Saprophytic fungi are special organisms that feed on the remaining parts of plants or animals. A large number of fungi currently belong to the category of saprophytes. They feed on substances that they independently extract from the remains. The following remains serve as substrate:
- humus;
- straw;
- branches, stumps;
- trunks;
- feathers, horns;
- charcoal and others.
But not all saprophytes prefer a variety of substrates. For example, the famous summer honey fungus mainly feeds on the remains of deciduous trees. False honey mushrooms prefer only coniferous trees. Other species, for example, white dung beetle or yellowish rhizopogon, live well in areas where there is a high concentration of nitrogen.
While they are useful organisms for nature, they are not for humans. These fungi can appear on food products, which can then no longer be consumed.
Yellowish rhizopogon lives in areas with excess nitrogen
The meaning of mushrooms in nature
Nutrients decomposed by mushrooms are subsequently absorbed by other plants. Living creatures (animals and insects) feed on cap species. There are also mushrooms that are specially grown artificially. These are champignons and oyster mushrooms. Mold fungi (aspergillus, penicillium) are used to produce antibiotics and even hard cheeses. Ergot (formed on cereal crops) is used to combat malignant tumors.
Many parasitic fungi cause harm to living organisms and plants, causing diseases. Considerable damage is caused to wood. It is not recommended to use contaminated building material for wooden buildings. Since the mushroom culture can cause fatal poisoning, experts advise collecting it with great caution.
Mukor
This representative belongs to the generic branch of lower mold fungi of the class zygomycetes. In total, the class includes 60 species of various mushrooms. They can be found in the top layer of the earth; they can develop on food and organic parts. A certain amount of mucor can cause disease not only in animals, but also in humans.
But there are a number of mushrooms that are intended for use in the production of antibiotics or as a starter. Only those mucor mushrooms that have high enzymatic activity are used in production.
Reproduction of mucor fungi can be asexual or sexual. In asexual reproduction, the shell of a mature mushroom quickly and easily dissolves from moisture, and several thousand spores come out. Two branches take part in sexual reproduction: homothallic and heterothallic. They unite with each other to form a zygote, after which a hypha with an embryonic sporangium begins to germinate. People use Chinese mucor and snail mucor as leaven. Many people call these mushrooms Chinese yeast.
With the help of such yeast, people can obtain ethanol from potatoes.
Mucor can cause illness in humans and animals
Symbiont mushrooms
Symbiosis is the cohabitation of different organisms in which both benefit. Symbiont fungi participate in the formation of two symbioses:
- lichens formed as a result of interaction with algae and bacteria;
- mycorrhiza - with the root system of plants.
Nutritional Features
Mushrooms, entwining the small roots of plant organisms, feed on the organic substances that make up their composition. Such actions do not harm plants, but promote the absorption of nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, microelements) and water from the soil.
Names and descriptions of popular symbiont mushrooms
Typically, cap mushrooms are classified as a mixed type of nutrition, which can receive organic substances from both plant roots and humus.
- Boletus. Interacts with aspens, oaks, willows and poplars. The brown hemisphere-shaped cap has a reddish or orange tint. It is impossible to separate the layer of skin without pulp. The height of the gray leg is up to 18 cm. The fruit body is fleshy and dense. Young individuals are elastic, while old ones become loose. At the break, the white flesh turns blue over time and then turns black. Does not have a pronounced aroma.
- Boletus. Grows near birch roots. Over the course of its life, the mushroom cap changes from a spherical shape to a flat, pillow-like shape. At high humidity it becomes sticky to the touch. The white pulp with a dense structure oxidizes at the cut site. In older individuals it becomes watery and loose. Cylindrical leg covered with dark gray scales.
- Oiler and saffron milk cap. They live under coniferous trees. Butterflies are characterized by a slimy skin that appears to be coated with oil. Hemisphere-shaped hats reaching 16 cm in diameter are painted in a spectrum of colors from brown-chocolate to yellow-brown. As they grow older, the shape straightens out, becoming flat. The color of the stem is usually lighter. The pulp is juicy. The saffron milk cap is characterized by a round cap with concentric circles and a depressed center. The orange pulp oxidizes when it comes into contact with air, acquiring a greenish tint.
If you destroy the host tree, the mushrooms growing underneath will also disappear.
Saprophytic mushrooms
Saprotrophic organisms (decomposers, saprophytes) feed on organic compounds obtained as a result of the destruction of dead animals and plants.
Features of structure and nutrition
Saprophytes include many large fungi, consisting of a large number of light spores, allowing them to spread effortlessly to other food sources.
This population of fungi prefers to settle on plant debris:
- fallen needles, foliage;
- feathers and horns;
- twigs;
- cones;
- stems of annual grasses;
- tree stumps
Saprophytes extract nutrients from dead sources. Depending on the substrate, certain types of mushrooms grow.
Examples of saprophyte fungi
Since all living organisms have a beginning and an end, saprophytes play an important role in the cycle of substances, destroying natural biomass consisting of monoorganic substances. Edible mushrooms include:
- morels;
- dung beetles;
- Champignon;
- umbrellas.
Among saprotrophic organisms there are also unsuitable for food, which pose a danger to human life.
Is it harmful to humans?
Many people believe that penicillium fungi are bacteria. However, this is not the case. Some varieties of this plant have pathogenic properties against animals and humans. The greatest harm is caused in cases where mold affects agricultural and food products, intensively multiplying inside them. If stored improperly, penicillium infects feed. If it is fed to animals, their death is possible. After all, a large amount of toxic substances accumulate inside such food, which negatively affect health.
Mushrooms are parasites
Unlike fungi, which perform useful activities, parasitic organisms do not benefit the host plant, but destroy it during their lifetime. Tree infection occurs through damaged bark. Fungal spores, transported by air flow, penetrate through bare areas and settle on wood.
To avoid infection of fruit trees, it is necessary to take preventive measures in a timely manner: watering in the summer months, shelter for the winter, isolating wounds with garden varnish. If a parasitic growth appears on the trunk, it is recommended to destroy the tree, preferably burn it.
Appearance and nutrition
Parasitic fungi are either annuals or perennials that can live up to 25 years. Different species of individuals differ from each other in color, shape, structure, size and life expectancy. The shape of the fruiting bodies is hemispherical or cap-shaped , and also similar to a hoof or the tip of a pike. There are also shapeless growths in the form of convex or layered bodies. Perennials are capable of gaining up to 10 kg of weight and growing to a size of one meter. The color spectrum of parasites is also diverse. The structure of the body is similar to wood or soft skin.
When settling on living plants, fungi feed on organic substances from living cells of the host. As a result, the tree suffers enormous damage. Having settled on agricultural crops, they lead to the formation of dangerous diseases and reduce yields.
Some parasites are able to adapt well to the host, stimulating its development in the initial stage. They feed on the growths formed, without developing mycelium inside the tree.
Edible types of parasitic mushrooms
Cap mushrooms are usually classified as saprotrophs. Less common are parasites, such as honey fungus. Entering into symbiosis with the root system, the fungi penetrate it with mycorrhizae, entwining the root processes.
The presence of a ring on the stem of the honey fungus formed the name of the mushroom. Prefers to grow in large colonies. It is salted, fried, pickled. Valued for its high mineral content. Just 100 grams of product contains the body’s daily need for these elements.
Since honey mushrooms cause wood rot, they are dangerous parasites. The black laces of the mycelium penetrate the bark and, releasing toxic substances, affect the wood. As a result, a young tree may die within 1-3 years. The old specimen dies after 10 years. Once a fungus settles on a tree, its growth slows down. The protective substances that the tree produces cannot stop the process, but only slow it down.
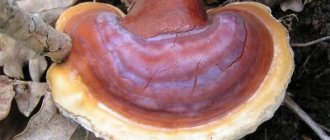
A parasitic fungus that feeds on tree sap is the tinder fungus. There are several varieties of this population. Although there are very few poisonous representatives, they are mainly used in cooking due to their solid body. Some species are considered delicacies. The sulfur-yellow tinder fungus tastes like chicken meat. In some countries, tinder fungi are specially cultivated on farms.
Young specimens of polypores collected on deciduous trees should be eaten. Individuals growing on coniferous trees are at risk of mild poisoning. Experienced mushroom pickers recommend eating only well-known mushroom populations.
Main differences between saprophytic fungi and parasites
It is incorrect to assume that any microorganisms that feed on organic food are parasitic. Parasites include those organisms that survive at the expense of others. They can settle both inside a body and outside.
Saprophytes feed only on the remains of plants or animals. These include soil and mold fungi, as well as mold bacteria. Thus, the main differences between saprophytes and parasites are several features:
- Method of existence and nature of nutrition of organisms: parasitic individuals feed on the organic structures of a living host; saprophytes live on dead plant bodies.
- Unlike parasites, saprophytes usually do not cause harm to the human body.
- The habitat for saprophytes can be both living and non-living structures. Parasites live only in a living organism.
In some cases, fungi turn from parasites into saprophytes, which initially settle on living plants, and after their death continue to live, feeding on dead wood. Such fungi are called symbionts.
Application
In pharmaceuticals
Molds of the genus Penicillium are a natural material for the production of the drug penicillin, which is part of the group of antibiotics.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
In the early years of production, penicillin was produced using fungal strains isolated from natural sources (Penicillium notatum and P. chrysogenum). Then a mutant strain Q-176 with high productivity was obtained. Highly productive strains are obtained mainly with the help of potent factors - X-rays and UV rays, chemical mutagens. In 1946, penicillin was synthesized, identical to natural, biologically obtained.
Penicillin fungi produce substances that neutralize and suppress the vital activity of bacteria, preventing the development of prokaryotic organisms.
In the food industry
Some varieties are used in the food industry for cheese making. Under the influence of lipolytic and proteolytic enzyme substances contained in fungi, which have an active effect on milk fats and proteins, cheeses acquire a loose and oily structure, specific gastronomic qualities and smell. These blue cheeses, distinguished by the green-bluish color of the cheese mass, are produced using certain types of penicillium, the so-called. "noble mold", for example Penicillium roqueforti.