restore the condition of the systems and organs of the poisoned person. | During the treatment period, you should eat only light cereals and soups, fermented milk products, and lean meat. |
During the treatment process, one should not forget that failure to follow a balanced diet can lead to serious consequences, for example, disruption of the digestive tract.
What to do if intoxication occurs with false honey mushrooms
The development of false honey mushroom poisoning requires an immediate call for emergency medical assistance, as it can threaten the patient’s life. Before the arrival of doctors, it is recommended:
- carry out gastric lavage according to the standard scheme (the victim is given several glasses of warm water to drink, and then, pressing on the root of the tongue, induces vomiting) until the lavage water is clean,
- you can do a cleansing enema or give the patient a laxative if he does not have diarrhea,
- Give half a glass of boiled water every 20-30 minutes to prevent dehydration,
- if there is no longer vomiting, water can be replaced with warm tea with a little sugar,
- the patient is wrapped in warm blankets, covered with heating pads or bottles of hot water.
Symptoms of false honey mushroom poisoning are especially dangerous for young children and the elderly, as their nervous systems are more susceptible to toxins.
If several people ate mushrooms, and symptoms of intoxication appeared in only one person, then gastric lavage is carried out for everyone who ate them!
Prevention of poisoning by poisonous mushrooms of the false type
Since the ingestion of false mushrooms and their subsequent poisoning are not natural processes of the body, but are provoked from the outside, prevention in this case cannot be any permanent measures, consisting of taking medications or changing lifestyle. Unfortunately, the organs of a healthy lifestyle person and a person who mindlessly consumes fast food are equally seriously affected by the poisons of the mushroom.
This means that the only way to avoid poisoning is to take certain precautions when picking mushrooms.
- First of all, you should understand that you can only buy or collect mushrooms in the forest that are easily identified. These include chanterelles, milk mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, russula, and other mushrooms, the external features of which are well known to you.
- Old and wormy mushrooms should not be collected; toxins also form in them, due to the fact that over time the mushroom begins to rot and deteriorate, in addition, the worms deposit their own waste products inside it.
- Before preparing mushrooms, during their cleaning, it is necessary to carefully inspect the stems and caps to detect: worms, rotting, or discrepancies with the appearance features accepted for this variety of mushrooms.
Possible complications
If the patient receives help at the first symptoms of intoxication, the poisoning will disappear without a trace within a few days. As you might guess, porn can be presented in different ways. But here’s the most interesting version of Russian porn on the entire porn scene - Russian porn casting rus-porn.tv/kasting. Here the brightest emerging stars of the porn scene express themselves to the maximum, squeezing all the juices out of themselves. But not only from myself. If the victim delays seeing a doctor, and a large amount of toxins enters the blood, the following complications may develop:
- various disorders of the nervous, cardiovascular, urinary systems,
- development of liver pathologies,
- severe dehydration with impaired functioning of the entire body,
- death.
Intoxication is most severely experienced by young children who have not yet turned three years old, as well as older people. Violations of water-salt balance and pathological changes in the functioning of organs also develop faster:
- in pregnant women,
- people with weakened bodies,
- patients who have recently suffered any serious illness or poisoning,
- in victims with chronic diseases of target organs for toxins (kidneys, liver, heart).
Contraindications for use
For some categories of people, possible poisoning or even simple consumption of this mushroom poses an increased threat. After all, the fungus grows on trees and dries them out after a while (for this it is called a forest parasite). As mentioned earlier, honey mushroom poisoning can ultimately be fatal. Therefore, it is necessary to know the categories of people who cannot tolerate poisoning and mushrooms in general, and then make the right choice for yourself:
- Children under seven years of age. A toxin that enters a child will have a much more destructive effect on him than on an adult.
- Women during pregnancy and breastfeeding. There is a possibility of poisoning not only yourself, but also the fragile baby.
- People suffering from gastrointestinal diseases. The already unstable digestive system will take a new blow extremely painfully.
- People with individual intolerances and allergies. In this case, allergic shock is possible, which is in no way inferior in destructiveness to poisoning.
- People suffering from hypertension and heart disease. Poisoning in this case is extremely difficult for a person to tolerate.
Preventive measures
To prevent poisoning from edible mushrooms, it is necessary to carefully select places for collecting mushrooms. Forests or fields are not suitable if there are:
Read also: Poisoning in humans with hydrochloric acid
- railways,
- highways,
- industrial enterprises.
It is also prohibited to collect mushrooms in large cities, where the concentration of exhaust gases, and therefore lead compounds, in the air is always high.
It is not recommended to buy mushrooms from strangers. Honey mushrooms are also not purchased if the integrity of their stem or cap is damaged, since it is in the mushroom debris that pieces of fly agarics or pale toadstools most often end up undetected.
When preparing honey mushrooms, you need to remember the basic rules. To avoid poisoning from salted mushrooms, they are soaked for at least three days, changing the water every three hours. Heat treatment of honey mushrooms should last at least 30 minutes. It is strictly forbidden to store mushrooms in dishes made of clay or aluminum, as well as in galvanized pans.
Have you ever had honey mushroom poisoning?
- Yes it was
- No, it was not
- There are symptoms now
- I don't eat mushrooms
ResultsPoll Options are limited because JavaScript is disabled in your browser.
- No, there were no 76%, 128 votes 128 votes 76% 128 votes - 76% of all votes
- Yes, there were 15%, 25 votes 25 votes 15% 25 votes - 15% of all votes
- Currently have symptoms 7%, 12 votes 12 votes 7% 12 votes - 7% of all votes
- I don't eat mushrooms 2%, 4 votes 4 votes 2% 4 votes - 2% of all votes
Total votes: 169 08/08/2017 You or from your IP have already voted. Vote
- Yes it was
- No, it was not
- There are symptoms now
- I don't eat mushrooms
You or from your IP have already voted. results
Why can you get poisoned by mushrooms?
Honey mushrooms, like many other species, are divided into edible and poisonous. Under special conditions, even a correctly selected and prepared honey mushroom can poison and even kill a person, let alone its poisonous counterpart. Inedible species are divided into several others with different shades of caps:
- Sulfur-yellow false fungus. This species is very similar to its edible counterpart, so it is worth paying special attention to. The color of the cap is bright with a yellow tint. The plates on the underside of the caps, in contrast to the desired white, have a brown color.
- Brick-red false foam. The cap of this mushroom is reddish in color, the plates are either brown or yellow.
- Candoll's honey agaric. This fungus grows on rotten stumps and ordinary wood during almost all warm months. The cap is watery, brown in color, and easily breaks when exposed. The plates are often dark purple, but may be gray-pink.
- Watery false foam. The mushroom cap is dark brown in the middle and yellow-brown at the edges. The plates are light brown, darkening with age. Be careful! From above, this mushroom looks like a real honey mushroom.
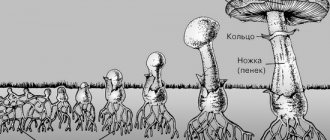
On a note! False mushrooms have a bright and rich color, an earthy and damp smell, and a bitter taste. The most important thing that you should always pay attention to is that false mushrooms never have a ring-skirt on the leg.
Now you know the types of inedible mushrooms that are unsuitable for consumption. What about edibles?
Edibles are divided into three types: winter, summer and autumn. Each of these species is different from each other and has a large number of false mushrooms similar to these.
- Winter mushrooms.
During the winter thaw, you can find winter mushrooms on willows or poplars. The width of the cap of winter species reaches eight centimeters. The color of the cap of these mushrooms is honey or ocher-brown. The cap itself is glossy and very smooth. The taste of the pulp is very delicate, its color is creamy, its aroma is soft and very pleasant mushroom. The leg is approximately six centimeters long and hollow.
- Summer honey mushrooms.
The summer species has a brown-orange cap up to five centimeters wide with a watery area in the middle. The leg is thin, six centimeters long. They are usually harvested between May and late autumn.
From May until the end of summer you can find meadow mushrooms. They have a beige-orange cap three centimeters wide. Their blades are beige in color and the flesh is slightly yellow with a sweet taste. These honey mushrooms grow in colonies, lining up in a circle, most often in meadow grass and on the edges.
- Autumn honey mushrooms.
Autumn species most often grow on aspen, birch and maple. This species is rightfully considered the best among all honey mushrooms, since:
- it is large in size (the diameter of the cap varies from 5 to 12 centimeters);
- according to reviews, it has the best taste among other honey mushrooms;
- autumn mushrooms have the widest variety of possible recipes
The characteristic color of the cap is brown, the plates are white. The height of the leg can reach ten centimeters, it has a characteristic ring-skirt.
Any honey mushrooms can lead to serious consequences if they are:
- Collected near roads and factories, that is, they contain increased levels of lead, mercury, zinc, cobalt and cadmium.
- Poorly or incorrectly processed and prepared.
- They are stored incorrectly, that is, they provide a favorable environment for the proliferation of harmful microorganisms.
- Affected by insects. The secretions of some types of insects can cause an allergic reaction or be poisonous. Moreover, these secretions cannot always be removed even after prolonged heat treatment. In addition, cavities left by insects can be an excellent home for harmful microorganisms and parasites.
- They have expired.
However, the main reason is still the use of poisonous mushrooms instead of edible ones, which have already been discussed earlier. Poisonous honey mushrooms contain amatoxins, which negatively affect the functioning and health of primarily the liver, and then the stomach, intestines and kidneys.
Mushroom poisoning can also be caused by intolerance to this species or by eating it raw. You should not overuse honey mushrooms, because even if properly prepared, they can cause signs of poisoning if you eat 40 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Signs of honey mushroom poisoning do not appear immediately, but at one moment they produce a powerful blow to many body systems. Moreover, this can happen with a small proportion of poisoned or poisonous mushroom.
Difference between edible mushrooms and false mushrooms
False honey mushrooms are sometimes so similar to edible ones that it is difficult to distinguish them even for an experienced mushroom picker. Poisonous mushrooms differ from edible ones in their brighter color, the absence of a “skirt” on the stem and scales on the cap, and the smell of mold. Beginning mushroom pickers who do not want to get poisoned are advised to avoid collecting these mushrooms altogether.
Cases of honey mushroom poisoning during the mushroom season are recorded by doctors quite often. To protect yourself and your family, you need to know the symptoms of intoxication and how to provide first aid. It is best for beginner mushroom pickers to go into the forest accompanied by more experienced people!
Honey mushrooms are one of the most desirable prey for mushroom pickers.
Honey mushrooms are one of the most delicious mushrooms, very popular among residents of Russia and other countries. Festive tables are often decorated with bowls of these creamy-brown mushrooms. They are fried and added to soups, salads and other traditional Russian dishes.
These wonderful mushrooms are sold frozen, and sometimes even fresh, in almost every supermarket today. However, their cost can scare off even the most ardent gourmet. On the one hand, it is justified, because the mushrooms were grown especially for you, collected, cleaned of contaminants, frozen and placed in neat packaging. However, as residents of the post-Soviet space say, saving should be economical, therefore, we proudly walk past refrigerated chests filled with mushrooms and go into the forest.
Mushroom picking is a traditional activity in our country and many others. However, seasonal visits to the forests always border on some danger, which consists in collecting inedible mushrooms.
Honey mushrooms are one of the most desirable prey for mushroom pickers. In the case of them, the danger increases several times, because, having aimed at collecting them, you can put in the basket not just an incomprehensible toadstool, which is simply thrown out when inspecting the prey at home. The fact is that honey mushrooms have, so to speak, twin brothers, called false honey mushrooms.