Every plant and living organism is useful in the ecosystem and performs its own functions. The same can be said about mushrooms. They participate in the metabolism of living nature, and also participate in the decomposition of various remains. There are many types of mushrooms, according to this, there are several classifications.
We are accustomed to dividing all mushrooms into those that can be safely eaten and those that cannot be eaten, and a separate type - medicinal. But there is also a generally accepted classification. Today, many species of mushrooms are considered endangered and are listed in the Red Book. The mushrooms from the Red Book are varied, but all are worthy of attention and detailed study.
White boletus
This mushroom has another name - white aspen. It is similar to Red Boletus, a fairly common type of mushroom, but differs in color.
This rare representative of the Agaricomycetes class has a fairly large white cap, reaching about 25 centimeters in diameter. The stem of the mushroom is also white and has a thickening at the bottom. White aspen grows in pine-spruce forests in the countries of the former Soviet Union. These mushrooms can be found from mid-July to August. And although they are edible, cutting and eating them is prohibited, because the species is endangered.
White boletus
What have we learned?
The Red Book of Tatarstan is designed to protect rare and endangered species of plants and animals. Among the Red Book plants, herbaceous ones predominate: cornflower, buttercup, carnation, water lily, ferns. The animals included in the Red Book include the river otter, muskrat, marten, saker falcon, peregrine falcon, harrier and others.
Previous
The world around us The Amur tiger of the Red Book - a brief description for the report (grade 2, the world around us)
Next
The world around usRed Book of the Krasnodar Territory - a list of animals and plants, a brief description for children (2nd grade, the world around us)
Girlish umbrella mushroom
This mushroom is also a representative of the Agaricomycetes class and is safe for the human body. The mushroom has a thin white cap. It is quite large in diameter, reaching ten centimeters. The leg is also white, very thin and tall. The maiden umbrella mushroom is found in mixed or pine forests from mid-summer until September. At the same time, its range is quite wide; the mushroom can be found almost throughout the entire territory of Eurasia.
This mushroom often grows alone, but sometimes it can be found in groups.
Girlish umbrella mushroom
Mushrooms of the Red Book. General information
Until recently, microflora was not well studied, fungi were given little importance, and strict records of species were not kept. In addition to the generally accepted biological classification, mushrooms have another: edible, inedible, poisonous, medicinal, forest and crop pests, and others.
The Red Book considers rare mushrooms in the “Plants” section. It includes 17 types of mushrooms.
Grifola curly (ram mushroom, tinder fungus foliose), Sparassis curly (Mushroom cabbage), Mutinus Ravenel, Violet cobweb, Rogatik pistil (Rogatik club-shaped), Gyropor chestnut (chestnut or chestnut mushroom), White boletus, Double netweed (Dictyophora double), False birch fungus, Maiden's umbrella mushroom, Cone mushroom, branched tinder fungus (Grifola umbellata), Blue gyroporus (bruise), Coral bramble (Horicium coral), Red trellis (Clatrus red), Fly agaric cone-shaped, Mutinus canis
Basidial fungi have special structures for producing spores - basidia. As can be seen from the list, all mushrooms listed in the Red Book belong to only one class - Agaricomycetes. The list contains only higher mushrooms.
A more detailed description of some types will be provided below.
Mutinus canis
The shape of this mushroom is elongated, and the cap is weakly defined. The length of the canine mutinus reaches 18 centimeters, while the diameter of the leg is small, about one and a half centimeters. As a result of full ripening, its crown opens, and a pale tip becomes visible. Mutinus canis is a very rare mushroom, found mainly in Europe. There are also cases of its appearance in North America. It loves coniferous forests and often grows alone. You can see mutinus on rotten snags or stumps.
The mushroom is considered edible, but only when it is not yet ripe, that is, when it is in the egg shell. The canine mutinus itself has a specific smell, which, in turn, attracts various insects. They flock to the smell and begin to gnaw at the mushroom. After which, it begins to quickly decompose.
Mutinus canis
Wild animals of Tatarstan
Predators
Wolf
A couple of decades ago, the republic’s wolves were shot according to state policy. Predators were subject to complete destruction. Later studies showed that wolves are needed as forest nurses.
First of all, predators kill sick animals, for example, deer. This stops the spread of the infection. Prey viruses are generally harmless to wolves.
A wolf's brain is a third larger than a dog's. This indicates the greater mental potential of a wild predator.
Ermine
Until the middle of the last century, these wild animals of Tatarstan were numerous. Hunters annually hunted from 4 to 14 thousand individuals. In the 21st century, ermine is found and harvested less frequently.
The ermine belongs to the mustelidae family and is a predator. Externally, the animal looks like a weasel. The animal is dexterous, agile and quiet. Therefore, meeting an ermine is good luck. An animal can run nearby without being noticed.
Marten
It deftly jumps from branch to branch and just as skillfully moves along the ground. The predator's habits resemble a cat. However, animals are competitors. Forest cats and martens divide the territories of Tatarstan without entering the territory of a competitor.
Nosy animals love to climb into people's farmsteads, feasting on eggs and chickens. Catching martens is difficult. Hunters often remain invisible. Farmers found a way out in the grid, which was under low voltage. It scares away martens, leaving them alive.
Otter
Prefers to live in the rivers of Tatarstan. Rarely found in lakes and ponds. In the warm season, otters choose a permanent place of residence. In winter they can walk 20 kilometers a day. Hunger forces me to move. Predators roam in search of food.
Adapting to environmental conditions and food supply, otters can be active both day and night.
Ungulates
Elk
It leads the animal world of Tatarstan in size. There are no animals larger than moose in the republic. Males of the species gain 500 kg mass.
Being monogamous, moose choose one partner. The exception is especially large males. Feeling their superiority, they simultaneously cover 2-3 females.
Roe
A stable population lives in the Igimsky forest, in the east of Tatarstan. A few groups live in the Aznakaevsky and Almetyevsky districts.
The roe deer's back is slightly arched. Therefore, the height of the animal’s croup is greater than at the withers.
Rodents
Steppe pied
A small rodent of the hamster family. The length of the animal is 8-12 centimeters. The pestle weighs about 35 grams. The rodent has small round ears, black button eyes, and a dark stripe of fur along its back. The main tone of the pestle is gray.
Pieds settle in the steppes, choosing areas with easily cultivated lands, usually black soil. The rodent lives in burrows. Digging them among dense clay or stones is difficult.
Red vole
Features a short tail. Its length rarely exceeds 4 centimeters. Other voles in Tatarstan have larger tails. The total length of the red rodent is approximately 12 centimeters.
The red-backed vole searches for pine nuts on the forest floor. Climbing into fields and vegetable gardens, the rodent eats plantings. Once inside houses, the vole cleans out food supplies.
Gray hamster
“The enemy that throws to the ground,” is how the word “hamster” is translated from the ancient Austrian language. People have noticed that when obtaining food, the rodent bends stems with grains to the soil.
For the winter, the gray hamster stores up to 90 kilograms of food. The animal cannot eat so much, but it collects food for future use. This is a guarantee of a well-fed life in the cold.
Chiroptera
Northern and two-tone leathers
These bats can be found in the Sarmanovo mine. Copper was mined in underground mines in years past. Now chiropterans have settled in the system of cave passages.
Both leathers are medium in size, weighing 8-14 grams. However, the northern bat has uniformly brown fur. In a two-color leather jacket, the chest and belly are light, and the back is earthy.
Giant Vessel
Weighs almost 80 grams. The bulk falls on the arms-wings. Compared to the body, they are disproportionately large, opening almost 50 centimeters.
Noctules settle in the hollows of old trees. 2-3 individuals live in one “house”.
Insectivores
Common hedgehog
Prefers mixed and deciduous forests of Tatarstan. Here the animals feed on insects. The hedgehog's love for fruits and mushrooms is a myth.
An ordinary hedgehog can eat arsenic, hydrocyanic acid, sublimate and remain alive. Poisons lethal to humans have no effect on the spiny mammal.
Toothless is tiny
This is a bivalve mollusk. The animal got its name because the halves of its shell do not have serrations. These are found, for example, in pearl barley, another bivalve mollusk. Parts of its shell have ridges that interlock like the teeth of a zipper.
Toothless is an inhabitant of fresh, clean waters. The clam needs a lot of oxygen. Accordingly, animals choose flowing water bodies.
Amanita cone-shaped
This mushroom is also called amanita pineal. It is poisonous. The fly agaric has a large white cap and rests on a stalk about 20 centimeters high.
You can meet the cone-shaped fly agaric in the CIS countries, in particular in Kazakhstan, Georgia, and Ukraine. It also grows in some regions of Russia. The mushroom loves mixed forests, where oaks, beeches or lindens predominate. You can meet him at the end of summer - beginning of autumn.
The fly agaric is very rare because it has high requirements for the habitat, as well as soil and temperature.
Amanita cone-shaped
water chestnut
The plant is also called floating hornet, chilim or floating nut. This is an annual aquatic plant from the genus Rogulnik. Its homeland is the southern regions of Eurasia and Africa. The fruits of the rogulnik have outgrowths resembling horns.
Chilim has a thin long stem, underwater leaves, and a rosette of leaves is visible on the surface of the water. The plant blooms in July with small white or pink flowers of four petals. In autumn, the fruits ripen - a brown-black drupe with a nut inside, which can be eaten. The fruits fall to the bottom, and in the spring they give life to a new plant. If stored properly, drupes can germinate within 50 years.
If a restaurant menu has water chestnut dishes, it is a bagel. Its fruits are fried, boiled, baked, and made into flour.
In medicine, water chestnut is used as a tonic and antiviral agent, in the treatment of dysentery, and for the manufacture of drugs for atherosclerosis.
Water chestnut: Wikipedia
Double net carrier
In appearance, the mushroom resembles mutinus canis, but differs in color. At first, the double networt has a weakly defined brown cap, and when it matures, it becomes gray. The double networt loves well-drained soil and often grows on decaying wood. The mushroom is found mostly singly; less often you can see groups of several representatives. Just like the canine mutinus, the double networt is considered edible, but only until it is ripe and is still in the egg shell. This mushroom is also considered medicinal and is used in folk medicine.
Double net carrier
Andromeda multifolia
Andromeda (podbel) is found in damp forests and peat bogs. It is an evergreen shrub of the heather family, 15–50 cm high.
The plant is similar to rosemary, which is why it is popularly called wild rosemary. Pink flowers appear in late spring, early summer. The flower, shaped like a jug, is pubescent inside, which protects it from small insects.
Pollen spills out of the stamens only when a large insect (bumblebee) gets inside.
Rice. 3. Andromeda polyfolia.
Podbel is poisonous, but is used in medicine and gardening.
Gyropor chestnut
It also has several other names: chestnut mushroom or chestnut mushroom.
Externally, the rare species is quite attractive, has a thick brown cap and a low stem, slightly widened at the end. The chestnut tree is found in many countries, in particular in the CIS countries, Europe, Asia and even North America. Basically, the mushroom grows on sandy or clayey soils, on the edges of broad-leaved or coniferous forests. You need to look for mushrooms away from trees.
The chestnut mushroom begins to bear fruit in August and ends in September.
Gyropor chestnut
White aspen
This mushroom from the Red Book must be promoted as a rare species that needs protection. Habitat: coniferous, birch, aspen forests. Fruiting - August-September. The mycorrhizal fungus white aspen grows in Eastern Siberia, Murmansk, Moscow, Leningrad regions, near Lake Baikal. Abroad, the plant is found in North America and Western Europe.
To identify new habitats, it is necessary to more carefully study the possibilities of its growth in the European part of the Russian Federation, in the Non-Black Earth Region. The mushroom belongs to the boletaceae family of the genus Leccinum.
Grille red
This mushroom is the only mushroom of the Lattice family that is listed in the Red Book. He loves a mild climate, so he can be found, for example, in the Krasnodar region. This rare mushroom grows mainly in deciduous forests and can only be found singly. Due to its interesting appearance, it is often grown in greenhouses. There is no general consensus regarding the edibility of the mushroom. Some say that it is poisonous, although the nutritional status of the red grille remains unknown to date.
Grille red
About Langermania, spiderwort and other rare mushrooms
Published: 09/22/2009 0:00
Many biologists in the modern scientific world believe that, along with the animal and plant world, there is another independent kingdom of living organisms - mushrooms. Moreover, according to paleontological studies, they have been living on Earth for about a billion years.
There are a great many representatives of the mushroom community, all specimens are very interesting, each worthy of attention and a separate story. But today we will talk about unusual and rare mushrooms - listed in the Red Book of the Republic of Tatarstan. It includes 40 species of mushrooms that are subject to protection on the territory of our republic.
Among them there are some very strange ones that do not look like mushrooms at all. For example, fringed starwort. Initially, it looks like an egg, which in the fall breaks up into petals, or blades, there are from 5 to 15. And in front of you is a flower blooming on the forest floor. I had to meet this unusual mushroom in a deciduous forest near Pestretsy. And my brother, who is passionate about mushrooms, read that some stunning medicine can be prepared from fringed starwort in the egg stage. He is still trying to find such an egg, alas, the fringed star, as well as the similar Red Book mushroom, the triple star, is very rare in our area.
Grifola curly also bears little resemblance to the mushroom we are used to and is a branched, lush bush. Its small ocher mushroom leaves are pressed so tightly together that it is almost impossible to separate them. The diameter of such a mushroom house can reach 50 cm, its weight is 10 kg. Grifola curly, as well as its related Grifola umbellata, are listed not only in the Red Book of the Republic of Tatarstan, but also of the Russian Federation.
The white truffle from the truffle family is listed as an endangered species in the Red Book. This is an underground marsupial tuberous mushroom weighing 500 g or more, up to 15 kg, with a peculiar pleasant aroma. Truffles, as a rule, grow underground at a depth of 10-20 cm; specially trained dogs search for them by smell. The most valuable varieties include the black truffle, a very large mushroom that resembles in appearance a dark tuber covered with warts. But the white truffle, which looks like a potato, is said to be not as tasty as the black one. But it has a slight garlic flavor and goes well with meat dishes. The truffle season in Europe lasts from October to December, and during this time truffle dishes appear not only in prestigious restaurants, but also at summits, diplomatic receptions, and social events. In Tatarstan, truffles were found in the Tetyushsky district near the territory of the Dolgaya Polyana nature reserve.
Another rare mushroom of our republic, curly sparassis, listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation, has the shape of a coral ball with a diameter of up to 35 centimeters. Prefers coniferous forests, which, as you know, are not so numerous in Tatarstan. But the pistillate horntail, which looks like a small, 2 to 6 cm, light yellow mace, grows in deciduous and mixed forests. It is rare, which is explained by the intensive exploitation of forest areas.
Once, in a birch-ravine planting not far from Arsk, I spent a long time admiring a strong snow-white mushroom. I decided that it was a white aspen tree. But the mushroom, as soon as I touched it, immediately turned desperately blue. Aspen trees, I know, also turn blue, but only when you cut them. Later I learned that this touch-me-not is a blue gyroporus. It is found in the European part of Russia, the North Caucasus, and the Far East. The mushroom is edible, but the population rarely collects it - the blue color scares it away.
But I once had a meeting with a handsome white aspen tree, listed in the Red Book of the Republic of Tatarstan and the Russian Federation, on one of the islands of the Kuibyshev reservoir in the Spassky district. My friends and I went to the islands to relax, fish and hunt ducks. I went for a walk around the island and, unexpectedly for everyone, brought an armful of huge red-headed boletuses. The people immediately threw down their fishing rods and guns and rushed to look for mushrooms, of which there were many on the island. In one clearing I saw an unusual white aspen tree, like a white crow in a flock of red brothers...
For a long time now, in the fall, especially if there are few other mushrooms, I have been collecting cobwebs, which are also called yellow marsh mushrooms. These are such specific strong mushrooms with smooth red caps and legs covered with scales of the same color. I read in my reference “mushroom book” that there are many species in the spider web family, there are more than 400 of them in Russia alone. Some of them are deadly poisonous, and some are edible after preliminary boiling. Probably, it was the cobwebs that were considered the devil's mushrooms in the Middle Ages, because they are capable of forming intricate circles, the so-called witch's rings. A very interesting purple web spider is listed in the Red Book of the Republic of Tatarstan - as if covered in ink. By the way, its status is sad - an endangered species. In the republic, a single specimen of the purple webweed was recorded in the Vysokogorsk region in a forest area with fir undergrowth. In general, this mushroom grows in Karelia, the Baltic countries, Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, as well as in Siberia and the Far East. The purple web spider is protected in a number of reserves in Russia, including our Volzhsko-Kama, in Raifa. But in the Saralinsky section of the same reserve, another rare mushroom is protected - fire flake. It’s not called that for nothing - the color of the mushroom is bright yellow, and the taste is as if you were chewing a radish.
In the large Russula family, the rarest for our area is the blue Russula. Unfortunately, we can probably already say that it was, because in the Red Book of the Republic of Tatarstan this mushroom is listed as a species that has apparently disappeared. Blue Russula is also very rare in Europe.
Finally, I just can’t help but remember another wonderful mushroom from the Red Book, which is called Langermania gigantea, and is popularly called puffball. One day in August I had the opportunity to explore, together with the inspectors of the Stepnoy nature reserve in the Leninogorsk region, quite remote forest corners. And suddenly, in one of the clearings, we found a team of large white balls. They immediately determined that these were representatives of the puffball family, which are not only edible, but also have useful bactericidal properties. Mushrooms can reach 50 cm in diameter and weigh 20 kg! It is interesting that Langermania gianta had never been found in the Leninogorsk region before. These mushrooms belong to the so-called meteoric species, which after fruiting can disappear in a given place and not appear here for a very long time.
Author of the article: KARTASHOVA Lyudmila Issue: No. 190 (26567)
Add “Republic of Tatarstan” to your favorite sources on Yandex.News Subscribe to the “Republic of Tatarstan” channel in Yandex.Zen
- Potapov Kim Olegovich:
02.12.2010 at 20:33
Re: About Langermania, spiderwort and other rare mushrooms
Hello! Please tell me how I can contact the author of the article?
Answer
Add a comment
Click to cancel reply.
You may also be interested in
03.03.2022Beautiful, smart, successful “You are beautiful, smart and successful,” said President Rustam Minnikhanov at a traditional meeting with media representatives, which takes place annually on the eve of March 8th. |
03.03.2022The subsoil has also switched to digital The creation of a register of unscrupulous subsoil users, holding auctions for the right to use subsoil only in electronic format - this is not the entire list of legislative innovations that have come into force since the beginning of this year. |
03.03.2022We have one home - Russia The Presidium of the Council of the Assembly of Peoples of Tatarstan made an appeal to the multinational community of the republic. |
03.03.2022Unite in the face of external challenges Director of TAGTOiB named after M. Jalil Raufal Mukhametzyanov shared with Tatar-inform his opinion on the special operation in Ukraine. |
03.03.2022Zelenodolsk residents expressed their civic position An action was held at the Zelenodolsk plant named after Gorky in support of the Russian army and Russian navy. |
Coral hedgehog
The mushroom got its name solely because of its appearance, since it really resembles coral. The coral hedgehog is also called hertium coral, it is very beautiful and unusual. It grows mainly on the trunks of trees such as elm, aspen, linden, oak or on stumps. When the mushroom is mature, it grows strongly and looks impressive in the dark.
The coral hedgehog is a rare mushroom that begins to bear fruit from the second half of summer until the end of September.
Coral hedgehog
Crested hedgehog
0
Source:
In France it is called pom-pom, in China - monkey's head, in England - lion's mane. In Russia they call it a bearded tooth and a grandfather's beard. Outwardly, he is shaggy, with braids. They are found in the Primo region, Western Siberia, the Caucasus and Crimea. They mainly prefer birch, oak and beech. The shape of the hedgehog's body is irregular, pear-shaped. The color is variable - from light white, and in adults - to brown or yellow. The lower surface is covered with a large number of soft growths hanging down, up to 6 cm long. The taste is reminiscent of crabs or shrimp. The mushroom has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. It is used to make medicines that help fight leukemia, stomach cancer and chronic gastritis.
Grifola curly
Another name for the mushroom, more popular, is the ram mushroom. The ram mushroom is very large in size, its weight can reach 10 kilograms. The diameter of the mushroom is 80 centimeters. The fruiting bodies consist of many small spade-shaped caps that are supported by branching stalks. As a result, all these legs merge into a common base, forming a multi-tiered body of the grifola curly. Grifola curly can be found in deciduous forests in August and September. Mushrooms grow on the trunks of old oaks or maples, most often at their base. It is worth noting that they can grow very quickly and form white rot.
Grifola curly
Gyroporus blue
This species is a tubular cap mushroom, also called bruise.
The mushroom grows in deciduous or mixed forests, loves sandy soil, and often forms its mycorrhiza under birch trees. You can also find blue gyroporus near chestnuts or oaks. You can find the mushroom from July to September, but it rarely grows in Russia.
Gyroporus blue
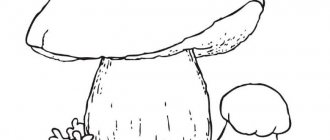
White boletus
This mushroom has a cap, the size of which reaches 15 centimeters in diameter. When the mushroom ripens, the cap becomes cushion-shaped and changes its color to yellowish. But at first, the white boletus has a white color with different shades. Its flesh is dense, and if you cut it, it will quickly begin to turn blue, and subsequently turn black. The mushroom's stem is tall, thick at the bottom and has white scales. Later they begin to darken and have a fibrous structure. White boletus is found in pine and mixed forests on the territory of the Russian Federation in the summer. It grows rarely, but in large groups.
White boletus
Rare plants of the Red Book of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan is a country with an amazing landscape. The steppe and semi-desert zones, swampy areas, and forests surprise with their picturesque and exotic vegetation.
Due to environmental degradation and human economic and scientific activities, many species are disappearing. To preserve rare plants of Kazakhstan, take an interest in the records of the national Red Book.
esgrs.org
The Red Book of Kazakhstan is clear evidence of man’s consumerist and thoughtless attitude towards nature.
When you pick a flower, dig up a plant to use its root as medicine, plow up land or turn back rivers, it seems that the plant world is indestructible. However, this is an illusion in which humanity has lived for a long time.
The consequences of such an irresponsible attitude towards nature are obvious: endangered species have appeared that require special conservation efforts.
There are Red Book plants on the territory of our country. Moreover, the Red Book of Kazakhstan has been created. The plants included in it constitute a unique natural resource of our region.
We invite you to learn more about what the flora of Kazakhstan is like, what species require close attention, protection, and even selection:
Schrenk's spruce
cco.ru
This is a majestic coniferous tree that reaches a height of up to 60 m, and a trunk diameter of up to 2 m. It has green or purple cones.
In Kazakhstan, this species is found in high mountain areas.
Spruce belongs to the category of valuable tree species, so it was mercilessly cut down for household needs.
Eastern juniper
vladgarden.ru
This representative of the cypress family is relatively low - up to 10 meters. It has a lush and dense reddish crown.
You will find it mainly in the southeast of our country.
The extermination of this species is due not only to the value of the wood, but also to the essential oil qualities of the leaves and cones.
Steppe almond
web03.bruns.de
This plant has long been the object of selection and industrial production.
You can find its cultivated variety in many gardens. However, in the wild, almond bushes with delicate pink flowers are exceptional.
Sogdian ash
atorus.ru
These plants from the Red Book of Kazakhstan are representatives of relict forests that once grew on the territory of Kazakhstan. The species belongs to the olive tree family. The ash tree reaches a height of 25 m, and the girth of the trunk is one and a half meters in diameter.
According to scientists, Sogdian ash is more than 25 million years old. This species survived the Ice Age, but due to the activities of modern man it almost disappeared.
To admire the Sogdian ash tree, go to the grove on the banks of the Charyn River.
Schrenk's meadowsweet
This shrub is also a representative of the most ancient plant species on earth. It is more than 30 million years old.
Now such shrubs with delicate white or white-pink flowers can be found in two places in Kazakhstan - the Betpak-Dala desert and the Karatau mountains.
Nut lotus
A beautiful but rarely seen species of perennial aquatic plants.
The lotus is beautiful: it has large flowers with delicate petals of bright pink color. Since ancient times, the root of this plant was used as food: stewed, boiled.
Since it reproduces precisely by rhizomes, such a consumer attitude has brought the plant to the brink of extinction.
In Kazakhstan, the lotus can still be seen on the coast of the Caspian Sea.
Allochruza cacimovidae
plantarium.ru
This plant is called Turkestan soap root because of the special substance (saponin) contained in the leaves and stems.
The species is rapidly declining, since the plant is actively used in industry: food, paint and varnish, textile. In addition, it is also used in cosmetology.
This species can be found in the western foothills of Karatau and Talas Alatau. The plant is very fastidious in terms of vegetation (it is propagated by cuttings) and has very poor germination. Therefore, in the wild, its numbers decrease every year.
The botanical gardens of Kazakhstan are involved in the preservation of the species.
Adonis spring, or Adonis
Medicinal plants of Kazakhstan are a special section of the Red Book. This category includes adonis, a herbaceous plant of the ranunculaceae family with a light yellow flower. It grows in the north and northeast of Kazakhstan.
It is prepared for the home pharmacy: adonis helps with diseases of the kidneys, heart, and nervous system.
Rogatik pistil
The fruiting body of the hornet is club-shaped, thickened at the end. The color of the mushroom is bright, lemon and orange tones. If you press on it, the fruiting body turns reddish-brown. Closer to the base, the stem of the mushroom narrows. You can meet the pistillate cattail in the fall, among green mosses. He loves mixed or deciduous forests, where there is a lot of moisture.
Rogatik pistil
Gossamer violet
This mushroom is very interesting and has a bright and rich purple color, in addition, it is edible. The cap reaches a diameter of 10-15 centimeters. When the mushroom is small, the cap is slightly convex; later it becomes cushion-shaped with wavy edges. The plates that have grown into the teeth are clearly visible. They have a dark purple color.
The pulp of the violet cobweb has a whitish or slightly purple color and tastes quite pleasant. Purple cobweb is often found in coniferous or deciduous forests, in many European countries.
Gossamer violet
Mutinus Ravenel (another name for “smelly morel”)
It has an oblong shape. They sprout from white, ovoid formations up to 1.5 centimeters wide. The cap of the mushroom is oblong and has green mucous membrane. The smell is reminiscent of rotten meat and rot. Cannot be eaten. Mushrooms of this species can be found from early summer to early autumn in parks, gardens, and less often under coniferous trees. Most common in North America. It is quite rare in Europe.
Mutinus Ravenel
Growing at home and in the country
White boletus is a tasty, edible mushroom that gets along well in a prepared garden plot. To plant it, you will need to purchase mycelium, which is enough for 3 square meters. m. under one tree or bush. Planting process:
- The area at the roots of the plant is dug up and a depression of up to 15 cm is created.
- The mycelium is evenly distributed over the entire area of the pit.
- The top needs to be covered with garden soil mixed with humus in equal proportions.
- Cover with the remaining soil from digging a hole.
Any trees are suitable for planting; the mycelium will take root regardless of the time of year (in the southern regions it can be planted in winter). Water with a regular garden watering can; the planted area will need 30 liters of water.
The first harvest can be observed in autumn or spring, but not earlier than 5 months later. After planting, most often the first fruits can only be harvested the next year.
From a planted plot it is possible to collect about 1.5 kg in the first year and up to 14 in the next. Mushrooms will delight as long as the tree lives.
Pine cone mushroom
The hat is quite wide - up to 17 centimeters in diameter. In young mushrooms it looks like a ball, then becomes completely flat. The color of the cap is white, grayish, it is covered with almost black scales. The taste of the mushroom is bland without any noticeable taste or smell. The flesh of the mushroom immediately becomes reddish-orange, then almost black. The leg is quite long - up to 12 centimeters, dense, shaped like a cylinder. The color of the cap and stem are the same - grayish-black. The surface of the cap resembles flakes. Hence the name of the mushroom itself. It is found in coniferous and mixed forests.
Pine cone mushroom
Birds of Tatarstan
Passeriformes
White blue tit
For his noble appearance, he was popularly nicknamed the prince. The bird has a white head and belly. The back of the animal is gray-blue, and the wings are pure blue. The feathers on the blue tit's head are raised, looking like a cap.
In the vast expanses of Tatarstan, blue tits choose floodplain forests with thickets of willow and alder.
Common remez
Small bird weighing up to 11 grams. Typically, individuals gain 7 grams of mass. The name of the bird is German and translates as “reed tit.” The birds have similar, discreet colors and miniature sizes. Hence the analogy.
Remez prefer to settle in reeds. Accordingly, in Tatarstan, flocks of tits choose marshy areas.
Grebes
Red-necked grebe
The feathers on the bird's neck and chest are orange-red. This color is also present on the sides of the head. There are tufts of feathers red there, reminiscent of a drop of hair.
In Tatarstan, red-necked birds are found in small swamps, lakes, and oxbow lakes. The birds are similar in size to ducks, rarely weighing more than 500 grams.
Grey-cheeked grebe
Her neck is also red, but only in summer. There is no scarlet on the head. The toadstool's cap is black and its cheeks are gray. The general appearance of the bird is similar to a great grebe. However, this one has white lines between its cap and cheeks.
The grey-cheeked grebe lays 26 eggs and is a protected species. Given the animal's fertility, ornithologists are perplexed as to the reason for its extinction. They sin by destroying the nests of toadstools by predators.
Woodpeckers
three-toed woodpecker
Found in the northern taiga of Tatarstan. The bird's paws have 3 toes instead of 4. Another distinctive feature is the yellow “cap” on the bird’s head.
The three-toed woodpecker is little studied because it climbs into the taiga wilderness and leads a secretive lifestyle.
Pictured is a three-toed woodpecker
Hoopioformes
Hoopoe
Pronounces sounds that form the words “it’s bad here.” The sound of a hoopoe's song is deceptive. Birds of this species are talkative in the spring, during the breeding season. It is unlikely that birds will have a bad time during the mating season.
Listen to the voice of the hoopoe
The common hoopoe lives in Tatarstan. This is one of 10 subspecies of birds. The common one is brightly colored. On an ocher background, black stripes are visible on the sides. The hoopoe wears an orange crest on its head. It looks like a fan. Its tops are dark.
Storks
Great bittern
It reaches 70 centimeters in length and can weigh almost 2 kilos. The bird's cry is equally powerful, reminiscent of the roar of a bull. You can hear this at a distance of 3-4 kilometers from the bittern.
Listen to the voice of the great bittern
A large bittern nests on swamp hummocks. The choice of place is strange for other birds, as is the manner of building the house. The bittern makes nests unsightly. It's more like a haphazardly thrown heap of herbs.
Lesser bittern
The bird reaches 36 centimeters in length and weighs approximately 150 grams. Males and females of the species have different colors. This is an exception among storks. Female bitterns are brown with streaks. Males wear a black “cap” on their head. She has a green tint. The same tone of plumage on the wings of a bird.
The little bittern nests along the banks of stagnant ponds overgrown with grass. Among the vegetation, the bird camouflages itself. To be convincing, the bittern sways like a reed in the wind.
Little bittern
Collitza
It reaches a height of a meter, gaining a mass of about 2 kilograms. It differs from other storks by its beak that widens at the end. It is yellow and resembles sugar tongs. The birds seem to mow down the water with their beaks, simultaneously fishing out the larvae of mosquitoes and other insects.
Spoonbills prefer to settle in swamps. In Tatarstan, the species is protected due to its small numbers.
Flamingoformes
Common flamingo
Like other flamingos, of which there are 6 species, it was classified as a stork. The order “flamingiformes” was created by ornithologists a couple of decades ago.
Along with cormorants and terns, roseate flamingos are the most ancient birds on Earth. The species appeared about 50 million years ago. In the territories of the former USSR, flamingos are found in the steppes of Kyrgyzstan and on the lakes of Tatarstan.
The species is protected. In the old days, ancient birds were hunted. In spring, flamingos molt actively. Without feathers, animals cannot fly. This is what hunters used before.
Nightjars
Common nightjar
The size of a woodpecker, reaches 28 centimeters in length, weighs 65-95 grams. The feathered species is distinguished by short legs. The bird can stand, but it seems that it is sitting. The legs are not visible from under the body. It is covered with loose feathers, visually increasing the size of the nightjar.
The bird got its name due to popular belief. Noticing that the birds circled over the stalls at night, people decided that the guests were sucking on the cattle while drinking milk. In fact, nightjars catch insects circling near ungulates. Birds hunt at night because they rest during the day.
Anseriformes
Brent goose
Of the geese, it is the smallest and rarest. The bird weighs no more than 2 kilos, and its length does not exceed 60 centimeters.
Despite its name, the goose is only partially black. The bird's tail is white. There are also light feathers on the wings. The body is brown. The head and neck are painted black.
Owls
Scops Owl
The bird got its name similar to its cry: “Sleep-oo.” The voice of the Scops Owl is heard at night. During the day the bird is inactive.
Listen to the voice of Scops Owl
The species is protected in Tatarstan. The number of Scops Owls is falling due to the use of pesticides in agriculture. When the poisons get into the rodents that owls feed on, they poison the predators and cause mutations and diseases.
Great Gray Owl
Black markings are visible under the bird's beak. From a distance they look like a goatee. Hence the name of the owl. It is a protected species, unlike the common and long-tailed owls, which also live in Tatarstan.
The Great Gray Owl prefers to live in dense, old forests near swamps. Sometimes owls nest on the border with clearings.
Thorn-footed owl
A small, compact owl. Her legs are covered in feathers, including her toes. Hence the name of the bird. She is predatory and attacks with her eyes closed. This is how the owl protects the organs of vision from damage. What if the victim begins to actively defend himself?
The owl's main prey is voles. By destroying mice, the bird stands guard over agricultural crops.
Falconiformes
Rough-footed Buzzard
It belongs to the hawks, but its legs are feathered right down to the toes, like those of eagles. The length of the predator is 50-60 centimeters. The wingspan reaches 1.5 meters, and the weight is 1700 grams.
Buzzards secure territories for themselves both on the ground and in the air, considering theirs approximately 250 meters above the surface. If a stranger enters this airspace, he will be attacked.
Steppe harrier
It stands out for its long, pointed wings and the same tail. Among other harriers, he is the lightest, as if gray-haired. Hence the name of the bird. The color of its plumage resembles the surface of the moon.
In Tatarstan, the harrier is found in steppe and forest-steppe regions. There the predator hunts rodents, lizards and small birds.
Steppe Harrier
Vulture black
Among the birds of Tatarstan, the black vulture is the largest. The wingspan of the bird reaches 3 meters. The animal weighs about 12 kilograms. The vulture maintains such a mass by feeding on carrion. The bird tears it apart with sharp claws and a strong beak.
In Tatarstan, the black vulture is found in the Aznakaevsky district, as it prefers mountainous areas. The species is considered a migrant to the republic. The scavenger nests in Southern Europe.
Pigeonidae
Klintukh
This is a wild pigeon. Unlike the urban one, it avoids people, settling in the forests. There the birds settle in the hollows of old trees. Cutting them down leads to a reduction in the number of the species.
Externally, the clintukh is almost indistinguishable from the rock pigeon. The forest bird is distinguished by the sound it makes when taking off. Klintukh produces sharp, whistling “notes” with its wings.
Common turtledove
The animal is 30 centimeters long and weighs 150 grams. The dimensions correspond to a regular pigeon. However, a dark ring is visible on the neck of the turtle dove. This is what distinguishes the species.
The turtle dove is migratory. From September to May the bird lives in Africa. Turtle doves return to Tatarstan at the beginning of summer.
Charadriiformes
Lieutenant
This is a small bird with long legs and a thin, elongated beak. The porridge is rare and is classified as migratory. In Tatarstan, representatives of the species settle in fields in floodplains.
The population is suffering due to the plowing of fields. As a result, floodplains are drying up. Cattle grazing in the fields also bother the guards.
Crane-like
Gray crane
In the last century it was widespread in the north of Tatarstan. The population has declined in the 21st century. The gray crane is not included in the country's Red Book, but is close to being included in the list.
The height of the gray crane reaches 115 centimeters, spreading its wings almost 200 centimeters. The bird weighs 5-6 kilograms.
Porphyrovik
At first glance, a rather attractive mushroom. In any case, it is considered an edible mushroom. The leg is quite long - up to 12 centimeters. The shape of the hat resembles a hemisphere of quite large diameter. The color of the cap is brown, brownish in color. The smell of the pulp of the mushroom itself is unpleasant. When cut it turns bluish, green, black and even red. Found in Europe and North America in mixed forests from late summer to early autumn.
Porphyrovik
Edible popular varieties with descriptions
In Tatarstan you can find almost all known and favorite types of mushrooms. Butterfly, boletus, chanterelles, saffron milk caps and other delicious representatives of the mushroom kingdom have settled here.
Porcini
Porcini mushroom is one of the most colorful mushrooms. It grows in many regions of Russia, and there are many of them in Tatarstan. All varieties of boletus mushrooms have an amazing, refined and unusual taste, but the porcini mushroom occupies a leading place.
You can recognize it by the following parameters:
- the cap has a diameter of about 25 cm, its color is whitish or dark brown (may vary depending on the location of the fruit);
- the leg is very dense, massive, up to 20 cm high and up to 5 cm wide;
- The pulp is white and has a high density. Thick, does not change color when broken.
The true boletus has a double that is unsuitable for consumption. Gorchak is very similar in appearance to the edible specimen, but, unlike it, it changes its color when its pulp is damaged.
You can find boletus mushrooms in mixed and coniferous forests of Tatarstan. For their fruiting, the most optimal period is from the first weeks of summer to the end of October.
Ryzhik
Saffron milk caps belong to the Milky family. They have a characteristic color, for which they received their name. Their main parameters are as follows:
- the cap has a diameter of 5-18 cm, orange-yellow in color with dark concentric areas, round in shape;
- the flesh is dense, matches the color of the cap on top, but is whitish when cut;
- the leg is of medium height - about 9 cm.
Saffron milk caps prefer to settle in coniferous forests. In particular, large concentrations of them can be found near pine trees. But certain varieties of this fruit are also found in mixed plantings or forests. The approximate collection period is from July to September.
Chanterelle
Common chanterelles are valued not only for their excellent taste, but also for their high resistance to insects and parasites. This is their main difference from false chanterelles, which are often worm-eaten or damaged.
The main features of these delicious mushrooms are as follows:
- the cap is yellow or orange with drooping edges and has an irregular shape, and its diameter is 3-14 cm;
- the leg is thick, solid, widened upward and has a color corresponding to the cap color;
- The pulp is white in color, very dense and fleshy in structure, sometimes fibrous, and when pressed it acquires a reddish tint.
The taste of chanterelle is spicy, with a slight sourness. The aroma is very similar to the smell of tropical fruits.
Chanterelles can be found in the forest from the second half of July to the beginning of October. They grow in almost all forests.
Oiler
Butterfly belongs to the tubular edible mushrooms of the Boletaceae genus. Among these representatives there are also conditionally edible and inedible specimens.
In young individuals, the cap is shaped like a hemisphere or a cone, but over time it straightens out. The largest adult butterflies have a cap section reaching 15 cm in diameter.
The main feature of butterfish is the film that covers their cap. It is slippery and sticky, as if it has an oil base. It is for this reason that these mushrooms have such a name - boletus.
The flesh of the butterdish is soft, but at the same time quite dense. It is colored whitish or yellowish, and when cut it can change, acquiring a reddish or blue tint. It does not have a distinct odor, but sometimes light pine notes can be felt.
The oiler leg is cylindrical in shape, measuring from 1 to 3.5 cm in thickness and 4-10 cm in height. The color is white, but often darkish below.
In Tatarstan, the oiler likes to settle in coniferous forests. However, they can sometimes be found under birch, oak and other types of deciduous trees. The growing period lasts from June to October.
Gruzd
The real milk mushroom belongs to the conditionally edible mushrooms, and is a representative of the genus Mlechniki. Its main characteristics are as follows:
- Hat. Its diameter is 5-20 cm. The shape is initially flat-convex, but over time it becomes funnel-shaped. The edge of the cap is pubescent and rolled inward. The color is often off-white.
- The leg grows up to 3-7 cm in length and 2-5 cm in thickness. Smooth to the touch, white or yellowish in color. Yellow spots may appear on its surface.
- The pulp is quite dense, but brittle. It has a characteristic odor similar to fruit. When broken, it begins to secrete abundant milky juice.
Milk mushrooms grow in deciduous and mixed forests. Most often they are found in the northern part of Tatarstan between July and September.
Morel
The common morel is a mushroom that cannot be ignored, if only for the reason that it has a rather unusual appearance. Its cap is egg-shaped and tightly attached to the stem. The color is blackish or black-brown. The length of the leg varies from 2 to 3.5 cm, and the width from 2 to 4 cm.
Looking at the photo of the mushroom, you might think that its cap part is generously sprinkled with bran. It is dotted with potholes, which are called mittens. Their depth sometimes reaches half a centimeter.
The leg is not very high: its length usually does not exceed 4 cm. But there are also specimens that are taller. The morel reaches 6 cm in width. The stem inside has a cavity, narrowed at the bottom and expanded at the top.
The morel tastes bitter and noticeably watery. However, it has a very pleasant smell, although weak.
Advice!
It is recommended to look for morels under bushes, in ravines, and also in areas where deciduous trees grow. They love soil that is generously fertilized with humus. Mushrooms appear in April and grow until about mid-May. But there are also more resistant types of morels.
boletus
There are several varieties of boletus. They are all delicious and unique in their own way.
The cap of the mushroom is white or grayish in color, and its diameter is 4-12 cm. Depending on the type of fruit, it can be gray, brown, sometimes almost black or brown.
The leg is colored grayish or white. There are small scales on its surface. The thickness varies between 1.5 - 4 cm. Closer to the cap it becomes thicker. The pulp is light, evenly colored.
Boletuses begin to appear in the last weeks of July, and their fruiting period ends in early November. You can find these fruits in deciduous forests; they grow mainly near birch trees.