Mushrooms
2
1962
Article rating
Kira Stoletova
Edible forest mushrooms are a storehouse of useful vitamins and nutrients that can completely replace a meat product. For their high nutritional value, it is not for nothing that they are called “vegetable” or “forest” meat. They are healthy, tasty, nutritious and, most importantly for mushroom pickers, they grow quickly. Active reproduction and growth of mushrooms, starting from the first spring collection season and ending with the last, autumn, is due to their unique biological characteristics.
Features of mushroom growth in the forest
The structure of mushrooms
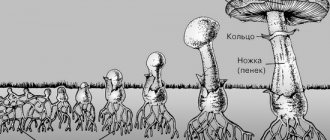
A common mushroom that grows in the forest consists of a stalk (stump) and a cap, which together make up the fruiting body of the mushroom. The base of the stalk is connected to a mycelium (mycelium), very reminiscent of a tangled interweaving of thin threads (hyphae).
The mycelium itself is located in the loose top layer of soil, including rotted leaves, dying plant remains, humus and other soil organic matter. The threads of the mycelium form the entire fruiting body of the mushroom - from the base of the stem to the cap. It is through them that organic nutrients obtained from symbiont trees enter the mushroom cap.
This is very important for the propagation of the fungus, because There are spores in thin plates or tubes on the lower surface of the cap. After ripening, the spores fall off the surface of these formations (plates, tubes) and are carried throughout the forest by the wind, insects or animals.
When an edible mushroom can become dangerous
Any mushroom, even an edible one, can become dangerous to human health. It all depends on:
- Correct choice of terrain. The mushroom is known to absorb all toxic and radioactive substances. Therefore, if the soil is heavily polluted or the air is full of harmful gases, you should not harvest in this area. It is necessary to ensure that there are no vegetable gardens or greenhouses nearby, since mushrooms readily absorb the chemicals contained in pesticides. Also, there should be no cemeteries or burial grounds nearby, because fruiting bodies absorb cadaveric poison;
- Age of the fruiting body. The older the mushroom, the more toxins it has absorbed. Also, many parasites and bacteria accumulate on its tissues, which can cause various intestinal diseases in humans. The presence of bacteria cannot be accurately determined by the appearance of the fruiting body. It is necessary to collect strong and young specimens, and ignore old and flabby ones;
- Presence of poisonous species. It is strictly not recommended to put both edible and inedible mushrooms in the basket;
- Correct use. If you do not follow the rules for preparing or preserving mushrooms, you may encounter a serious disease such as botulism. Also, you should not taste the raw gift of nature to determine whether they are dangerous or not;
- Places of purchase. You need to buy them only in places where there is a certificate from a veterinary laboratory about the safety of the product. Also, you should not buy canned or pickled mushrooms that have already been prepared at home at the markets.
Most mushroom pickers visit the forest not only to enjoy these gifts of nature, but also to enjoy the process itself. A person who is interested in this business must have full knowledge of the growth of mushrooms.
You can find out where which mushrooms grow in the following video.
There is a stereotype that after a good rain you should go mushroom hunting. But few people can specifically answer the question of how many days after rain mushrooms appear. Different species grow at different rates - some require a few hours, while others can take weeks. In order to know exactly when to go on a quiet hunt after the rain, you need to study the individual nuances of the growth of different mushrooms.
Reproduction
Once in a warm and humid environment, fungal spores begin to germinate quickly. This is how a new independent mycelium is formed, lying underground up to 15 cm from the soil surface.
The mycelium has many important functions:
- promotes maximum consolidation of the entire fungal organism in the soil;
- “distills” mineral substances obtained from the soil into the cells of the roots of symbiotic trees, and then delivers organic substances formed during photosynthesis by the trees into the fruiting bodies of the fungi;
- fulfills responsibilities for adapting to environmental changes;
- responsible for sporulation and preservation of fungal spores.
Mushrooms grow most quickly in mature perennial myceliums, which have a numerous and branched micellar system that is resistant to unfavorable conditions for growth and development (frost and drought). When the mycelium becomes sufficiently developed, formation begins. Mushroom threads intertwine more strongly with each other, forming small lumps - future mushroom legs and caps.
Rain and other factors affecting mushroom growth
The fact that mushrooms grow rapidly after rain is not a completely true statement. Rain alone cannot cause massive mushroom growth. A lot of other factors also influence the growth rate. The most significant of them are the following:
- Temperature.
- Humidity.
- Lighting.
- Chemical composition of the soil.
- Harmful insects.
The humidity factor involves two components: air humidity and soil moisture. Each species has its own preferences in this regard, but, if we take the statistical average, the optimal humidity level for good growth is considered to be 70%. Soil moisture should correspond to air humidity. If a prolonged drought occurs after heavy rains, the mushrooms will grow slowly because the moisture in the soil will evaporate quickly. Thus, the soil will become dry and the air will become waterlogged, which will upset the balance.
Features of growth
Mushroom growth is affected by humidity
It takes approximately 3-5 days for the mushroom to reach medium size. It is these young and strong mushrooms that professional mushroom pickers prefer to collect. But not all mushrooms grow and develop at the same speed.
How quickly a mushroom grows is directly affected by:
- the nature of the area where the mycelium grows;
- humidity and temperature of both air and soil;
- a type of edible mushroom.
For example, boletus, russula and boletus mushrooms gain the mass of the fruiting body the fastest, so you can go to the forest to collect the harvest just a few days after the previous one - you will find a lot of young mushrooms.
You can wait almost a week for boletus and porcini mushrooms to fully ripen. And chanterelles are considered the slowest in the mushroom kingdom; they grow much slower than other varieties.
How many days do mushrooms grow after heavy rain?
A mushroom is a living organism. It absorbs both beneficial and harmful substances. If it grows in an ecologically clean area and optimal conditions are created for it, then after precipitation this growth accelerates significantly. In just a day, an ordinary mushroom can reach a significant size and can be picked. Knowing how many days mushrooms grow after rain, you can always arrive in the forest on time and enjoy what you love.
To ensure that picking mushrooms and their further consumption are completely safe, you should follow a few simple rules, namely:
- since mushrooms absorb absolutely all the substances with which they are surrounded, they should not be collected near roads or in overly polluted areas;
- The product will only be beneficial if you manage to collect the mushrooms before the end of their growth period - after which the decay process begins;
- Some inedible mushrooms are very similar to those that can be eaten, and therefore it is worth learning to distinguish them, and always being careful.
Mushroom pickers have three periods of the year when they can do what they love.
- The first begins at the end of May and lasts throughout the next month.
- The second will need to wait until the end of July, and the third in the fall, when the first leaves begin to fall.
- And the closer we get to autumn, the slower the mushrooms grow after rain, because it gets colder.
Optimal conditions
In order for future mushrooms to develop intensively in the mycelium and grow quickly, the fungal organism requires certain conditions.
Temperature
The low temperature regime has a negative effect on young mycelium, and sudden spring frosts are detrimental to developing mushrooms. Cold weather with sudden temperature changes can greatly slow down and even completely stop the growth of the fruiting body. Intensive and accelerated ripening of mushrooms begins at temperatures from 18℃ to 30℃, but only with sufficient humidity, at least 60%.
Humidity
The humidity level should be about 60-70%, both in the air and in the soil. If the soil is not moist enough, the mushrooms stop actively growing, although the development of the fruiting body does not stop completely.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
The development of fungi is especially active when the soil moisture is 80-85%. However, if the substrate humidity reaches 95-100%, growth and development will begin to be delayed due to a lack of oxygen, which fungi, like all living organisms, need for their development. Thus, swampy soils contain only traces of free oxygen (O2) and due to this state of affairs, only species adapted to such unfavorable conditions can be found in them - emericellopsis, some fusariums, etc. The “killer” combination has a particularly unfavorable effect on the development of fungi - high humidity and low temperature. Therefore, harvesting a good harvest in a cold, rainy summer is just as unrealistic as a hot but dry summer.
Soil acidity (pH) is also very important for mushrooms - the active acidity of the environment, the value of which shows us the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the environment. The normal life of the fungus and its vital processes, such as, for example, enzyme activity, spore formation, the entry of nutrients into the cell, and the synthesis of antibiotics and pigments, depend on it. Most mushrooms prefer acidic soils, while a smaller number prefer alkaline soils.
Pests
The growth of forest mushrooms is also influenced by insect pests. When the mycelium and fruiting bodies are infected by the larvae of parasitic insects, the active life of the fungi deteriorates significantly - the fungus becomes sick. Outwardly, this may not be initially noticeable. But as it develops, “worms” appear—insect larvae—and the apparently healthy mushroom becomes unsuitable for collection.
When optimal conditions for fungal organisms occur - warm and humid weather in the absence of pests and diseases, the ripening time of fruiting bodies is reduced, and new young mushrooms grow by leaps and bounds.
The process of active growth does not stop either day or night - this is a distinctive feature of the entire mushroom kingdom and one of the characteristic features of the Plant kingdom.
Fruiting bodies grow especially vigorously in the warm season, after rain, when the sun begins to warm up the soil saturated with moisture. Under these conditions, young mushrooms form to an average size in just a few days, and then within 10 days they gain the mass of the fruiting body, which greatly pleases lovers of “quiet hunting”.
However, mushrooms are not only the fastest-growing forest inhabitants, but also the most short-lived. After the mushroom spores have fully ripened, the fruiting body enters the phase of decay of the reproductive parts. The entire fruiting body begins to collapse. Mature spores form new mycelium, and the life cycle begins anew.
What affects the growth rate of mushrooms
In rainy autumn, mushrooms can be found in any forest clearing. It is more difficult to find them in dry autumn weather, as they hide under trees in the shade.
The speed and quality of the fruiting body is affected by:
- Temperature conditions. The growth rate begins at temperatures ranging from 18° C to 30° C. The development process may decrease noticeably if the temperature begins to fluctuate;
- An indicator of soil and air humidity. It should be 70%. If after heavy rains there is a period of prolonged drought, the growth rate is significantly reduced as moisture evaporates into the air;
- Parasites. Development is also affected by the appearance of various insects. As a result of infection of fruiting bodies and myceliums by the larvae of various parasites, their vital activity significantly deteriorates.
Growth is due to many factors that prevent the rapid development of fungi. Before you go to collect a natural harvest, you need to study the weather and its effect on the mushroom.
You can learn what an analytical mindset means from the publication on our website.
Read about the longest hair in the world in this article.
From here you will learn how to correctly determine the size of a woman's breasts.
White mushrooms
The porcini mushroom (boletus) is rightfully considered the king of edible forest mushrooms. In terms of nutritional value, it ranks 1st, and only after it come saffron milk caps, milk mushrooms, boletuses, aspen mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, boletus mushrooms and other inhabitants of the mushroom kingdom. Its mycelium begins to grow in early spring with the onset of stable warm weather. Growth continues until late autumn, and with the onset of autumn frosts it stops until the next warm season.
Porcini mushrooms grow at temperatures from 18°C to 28°C; mycelium can grow at temperatures of 8°C. Relative air humidity is in the range of 60-70%.
If there is a drought in the growing area, the growth of porcini mushrooms slows down greatly until it stops completely, and the ripening time of spores increases significantly. Moreover, with a decrease in air humidity, the fruiting body also slows down its growth, because it is not protected from moisture evaporation and dries out, unlike other varieties of mushrooms.
There are often cases when, after heavy warm rains, boletus mushrooms with a cap diameter of up to 18 cm and a stem of up to 12 cm are collected.
In favorable conditions (rainy and warm weather), boletus mushrooms grow quite quickly - after 4-5 days the weight of the young mushroom reaches approximately 180 grams. Further, their mass continues to increase. The life of adult boletus takes about 2 weeks. When the spores mature, the fruiting bodies quickly age and wither. Such fruiting bodies are quite suitable for forest inhabitants. The life cycle closes, but life continues its victorious march.
Duration of the ripening period
The rate of maturation of organisms largely depends on their species:
- Fast-growing, capable of growing by 1-2 cm per day. These organisms appear on the surface 2-3 days after warm rain. Such intensive growth is explained by the fact that their mycelium does not fall below 10-15 cm of the earth's surface, due to which the mycelium threads are quickly heated and moistened. Representatives of fast-growing species include boletus, boletus, russula, saffron milk caps and boletus.
- With a slow growth rate (0.2-0.3 cm per day). It takes about a week for them to fully ripen. These include boletus mushrooms, chanterelles, honey mushrooms, and milk mushrooms.
The speed of mushroom ripening largely depends on their type. The illustration for the article is used under the standard license ©ofazende.com
Boletus (white) and chanterelle
Real mushroom pickers also know how long the porcini mushroom grows (from five to ten days). Armed with this knowledge, it is easier to “hunt” whites during mushroom season. Moreover, if the average weight of a mushroom is approximately two hundred grams, then mushrooms grown in warm rainy weather can weigh even more than a kilo! After the formation of spores, the giant quickly ages, but in the fall this process may slow down.
How long do chanterelle mushrooms grow? Quite a long time - from one week to two.
When a mushroom picker knows how long it takes for mushrooms to grow to a ripe state, he will never come out of the forest with an empty basket.
The best time to collect different types of mushrooms is in summer and autumn
The first mushrooms appear in April, but May is considered the official opening month of the mushroom season. Usually mushroom hunting lasts until October inclusive. But if weather conditions are favorable, new mushrooms grow in November and even in December.
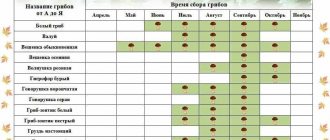
It is better to harvest according to the mushroom calendar. Based on his data, the mushroom picker is less likely to run into an inedible double. The following table details the entire growth period of certain edible species.
| Species name | May | June | July | August | September | October |
| Porcini | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Valuy | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Volnushka | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Volnushka white (Belyanka) | + | + | ||||
| Gorkushka | + | + | + | + | ||
| Gruzd | + | + | + | + | ||
| Raincoat | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Greenfinch | + | + | + | |||
| Kozlyak | + | + | + | + | ||
| Cap | + | + | + | + | ||
| Chanterelle | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Oiler | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Mosswort | + | + | + | + | ||
| Honey fungus | + | + | + | |||
| boletus | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Boletus | + | + | + | + | ||
| Ryzhik | + | + | + | + | ||
| Ryadovka | + | + | + | |||
| Serushka | + | + | + | + | ||
| Violin | + | + | + | |||
| Morel | + | |||||
| Russula | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Champignon | + | + | + | + |
The first harvest is much smaller than the harvest collected during the period of active mushroom growth. The following provides data on the peak growth activity of certain edible species.
| Species name | May | June | July | August | September | October |
| Porcini | + | + | ||||
| Valuy | + | + | ||||
| Volnushka | + | |||||
| Volnushka white (Belyanka) | + | |||||
| Gorkushka | + | + | + | |||
| Gruzd | + | + | ||||
| Raincoat | + | + | ||||
| Greenfinch | + | + | ||||
| Kozlyak | + | + | + | |||
| Cap | + | + | ||||
| Chanterelle | + | + | ||||
| Oiler | + | + | ||||
| Mosswort | + | |||||
| Honey fungus | + | + | ||||
| boletus | + | + | ||||
| Boletus | + | + | + | |||
| Ryzhik | + | + | ||||
| Ryadovka | + | |||||
| Serushka | + | + | ||||
| Violin | + | + | ||||
| Morel | + | |||||
| Russula | + | + | + | + | ||
| Champignon | + | + | + | + |
An interesting fact is that during Indian summer you can find varieties from all seasons of the year. And after it, mushroom pickers can only collect the remains of the autumn harvest and winter honey mushrooms.
How fast do blueleg mushrooms grow? Where and when to collect blue root mushroom
How many days does it take for potatoes to sprout after planting?
The blue leg row mushroom prefers to grow on alkaline soils, which are found in meadows, forest glades, in areas of abandoned farmland or in pastures throughout Russia. Look at the photo visualizing the blue leg row:
This amazingly beautiful mushroom grows in large colonies, in the form of rows or, as people often say, “witch circles.” Bluelegged row is widespread in Russia, as well as in European countries. In addition, it is found in the forests of North and South America.
The collection season and active fruiting of the blue-legged mushroom occurs at the beginning of autumn, that is, in the month of September. Experienced mushroom pickers recommend that novice lovers of “silent hunting” collect these fruiting bodies only in dry weather, since during rains they become slippery and sticky. Look at the proposed photo of the lily-footed row, showing the conditions in which it grows and what it looks like during collection:
Even despite the strange specific color that scares off many, the lilac-legged rower has its fans. Once having tasted it, mushroom pickers immediately join the lovers of these mushrooms. Having found rows in the forest, they will definitely collect them in their baskets. Then you can prepare a variety of tasty and aromatic dishes from them.
It is worth saying that the two-color rower (we offer a photo for your reference) belongs to the Ryadovkov family, which has a large number of species:
the row is crowded, poisonous,
brindle, white lepista,
lepista gray, etc.
Beginning mushroom pickers are very interested in the question: where and when to collect blue root? First of all, pay attention to the photo and description of the purple-legged mushroom and compare it with the photo and description of the blue root mushroom
As you can see, this is the same representative. These mushrooms grow near rivers and lakes, near cattle farms right in the grass, in meadows and pastures. The growth of these fruiting bodies begins from mid-April to early June, and then continues from the end of August until the first frost. Sometimes mushroom pickers harvest 2 crops in a few months. A photo of the blue root mushroom will help you determine what this fruiting body looks like, as well as the places this mushroom prefers:
And now we come directly to the growth of mushrooms. At this stage there are no clear parameters; here you need to show creativity, observation and personal instinct. Since mushrooms will react to any climate change, all that remains is to observe the reaction, understand it and take the necessary measures in time.
Recommended Settings
- Air temperature from 17 to 19°C.
- Co2 in the air is up to 1500 ppm, there is no lower threshold.
- The speed of air movement is from 10 to 30 cm per second over the mushrooms.
- Air W 86-92%
Champignon growth, beginning of the first wave
However, you cannot be tied only to numbers; constant control over mushrooms is always needed. After all, they are the most accurate indicator of a suitable climate.
Mushroom picking
Before you start collecting mushrooms, 1-2 hours before you start preparing the growing chamber for collection, namely removing excess moisture from the surface of the mushrooms.
When collecting mushrooms, you must always follow the order of visiting the growing chambers - from new chambers to old ones. In order to reduce the risk of spreading diseases between cells. But as practice shows, it is not always possible to maintain order; in this case, after the old chamber, the personnel involved in mushroom picking need to change their outerwear and disinfect their working tools.
On average, the duration of collecting one wave is from 3 to 5 days.
Mushroom collection method
When harvesting, champignons are not cut off, but twisted out of the mycelium, since when pulled out there is a high probability that the cap will come off the stem. Also, too much covering soil with mycelium will remain on the mushroom stems, thereby damaging the young ovaries.
The champignons are collected in disposable containers; the desired weight of the box is no more than 5 kg. If the box is cardboard, then the cardboard should be of such quality that the box does not break when slightly moistened; if this happens, the mushroom will wrinkle against each other and lose its presentation. Ideally, of course, a disposable plastic box.
Often in practice we are faced with the need to thin out beds or so-called sorting out mushroom heaps. Thinning is done to ensure better growth of mushrooms. The distance between the mushrooms should be left such that they do not come into contact with each other. In cases where a dense cluster of mushrooms grows from one root system, the stems of the mushrooms should be broken off, and the roots should be removed only with the last mushrooms of this cluster.
Dense cluster of mushrooms
Important
When picking, mushrooms must be carefully placed in boxes or crates and not thrown away. When throwing a mushroom, it is severely damaged and quickly loses its presentation. When using a cardboard box, you should not stack it in large piles, since under the weight of the mushrooms the boxes begin to sag and push through the mushrooms lying underneath.
Mushroom categories
| Highest grade - According to generally accepted standards, a mushroom with a cap of 4 cm is considered ideal. It has a closed skirt and fits tightly to the stem of the mushroom. White, clean, dry with no peat particles, physical damage and neatly placed in a container - with the cap facing up. However, practice shows that the sale of mushrooms from 3-5 cm is no less successful at the price of the highest category. | |
| Premium quality mushrooms prepared for sale in plastic containers | |
| First grade – Mushrooms that have not retained their marketable appearance. For example, those that have received physical damage, turned gray from moisture, with an open skirt, weak (soft to the touch), having a thin long stem and mushrooms with peat particles on the cap. | |
| First grade mushrooms, weak, having a long thin stem and an open skirt |
Last day of wave collection, cleaning the beds
| All mushrooms up to 2 cm in diameter should be collected, and the bed should also be cleaned. Cleaning the bed – Remains of mushroom stems are removed. Sick and “dead” mushrooms. Dead mushrooms are mushrooms that have died for one reason or another. For example: due to lack of nutrition, dried out or drowned due to high air humidity or uneven watering. |
| Uncleaned bed |