Mushrooms differ in taste from traditional foods and are a favorite dish for most people. Among the numerous representatives of the mushroom kingdom, there are edible and hazardous specimens. A conditionally edible species, the flaked cone mushroom, is not capable of harming human health, but has low taste properties and does not have a large number of admirers.
Description
Pine cone fungus.
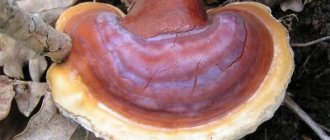
The flocculus mushroom, as the name suggests, looks like a cone in its cap and has a stalk covered with flake-like scales. Its appearance usually does not make mushroom pickers want to collect it, since many people mistake this mushroom for a toadstool.
hat
The cap of the goblin mushroom has a color from white-gray (at a young age) to black-brown (at an old age); there are often darker scales on the surface. The cap looks like a pine cone or an owl's plumage. Mature mushrooms have a cap up to 12 cm in diameter.
Leg
Mushroom-goblin.
The stem of the cone mushroom is long (up to 15 cm) and moderately dense (up to 3 cm in diameter). The color of the leg matches the color of the cap, and the surface is covered with the same scales. In the upper part, next to the hymenophore, white-gray remains of the spathe can be observed.
Spore-bearing layer
The spore layer of the goblin mushroom consists of small tubes. The length of the tubes is approximately 1.5 cm. In young specimens the tubes are whitish, their surface is covered with the remains of torn velum, similar in appearance to cotton wool.
With age, the tubular layer becomes darker (to dark brown). The pores of the tubes are very large, similar to a sieve. When pressure is applied to the hymenophore, black spots appear.
Old man mushroom.
Pulp
The pulp of the cone mushroom has a pleasant mushroom smell and taste. The consistency is dense, the color is white (in young specimens) or grayish (in old specimens). When cut, the flesh turns red, then acquires a purple tint, and later turns black.
Spore powder
The spores are grayish, round, with a rough (mesh) surface, large. Most of their powder is black.
Evaluation of taste qualities, primary processing and cooking recipes
The taste qualities of this representative of the Boletaceae family are low. The leg is tough and fibrous and has an unattractive black-purple color. The caps of young specimens that have undergone thorough culinary processing are suitable for consumption.
Before cooking, conditionally edible mushrooms must be boiled for 15–20 minutes.
Pickling
Boiled mushrooms can be pickled. Ingredients required for pickling 10 kg of fresh fruits (after cooking, their quantity will decrease by 3 times):
- rock salt - 400 g;
- cherry or black currant blossoms;
- Bay leaf;
- whole garlic cloves – 5 pcs.
Preparation:
- Place the mushrooms in a colander to drain excess liquid.
- Add salt and mix thoroughly in a large saucepan.
- Place into sterile jars.
- Place garlic cloves on top and cover with spices and leaves.
Roll up the jars tightly and put them in a cool place. Salting time is 1-1.5 months.
Pickling
Place the boiled and squeezed-out caps of young mushrooms (1.5 kg raw) into sterile jars, pour in hot brine and roll up.
The marinade is prepared from the following ingredients:
- water – 1 l;
- allspice – 10–12 pcs.;
- salt – 20 g;
- sugar – 10 g;
- laurel – 2–3 pcs.;
- cloves – 2 pcs.;
- garlic – 5 cloves;
- vinegar 9% – 30 ml;
- dill umbrellas.
Preparation:
- Mix all ingredients (vinegar and garlic are added before sealing).
- Cook for 5 minutes.
- Pour the prepared brine into the jars of mushrooms.
- Roll up with iron lids.
Pickled or salted flaked mushroom is a good cold appetizer that can be stored in a cool room all winter.
Distribution and collection
The flocculus fungus is distributed everywhere above the Equator, but can also be found further south due to introduction. However, it is not found abundantly or often, usually in one specimen or in a small group. Prefers acidic soils.
It can form mycorrhiza with both coniferous and deciduous species. Moreover, mycorrhiza formation with certain species depends on the area: in the lowlands, the cone mushroom prefers to grow next to deciduous trees, and in the hills - with coniferous trees.
Strobilomyces strobilaceus.
The pine cone mushroom bears fruit in summer and autumn.
Useful properties and restrictions on use
It is difficult to talk about the beneficial properties of the cone mushroom, since it is not often used in cooking. Also, due to its narrow prevalence, this fruit is not used either in folk or official medicine.
The restrictions on the use of this mushroom specimen are the same as for other breeds. That is, it is contraindicated:
- pregnant women;
- small children;
- nursing mothers;
- patients with stomach diseases;
- patients with pancreatitis or pancreatic enzyme deficiency;
- persons with disorders of the liver and gallbladder.
Important!
It is strictly forbidden to consume this mushroom if you have an individual intolerance to any of its components.
It is not recommended to add this fruit to the menu for older people. The reason lies in a decrease in pancreatic activity with a parallel decrease in enzyme levels. Also, in old age, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is inhibited, so mushrooms cannot be fully digested in the intestines. If you do not neglect contraindications, the mushroom will not cause harm to health.
Similar species
Strobilomyces confuses.
The old man mushroom looks so original that it is very problematic to confuse it with other mushrooms. There is only one similar species - Strobilomyces confuses , but it is smaller and more bristly. There are also microscopic differences between these fungi: the spores of Strobilomyces confuses are less reticulate. In addition, the latter species grows only in North American forests and is not found here.
How to cook cone mushroom?
You may be interested in: How do edible talkers differ from false mushrooms? How many days after rain do mushrooms grow? Bitter mushroom: photo and detailed description
The methods for preparing cone mushrooms are no different from those used for other mushroom varieties. So, this mushroom:
- boil;
- fry;
- salt;
- marinate;
- dried;
- stewed.
Primary processing plays an important role. First of all, the mushrooms must be washed well and any remaining soil, leaves and other debris must be removed from their surfaces. And in order to remove insects and contaminants that are located in hard-to-reach places, as well as to soften the pulp, it is necessary to carry out the process of soaking in brackish water. You need to keep the mushrooms for at least 20 minutes. If necessary, the water is drained and fresh water is added together.
When the preparatory stage is completed, the fruits should be thrown into a colander to drain. After 15-20 minutes they can be cut into pieces and used for their intended purpose.
Many housewives note that dried cone mushrooms acquire a bitter taste. Most likely, this is due to the harvesting of old fruits. Only young specimens can be collected and used in cooking, which, moreover, pose less of a health hazard.
Interesting facts
Pine cone fungus.
The goblin mushroom is listed in the Red Book as a rare species with significant distribution and small numbers. It is difficult to grow these mushrooms artificially, like all mycorrhizal symbionts, but a strain of such a fungus was isolated in the Kedrovaya Pad nature reserve in the Primorsky Territory.
The flocculus mushroom does not have any special nutritional value, although it is conditionally edible, so there is no point in collecting it. It is noted that although its taste is not unpleasant, it is bland. And, since the mushroom is listed in the Red Book, if such a specimen is found, it is better to leave it in place.
Edibility
If you come across a cone mushroom in the forest, do not rush to run away from it to a safe distance. We dare to assure you that the mushroom is absolutely not poisonous. However, it has several nuances that people with weak digestion should be aware of.
The mushroom has very hard legs. If at a young age they can somehow be checked, then at an old age they remain tough even after prolonged cooking and heat treatment. They are very poorly digested.
However, not everywhere people are as loyal to the cone mushroom as in Russia. For example, in Germany this mushroom was considered poisonous and inedible.
The mushroom received such a bad reputation as a result of the fact that cases of poisoning were recorded.
In America, the cone mushroom was classified as an edible mushroom. In Europe, the cone mushroom is also collected, but it is left for making tinctures and not for food. It is believed that it has low taste qualities, which are not able to somehow influence the dish.
Indeed, as a result of heat treatment, the cone mushroom somewhat loses its mushroom aroma and spicy taste. It becomes almost fresh, so its use in cooking is called into question.
Available on Wikipedia.
Giant champignon or Lagermania gigantea
One of the largest mushrooms in the world is a member of the champignon family, Lagermania gigantea. This unique mushroom can often be found in the steppes and meadows of central Russia. It has no legs, and the mushroom body itself looks like a huge round egg, lost by an extinct dinosaur, or someone’s head, for which the mushroom is popularly called “bighead.” And because bigheads appear during the rainy season, they are called raincoats.
The size of the head inspires respect: there are specimens whose diameter exceeds 0.5 m, and this takes into account the fact that they are edible. What a catch! It is not difficult to determine the maturity of the mushroom: young bigheads should be white, with flesh of the same color; in older ones, the shell darkens, and the flesh first becomes green-yellow and finally brownish.
Old bigheads should not be eaten - their flesh contains a large amount of toxins, which leads to poisoning, and symptoms do not appear immediately, but only on the second day.
Rare mushroom sarcosoma globulus
Brown barrels filled with dark liquid and covered with a shiny disk on top - it’s hard to imagine a more unusual mushroom. This is a unique spherical sarcosoma, listed in the Red Book. You can find it only among thickets of moss, in an impenetrable forest thicket. Sarcosoma is considered conditionally edible (some gourmets fry the fruiting body and claim that in this form it is very tasty), but the main value of the mushroom lies in its liquid. It has healing properties and is widely used in folk medicine.
To sum it up, one thing can be said: not everything that looks strange actually is. Unusual mushrooms can be edible and even very tasty, but if you are not sure about their edibility and do not know how to cook them, you should not put yourself at risk. Collect only mushrooms that are well known to you and boil them well to avoid unpleasant consequences.
Graceful fashionista – bamboo mushroom
If some mushrooms have a leg decorated with rings, then a bamboo mushroom has a whole lace skirt, and it’s very long, almost to the ground. The color is most often white, but there are specimens with yellow or pink skirts. It is noteworthy that initially the mushroom has the shape of an egg, from which a tall, up to 25 cm, white stalk with a small convex cap painted brown emerges.
The surface of the cap is mesh-like and covered with an unpleasant-smelling, greenish mucus that attracts insects. In Chinese cuisine, bamboo mushroom is considered a delicacy for its tender and crunchy texture.
The Latin name for the mushroom is phallus indusiatus, but it is most often found as:
- bamboo mushroom;
- lady with a veil;
- dictyophora reticulata;
- bamboo girl;
- odorous glaciers in bamboo;
- bamboo ginseng.
An excerpt characterizing the cone mushroom
Which of the Russian people, reading descriptions of the last period of the campaign of 1812, did not experience a heavy feeling of annoyance, dissatisfaction and uncertainty. Who hasn’t asked himself questions: how they didn’t take and destroy all the French, when all three armies surrounded them in superior numbers, when the frustrated French, starving and freezing, surrendered in droves, and when (as history tells us) the goal of the Russians was precisely that to stop, cut off and take prisoner all the French. How did that Russian army, which was weaker in number than the French, fight the Battle of Borodino, how did this army, which surrounded the French on three sides and had the goal of taking them away, did not achieve its goal? Do the French really have such a huge advantage over us that we, having surrounded them with superior forces, could not beat them? How could this happen? History (the one called by this word), answering these questions, says that this happened because Kutuzov, and Tormasov, and Chichagov, and this one, and that one, did not make such and such maneuvers. But why didn't they do all these maneuvers? Why, if they were to blame for not achieving the intended goal, why were they not tried and executed? But, even if we admit that the failure of the Russians was due to Kutuzov and Chichagov, etc., it is still impossible to understand why and in the conditions in which the Russian troops were located at Krasnoye and near Berezina (in both cases the Russians were in excellent forces), why was the French army with its marshals, kings and emperors not captured, when this was the goal of the Russians? The explanation of this strange phenomenon by the fact that Kutuzov prevented the attack (as Russian military historians do) is unfounded because we know that Kutuzov’s will could not keep the troops from attacking near Vyazma and near Tarutin. Why was that Russian army, which with weaker forces won a victory at Borodino over the enemy in all its strength, at Krasnoe and near Berezina with superior forces defeated by frustrated crowds of the French? If the goal of the Russians was to cut off and capture Napoleon and the marshals, and this goal was not only not achieved, but all attempts to achieve this goal were each time destroyed in the most shameful way, then the last period of the campaign quite rightly seems to be close to the French victories and is completely unfairly presented by Russian historians as victorious. Russian military historians, to the extent that logic is obligatory for them, involuntarily come to this conclusion and, despite lyrical appeals about courage and devotion, etc., must involuntarily admit that the French retreat from Moscow is a series of victories for Napoleon and defeats for Kutuzov.
Grifola curly
Another name for the mushroom, more popular, is the ram mushroom. The ram mushroom is very large in size, its weight can reach 10 kilograms. The diameter of the mushroom is 80 centimeters. The fruiting bodies consist of many small spade-shaped caps that are supported by branching stalks. As a result, all these legs merge into a common base, forming a multi-tiered body of the grifola curly. Grifola curly can be found in deciduous forests in August and September. Mushrooms grow on the trunks of old oaks or maples, most often at their base. It is worth noting that they can grow very quickly and form white rot.
Grifola curly
Early mushroom and aphrodisiac - Veselka
Another type of phallus is known as veselka. It also develops: at first the mushroom body has the shape of an egg, from which the mushroom itself subsequently grows on a high stalk with a small convex olive-brown cap. However, the growth rate of the Veselka is amazing: it takes only half an hour for the leg to completely come out of the egg.
The cap is covered with a slimy coating and smells disgusting, attracting insects. They also spread spores throughout the forest, while simultaneously cleaning the mucus. Without it, clearly visible cells appear on the cap.
Veselka is an edible unusual mushroom, which also has aphrodisiac properties, but only if you use young specimens (eggs) and remove the shell from them.
Edible mushroom picking season
The best time to pick mushrooms is autumn: from August to September. This is facilitated by numerous rains and the resulting dampness and fog. However, mushrooms can grow all year round. It is recommended to collect them early in the morning.
Autumn is the optimal time for picking mushrooms
Finding mushrooms is a whole science. Can be collected as a hobby or for sale or spinning. It is imperative to remember that there are a huge number of poisonous look-alike mushrooms; for this reason, you should carefully study the list of edible mushrooms and the edibility of conventional species. If even a fraction of doubt arises, then you should not take such a mushroom.
What edible mushrooms grow in your area? What do you cook with them? Share recipes in the comments.
How to distinguish an edible mushroom from an inedible one
Experienced mushroom pickers recommend that when picking mushrooms, pay attention to some details that will help you identify edible ones:
- frequency of the plates;
- spore coloring;
- method of attaching plates to the stem;
- change in color of the pulp when it is damaged.
In addition, mushroom pickers often check the color of the spores and the presence of volva or rings, which indicate the degree of maturity of the mushroom.
Characteristic signs of poisonous mushrooms Almost all types of edible mushrooms have a tubular tissue structure and plates at the bottom of the cap.
In addition, edible mushrooms are distinguished by their habitat, flavor, shades, and cap types.