You never cease to be amazed at the beauty of our forests, especially at the end of summer, in gold and crimson. You walk along the path and admire it. And under every bush and tree a sudden discovery may await you - autumn mushrooms, which in 2022 are not inferior to their summer counterparts in taste and beneficial properties.
In the light forest in 2022, here and there, colorful caps of one of the most numerous mushrooms - russula - flaunt:
- Russula itself and loadings;
- milkweeds (milk milk mushrooms, milk mushrooms, saffron milk caps).
Loadings
The most common loadings are:
- blackening;
- black (nigella);
- white (dry milk mushroom, cracker);
- valui (bull, fist).
Beginning mushroom pickers often confuse mushroom pickers with milk mushrooms. The first are stocky mushrooms with discreet funnel caps, always dry and full of debris, devoid of fringe and edges. For this they were nicknamed “dry” milk mushrooms. And they do not secrete milky juice. Unfortunately, loads are rarely collected. Perhaps their conditional edibility scares them away. And although they believe that these mushrooms are not for frying, the taste of dry milk mushrooms in oil or fat, with sour cream, is magnificent in its own way. Black podgrudok is good for pickling and caviar. But especially tasty (after saffron milk caps and milk mushrooms) are pickled dumplings. Many of them have a pleasant smell (fruity, honey, nuts, herring) and a mild taste. To make them crumble less and become less bitter, scald them with boiling water or soak them for two days (periodic changes of water are required). You can cook for 5-7 minutes.
Milkers
Despite the abundance of pungent milky juice, many milkweeds are also popular, including milk mushrooms with dense white flesh. The word “mushroom” is translated from Church Slavonic as “heap”: mushrooms often grow in groups. In deciduous and coniferous forests, light felt milk mushrooms are often found. In mixed forests, birch forests, olive-brown black milk mushroom grows in moss, on the litter, and in the grass near paths. Used when salted (turns purple-burgundy). Milk mushrooms are salted, pickled, fried, boiled, and prepared into snacks, salads, fillings, soups, and sauces. The milk mushrooms are first soaked in water for a long time or boiled.
Saffron milk caps
Not only in 2022, but also in previous years, saffron milk caps stand out from other autumn mushrooms with their excellent taste and beautiful appearance. Considered a delicacy in many countries. Similar to pink wave, which is produced by colorless milky sap and a heavily pubescent cap. The smaller one is white with a white cap. Both types turn yellow after soaking, but at the same time they are good for pickling, pickling, and main courses. Young curls with a cap diameter of no more than 3-4 cm are valued. Poorly cooked mushrooms have a weakly toxic effect, causing irritation of the mucous membrane and intestinal disorders. When salted, they can be consumed after 45-50 days.
Rows
The name “row” is the result of the ability of fused mushrooms to grow in a row, in groups. Pleasant taste and aroma are characteristic of the gray, crowded, poplar, and May row. Conditionally edible subspecies - yellow-red, yellow-brown, purple row. The rest are dangerous! The pulp of the crowded row (not to be confused with the lighter poisonous fused row!) is dense, elastic, grayish-brown, with a mealy smell and taste of chicken. Before salting and marinating, it is boiled for 20 minutes. Due to the aroma of fresh flour and dense grayish pulp, with a yellowish edge, the gray or streaked row is difficult to confuse with others. Suitable for all types of processing. When boiled, its flesh turns gray and brown. The greenfinch is similar to it, also called the green rower, greenfinch, and jaundice. It retains its green color even after cooking. It can be a loner or live closely with six or seven others of its own kind. It happens right up to November, when the other mushrooms have already gone away. The pulp is dense, white, later turns yellow, and does not change color when cut. Rarely worms. The smell is floury, especially in mushrooms from pine trees. Until now, brilliant green was classified as a conditionally edible mushroom. Now suspected of being poisonous. Affects skeletal muscles.
Honey mushrooms
Honey mushrooms, honey mushrooms... The most famous is the autumn honey mushroom, or the real one. Prefers old birch forests with dead wood and swampy alder forests with many dead trunks and stumps.
Variety of autumn mushrooms
Many mushrooms grow in the fall, but they can all be divided into three categories:
- Common summer-autumn mushrooms that bear fruit throughout the snow-free period. But some of them appear en masse in the fall - they can well be considered autumn mushrooms.
- Pure autumn mushrooms, mycelium [1] Mycelium is the underground part of a mushroom or mycelium in a simple way. which develops and accumulates resources over the summer, and throws out fruiting bodies shortly before the first cold weather.
- Extreme mushrooms, which also belong to summer-autumn or autumn, but they are not at all embarrassed by low, including sub-zero temperatures at the end of autumn.
There are also mushrooms, the fruiting period of which occurs in the summer and partially covers September. It seems like they can also be classified as autumn mushrooms. However, those ten days of September - when these mushrooms are collected - still show all the signs of summer, and as soon as real autumn begins, the mushrooms stop appearing. Therefore, I will not consider these mushrooms, since I am inclined to consider them summer mushrooms. But even if I agreed to do this, the article would have turned out to be colossal in volume and would not fit into one publication.
I also intend to state that in the following narrative we will talk exclusively about edible mushrooms. It is clear that in the fall, in addition to them, a lot of poisonous and inedible mushrooms appear, but they all require separate consideration.
How quickly do edible mushrooms grow after rain in the fall?
Mushrooms are the fruits of the growth of mycelium and mycelium. In general, mycelium grows several meters underground, like a spider’s web. From time to time it bears fruit. These are exactly the mushrooms that we collect. The largest mushroom harvest is observed in the fall after rain.
Mushroom growth time is 2 weeks. But most often you can see the mushroom already on the 5th day. At this time, a leg appears that connects the mycelium and the cap. Initially, the cap is small, but after 2-3 days its size rapidly increases. That is, after the rain you can go pick mushrooms in 1-2 weeks.
How quickly do edible mushrooms grow after rain in the fall?
Obabki
Obabki should be classified as summer or summer-autumn mushrooms, because during this period they are mainly collected. You can read more about these mushrooms - about their places of growth and fruiting periods - in the following articles:
- Boletus mushrooms: what they are, where they grow and when to collect them;
- Boletuses: what they are, where they grow and when to collect them (by the way, aspen boletuses - according to the scientific classification - are also little boletuses).
However, some of these mushrooms produce fruit even in late October. Next, I intend to look at the most “autumn” of the little things.
Obabok is harsh
It is also a harsh boletus or poplar boletus. So named for its very dense pulp.
It grows under poplars and aspens, in places with calcareous, loamy and sandy soils, but is quite rare. Fruits from late July to November .
Marsh boletus
Photo by: Olev Mihkelmaa
Known for its light color, through which the typical boletus tones barely show through, its love for damp places and loose pulp (especially after heat treatment).
It grows under birch trees - on the outskirts of swamps, in damp mixed forests, on mossy litter. It bears fruit throughout the snowless period (according to rumors, it can appear even in May, so it can also be classified as a spring mushroom). In autumn, this mushroom can be found in the forest almost until the very first snow.
Black boletus
Outwardly, it is the complete antipode of the previous mushroom, but in everything else it is almost similar to it - it also loves damp places and can appear in the midst of autumn.
I myself periodically observed this mushroom in the forests in late autumn - when the trees were bare and the first snowflakes were flying in the air.
White boletus
What’s interesting is that among boletuses there is also a light variety that loves damp places and is quite cold-resistant.
White boletus is a rare mushroom that bears fruit from June to September , but it can be found in the forest until the very first snow. Due to the lack of knowledge, it is not known exactly what trees it enters into symbiosis with. According to one version - with conifers, according to another - with birch.
Boletus yellow-brown
Mostly yellow-brown boletus is harvested in the summer, most en masse at the end of the season. However, its fruiting bodies, just like the previous mushroom, continue to appear until the first snow. Mycorrhiza [2] Mycorrhiza is a union of a fungus and a higher plant (for example, a tree). The essence of this symbiotic union is that the mycelium entangles the root of the plant and penetrates it. Next, a mutually beneficial exchange takes place between the fungus and the plant: the former provides water and minerals in abundance - much more than the plant could extract from the soil. It does not remain in debt and supplies the mushroom with valuable organic substances - carbohydrates, amino acids, etc. it forms with birch.
Description of later varieties
Forests in late autumn are no less attractive in terms of “silent hunting”. And even if we are not talking about the former diversity, going for mushrooms at the end of October and November will also give good results.
Autumn stitch
In late autumn, in the coniferous forests, on the remains of rotten wood and former fire pits, whole clearings of curly stitches appear with their cartilaginous body, which in its raw form has no aroma.
Typically, these fungi do not reach large sizes; they are used as food whole, but only after soaking and boiling until fully cooked, otherwise there is a risk of being poisoned by their toxic substances.
Late oyster mushroom
Despite its conditional edibility, which is justified by not the highest organoleptic qualities, oyster mushrooms growing on trees are very tasty when fried. The good news is that it forms entire colonies that can withstand even the first persistent frosts.
But you cannot eat oyster mushrooms raw, unlike champignons, since the substances it contains do not have the best effect on digestion.
Winter honey fungus
Flammulina velvety-footed, also known as winter honey fungus, also withstands sub-zero temperatures. These small yellow fungi do not have a pronounced taste or smell, and are an excellent raw material for preparing aromatic marinades. The variety differs from ordinary honey mushrooms because of its dry, velvety cap to the touch.
Deer mushroom
Larger fruits are produced by this variety, all parts of which are considered equally edible. Just like honey mushrooms, the deer mushroom selects trees, forming entire families on their trunks. It is considered a valuable variety due to its excellent taste and pronounced aroma.
Crowded row
One of the numerous species of the Ryadovkov family, the characteristic features of which include the light brown color of the cap, often covered with earth and other adhering forest debris.
The smooth cap of the variety has a different shape - from spherical to wavy and inverted. Because of its specific aroma, mushroom pickers are not very fond of the row, but it turns out very tasty when fried and pickled.
Gray talker
The shade of the talker's cap, which darkens with increased humidity levels, can vary in a fairly wide range of colors - from smoky gray to rich ash. It differs from other rows in its subtle floral scent, which is largely neutralized by heat treatment.
Butter
Once I had the opportunity to collect boletus in the third ten days of October. The culmination of autumn was frosty, the first snow was in no hurry. In the young pine forests - on the frozen “petrified” litter, among brittle, frost-covered grass - there were thousands of “freshly frozen” boletus, among which there were almost no worms. Nobody collected them, since people considered these mushrooms to be already spoiled. But in vain. After all, they were frozen once and have not yet been thawed. Yes, in the heat they became loose and dark, but they smelled good during cleaning. However, in boiling water, the butter quickly lightened and released all its aroma into the broth. The mycelium turned out to be breathtaking, and as it seemed to me then, even tastier than the one I ate in the summer - made from fresh, not frozen mushrooms.
Butterflies are another mushroom that grows in the fall, and at times they can be collected before the very first frost or even from under the snow. The main thing is that the weather is calm and clear.
You can read more about boletus mushrooms in the article: “Boletus mushrooms: 25 varieties.” In the list below I will describe the most autumn ones.
Summer oil can
He is also a grainy butterdish , an early butterdish .
Mycorrhiza forms with pine , bears fruit from June to October , but sometimes it is observed in the second half of May (for which, it would probably be worth classifying it as a spring mushroom) and early November.
Clinton grease can
Named in honor of the American naturalist, this mushroom is popularly known as chestnut oiler or girdled oiler , but most often it is confused with the very similar larch oiler.
Clinton's oil can grows under larches . Fruits from July to October .
Oil can Nyusha
Another mushroom named after the scientist - a German botanist.
Just like the previous butterdish - it forms mycorrhiza with larches . Distributed very widely in the temperate zone of the continent; it likes to climb high into the mountains. Fruits from July to October .
Swamp oil can
He is also the yellow swamp butterdish . It has a very expressive, memorable color towards yellow and golden tones. Purely autumn mushroom.
A lover of damp lowlands, river floodplains, the edges of lakes and swamps - all those places where it is more humid. Mycorrhiza forms with Scots pine and some other double-leaved pines. Fruits from September to October .
Oil can sour
It has somewhat loose pulp and is inferior in taste to ordinary boletus. The mucus covering its cap has a sour taste, which is how the mushroom got its name.
Mycorrhiza forms with five-coniferous pines, including Siberian cedar . Very common in Western Siberia. Fruits from July to early October .
Oil can yellowish
The lower surface of the cap of this mushroom has a pleasant ocher tint.
Distributed quite widely, found both in Eurasia and North America. Grows under double-leaved pines , including common pine . Fruits from June to October .
There is information that the skin of the cap of this butter dish has powerful laxative properties, so it should be peeled off before cooking.
Red-red oil can
He is also known as the Trentian butter dish, the Tridentine butter dish, known for its good taste.
A very rare mushroom that forms mycorrhiza with larches. The fruiting period is from June to October .
Bluefoot, or lilac-legged rower
The rows grow in so-called witch circles: in a good year, up to several bags of bluelegs can be collected from one place. Glades can reach 2-3 km in diameter. Today I collected one and a half to two buckets of rows from a small plot, but somehow I ended up on a strip of mushrooms about 300 m long, collected 4 bags of rows from it and left only because there was no more container.
- Sulfur-yellow tinder fungus, or “mushroom chicken” - you should definitely try this mushroom!
The purple-footed row plant grows en masse in cool, damp weather, usually in spring and fall. In the last couple of years, the weather has not been very favorable for the growth of mushrooms, but, nevertheless, they are there. If you spot even one blueleg, bend down, rake up the leaf litter and take a closer look: there are probably many more mushrooms nearby.
It is called blueleg because the stem of the mushroom has a bluish tint. Over time, the blue discoloration may become less obvious, but it does not disappear at all. There are edible rows with white legs, but this is a completely different species.
Ryadovki taste best in soups, but they can also be fried and pickled. They have a specific taste that is impossible to describe. The aroma of the rows also cannot be confused with any other.
Rows can also be grown on a plot, but keep in mind that this area cannot be dug up. It is not advisable to even mow grass on it. Dig up a leg with mycelium in the forest, transplant it to your plot to a depth of 15-20 cm, and in a year you will have mushrooms growing.
You can cut off the fringe from old mushrooms and sow the area with it. If you bury a mushroom or even a piece of a mushroom in a nutrient medium, for example, in humus or in the ground in an undug area covered with rotting leaves, mushrooms will probably begin to grow after a while. I planted mushrooms the year before and last year I already got a harvest of bluelegs. I haven’t tried growing rows in blocks yet, but I’m sure it’s quite possible.
Previously, rows of trees grew en masse near a farm where many cows were kept. The soil there was well manured, so the mushrooms grew very large - up to 30-40 cm in diameter. In the forest belt, the size of bluelegs is noticeably smaller.
By the way, I was asked what is the best way to collect mushrooms so as not to damage the mycelium: twist, cut or pick. Do as you please. Sometimes mushrooms that no one has found simply rot, and this does not affect the mycelium in any way. Nature anticipates any risks and knows how to protect itself from them. Therefore, do not participate in useless discussions, just try to behave in a non-barbaric manner in the forest, and it doesn’t matter whether you twist the mushroom or cut it.
- Boletuses in November - where to look, how to distinguish them from the satanic mushroom, can they be grown in a window?
White
Almost all porcini mushrooms collected in our latitude grow in the fall - you don’t even need to look in reference books to confirm this fact. However, in the summer they are observed to produce the most massive amounts of fruit, and in the fall (until about October ) they are seen less frequently. But they are still collected at this time, and the further south the region, the more often and for longer. There are several varieties of porcini mushrooms that form mycorrhiza with different trees - birches , pines , spruces , oaks and others. You can read more about the places where porcini mushrooms grow in the article “Where porcini mushrooms grow.”
Some practical tips for 2022:
- Many peeled mushrooms (boletus, saffron milk caps, boletuses), easily oxidizing in air, darken almost instantly. Therefore, immediately immerse them in water with salt and citric acid or in boiling water, where they will be boiled;
- salt mushrooms without aromatic herbs. Replace them with horseradish: it adds pungency and protects against souring and spoilage;
- autumn 2022 mushrooms absorb salt at different rates. You can enjoy saffron milk caps after they have been aged for 5 days, russula can be considered ready after 12 days, russula - after 40 days, etc.;
- Freeze tubular mushrooms only fresh: when cooked, saturated with water, they lose their taste. Repeated freezing is taboo, since in this case it turns out to be a tasteless, watery porridge.
In properly dried mushrooms, the concentration of nutrients increases 10 times with a decrease in weight by the same amount. Dry mushrooms contain more protein than others. And they are stored longer and easier, taking up little space.
Hedgehogs
Photo 15. Rufous hedgehog. Author: H. Krisp.
Their distinctive feature is unusual needle-like spines on the underside of the cap, instead of the usual plates or tubes.
Photo 16. Variegated hedgehog is a conditionally edible summer-autumn mushroom. Author: H. Krisp.
These mushrooms grow just as well in the fall as in the summer and can last until the first cold weather. They are found in different forests, because they can form mycorrhiza with various trees - both deciduous and coniferous.
Photo 17. Notched hedgehog. Photo by: Bubulcus.
In our country, hedgehogs are not collected everywhere, but in Europe they are considered very edible, and one of the species, the variegated hedgehog , is used as a seasoning.
Umbrellas
There are no large forests near me, but even in the neighboring acacia forest belt you can find a lot of mushrooms. Very good mushrooms are umbrellas. You don’t even need to boil them: cut them and fry them in oil - very tasty. Umbrellas are often confused with fly agarics, but in my area fly agarics are practically never found.
The stem of the umbrella turns a little red, and there is no need to cut it off - only collect the caps. These mushrooms are more like toadstools, only they are much larger.
Umbrellas grow from spring to late autumn in large clearings, and grow en masse from mid-August until frost. Sometimes these mushrooms completely cover an area of half a kilometer in size.
Russula
The bulk of russula (including edible ones) bear fruit in the summer and at the very beginning of autumn - when the foliage has not yet turned very yellow and the weather is warm. However, among russula there are some varieties that are found in forests in mid-autumn. I intend to list them.
Russula is caustic
It is so named for its pungent taste, so it should be boiled before cooking or salting.
Grows in damp pine and mixed forests, on the outskirts of swamps. It bears fruit from July to October and is quite common.
Russula brownish
It is also called purple russula or herring russula . It is notable for the fact that when dried, it smells very strongly of seafood. Does not require boiling before cooking.
Russula turning brown is found in coniferous forests - usually under pine or spruce . Fruits from July to October .
Valuy
The name heading this chapter has taken root well in reference books, but among the people (at least in our area) this mushroom is called in two ways: goby - this is how it is known among urban mushroom pickers, kulbik - this is how villagers prefer to call it. Being unprocessed in a special way, it is acridly bitter and has a strange smell, but after boiling it is suitable for pickling, and how! Properly salted and seasoned, the kulbik will not be inferior in taste to milk mushrooms. And some gourmets even prefer it to other salted mushrooms. But you should collect the youngest fruiting bodies with unopened caps, the diameter of which is from 5 to 10 cm. Older mushrooms, as a rule, are already wormy, eaten away, loose and smelly.
The habitat of the kulbik is birch forests and forests mixed with birch . The fungus can also be found under coniferous trees. He really loves shady and damp places, where he forms mass aggregations. It bears fruit from July to October , but not as abundantly in the fall as in the summer.
Name of September and October species
When going to the forest for mushrooms in the fall, it is recommended to undergo theoretical training by studying the appearance and structure of edible varieties growing in a certain area. This measure prevents the collection of varieties unsuitable for consumption, which could lead to serious food poisoning and possibly death.
Note!
It is important to remember that quiet hunting is not only an indescribable pleasure, but also a certain risk, which can be eliminated by many years of experience in successful gathering or a trip on an organized tour with professional mushroom pickers.
Boletus
It is quite fair to start any story about mushrooms with boletus, because this is the real king of the forest. The taste and aroma of this variety are so refined and strong that boletus mushrooms are widely used in cooking.
The white or creamy dense flesh of these wonderful giants is salted, pickled, fried whole steaks, added to meat, potatoes, beans and other vegetables, the most aromatic soups and stews are cooked from it, dried and even frozen whole or in thin slices.
It is almost impossible to confuse boletus with toxic varieties, because its massive velvety brown cap and even fleshier beige stem, reminiscent of a barrel, can be recognized even from afar. A distinctive feature of the mushroom is its tubular hymenophore, which, like other Boletaceae, resembles a greenish foam sponge.
Obabki
By boletus we mean boletus trees that grow in birch forests and groves mixed with conifers. They are rightfully considered one of the most common in Russia, found mainly in open sunny meadows.
A strong, stately mushroom has a dense, smooth cap of a reddish or brown color and a thick, even leg, dotted with numerous variegated specks. One of the advantages of the variety is its high nutritional value, almost comparable to red meat. Boletus mushrooms also have many useful substances and excellent organoleptic qualities.
Saffron milk caps
In the second half of September, the time comes for saffron milk caps - bright mushrooms with a uniform brick color. Both young and ripe fruits of this variety are good, from which excellent pickles are made.
At the initial stage of development, fungi have a convex conical cap, but as they mature, it becomes flat, and sometimes even turns slightly inside out, showing narrow plates. In addition, saffron milk caps can be either very small or reach 20 cm in diameter.
Chanterelles
One of the most beautiful mushroom varieties grows mainly in the acidic soils of deciduous and mixed forests, having a bright yellow color and a funnel-shaped shape with frequent lamellar hymenophores.
Unlike moss mushrooms and many other varieties, the nutritional value of these small mushrooms is practically zero, but this does not prevent them from enjoying enormous popularity among connoisseurs of mushroom dishes.
Indeed, chanterelle is good both fried and baked, in omelettes, and in soups. Mushrooms love moisture, appearing immediately after the first September rains. But at the same time, they are almost never wormy, which is another pleasant bonus.
Note!
It is important to remember that the chanterelle has an inedible counterpart, differing from it in an uneven edge, paler color and a dense leg.
Honey mushrooms
There are several varieties of honey mushrooms, the fruiting of which occurs at different periods. Summer, autumn and even winter mushrooms can be found on forest stumps and trunks almost all year round, but it is the autumn fungi that thickly cover the wood that are especially valued.
The lifespan of such a mycelium usually ranges from 13 to 15 years, so experienced mushroom pickers try to collect honey mushrooms with their miniature cap and thin curved stem without a protective ring in the same places.
Sometimes from just one tree you can pick up a whole basket of excellent fruits. As for cooking, honey mushrooms make not only delicious soups and stews, but also wonderful marinades.
Russula
This bright, strong mushroom is called russula not because it can be eaten raw, but because of the speed of preparation, usually taking a few minutes. A strong, tall-looking variety with a wide, fleshy cap, in fact, it has very fragile pulp and a shell covered with thin mucus, which is easily removed during the cleaning process.
In addition, these mushrooms are adored by other forest dwellers, which is why they often turn out to be wormy. Russula also has false doubles, both inedible and poisonous. You can distinguish them from a good mushroom by their unnaturally bright red or crimson cap and perfect snow-white leg.
Butter
These small moss mushrooms, also often found in Russian forests, got their name because of the unpleasant thick mucous layer that completely covers the mushroom cap, which rarely exceeds 15 cm in diameter.
Interesting!
It is not possible to completely get rid of this mucus even after prolonged heat treatment, and it is this mucus that thickens the marinades most often used to prepare these glossy fungi.
Surprisingly, boletus from open clearings look more faded and unpresentable than their counterparts growing in the thick of the forest, which is a consequence of an excess of sunlight.
Umbrellas
Despite their unsightly appearance, umbrellas are considered a real delicacy, valued no less than porcini mushrooms. There are several varieties of umbrellas, both edible and not, which have different colors, starting with plain white and ending with dirty gray or beige with numerous dark scales and inclusions.
Young mushrooms have a spherical cap, which flattens out as it ages, becoming perfectly flat with a slight bulge in the middle. By maturity, the umbrella leg becomes unnaturally long and completely hollow inside.
Milk mushrooms
Salted milk mushrooms are one of the most popular appetizers at Russian feasts. Pies with these unusual squat funnel-shaped fungi with a subtle fruity aroma are also good.
The short stem of these white mushrooms often prevents them from breaking through to the surface through a thick layer of foliage and dead wood, which makes their search very difficult. If mushroom pickers are still lucky enough to collect full bodies of milk mushrooms, then they should not forget about cleaning their hard, fleecy skin.
Champignon
Champignons cannot be called purely autumn mushrooms, because they begin to appear quite early, some as early as May. However, almost all of their edible varieties bear fruit in September, and some species are found until mid-October.
In our area, I had the opportunity to observe these mushrooms in different places - along the banks of rivers, in forests and meadows, but only where cattle are regularly driven. In the city, on the lawn is a common thing. But the only place where we “collect” champignons is the grocery store.
What are the benefits of drying?
Mainly porcini, boletus, boletus and other tubular mushrooms are dried, as well as honey mushrooms. Other lamellar mushrooms are most often bitter and break easily. After clearing the mushrooms of debris, wipe them with a damp cloth. Well dried, they are soft to the touch, slightly springy, but do not break and without droplets of liquid when squeezed. Before they dry out, the mushrooms are moist and bend easily. And when they dry out, they harden, darken, and crumble - in this form they are suitable for mushroom powder (grind them in a coffee grinder, mix with salt, store in a glass container tightly closed).
Drying methods:
- in a Russian oven (in several stages);
- in the oven;
- over a hot stove;
- on air.
For 3-4 hours, the mushrooms (cap bottom down in one layer) are dried at 40-45 degrees, then at 60-75 degrees. dry with the door open. Whole (small) mushrooms are air-dried, strung so as not to touch on a strong thread or knitting needles. Larger ones are cut into 2-4 pieces (no thicker than 10 mm) or crushed into noodles. But it is better to dry mushrooms in 900-watt electric dryers. First, each tier is filled with mushrooms, then the temperature is set to 55 degrees for 3-5 hours. To speed up drying, you can swap trays.
Store dry autumn mushrooms in 2022, after cooling, in a dry, ventilated room (temperature optimum - 11-15 degrees) for no more than 1 year in jars (glass, tin), tied with gauze in 2 layers or tightly closed with a lid. Can be hung in bags made of thick white cotton fabric. Mushrooms are picked at 2-week intervals. If they are damp, they should be dried in the oven.
Volnushki
Photo 23. Pink wave. Author: Tocekas.
both types of our trumpets - pink and white - in the middle - second half of September, and I always observed mass fruiting.
Photo 24. White volnushka. Author: AfroBrazilian.
Pink waveweed was found in tall birch forests , white - in young pine-birch woodlands . Both mushrooms bear fruit from summer to early autumn , but the pink one appears earlier than the white one - from the third decade of June , while the white one begins to appear only in August . The mushrooms finish bearing fruit in September , but it seems that the white trumpet does this later than the pink one.
Mushroom picker's autumn calendar
Those who like to pick mushrooms should have a calendar and a gift guide. By comparing them with each other, it is easy to understand which mushroom can be found in a given period. As weather conditions change, each variety has its own growing season.
Autumn calendar.
- September is a good month as a variety of summer mushrooms continue to appear while the fall varieties are growing en masse. In the second half of the month there are honey mushrooms, volushushki, svinushki, boletus mushrooms, white cape.
- October - the second half of the month signals the end of the mushroom season; the calendar can be postponed until next year. After the 15th, the air temperature drops to 5 degrees, and frosts begin at night. Although you can still find young honey mushrooms that have been preserved under the leaves, as well as saffron milk caps, saffron mushrooms, and white mushrooms.
October is open for picking a lot of mushrooms. It all depends on the climatic conditions and area of growth. The main thing is to put only edible mushrooms in the basket.
Milk mushrooms
There are several types of milk mushrooms, and most of them are collected in late summer - early autumn. You can read more about these mushrooms here: “Where milk mushrooms grow: about forests, places and mushroom “habits”.”
However, among milk mushrooms there are varieties that can be found in the midst of autumn.
Yellow breast
In some places it is also called “spruce mushroom” - and is sometimes confused with the blue milk mushroom, which is very similar in color. A distinctive feature is the almost smooth edge of the cap; in the blue milk mushroom it is pubescent.
You can find yellow milk mushrooms in coniferous and mixed forests - under spruce or fir trees. He loves mountain forests - there (at least in our area) they collect quite a lot of it. Fruits from July to October .
Breast red-brown
He is also a “ underwood tree ”. It is notable for the fact that it smells like herring (or seafood - according to some authors), and this aroma changes over time: in young fruiting bodies it is quite pleasant, in old ones it is more reminiscent of stale or even completely spoiled fish.
It grows in deciduous forests - under oak and hazel (also, according to some information, it can enter into symbiosis with spruce). She loves damp places and is not shy about climbing mountains - up to a height of 1 km above sea level. It bears fruit from mid-July to early October , in small groups.
Poplar milk mushroom
He is also an aspen mushroom . Somewhat similar to wavefish, in particular to whitefish, but smoother and larger.
Prefers to enter into symbiosis with poplars, aspen and even willow. Heat-loving, it is most collected in the southern regions, in particular in the Lower Volga region. Fruits from mid-July to early October .
Hairy breast
He is also a fringed milk mushroom . It is notable for the noticeable fringe along the edge of the cap, which sometimes hangs down as much as a centimeter. It is also famous for its very caustic milky juice, which is why the mushroom is considered inedible in some countries. Rumor has it that you can get rid of this inconvenience by soaking it and then boiling it.
Prefers deciduous forests, where it can be found under oak, beech, hornbeam, hazel, and even birch trees. Fruits from July to October .
Harm and precautions
But despite all the benefits they bring to the human body, there are still certain restrictions and culture of their consumption:
- For people suffering from gastrointestinal problems, eating mushrooms should be limited or eliminated completely. They are difficult for digestion due to the chitin they contain, and they weigh down dishes.
- Small children and pregnant women should not eat this product. Pregnant women may experience allergic reactions.
- It is better to combine mushrooms with potatoes, vegetable salads, porridge or bread to improve digestion. Consuming it with meat will make the food heavy on the liver and slow down digestion.
- Alcohol with mushroom dishes will “thicken” the protein in the stomach, which will complicate the process of digesting food. As a result, you may experience sensations similar to poisoning.
Saffron milk caps
There are about a dozen varieties of saffron milk caps, and almost all of these mushrooms grow in the fall, most of them also appear in the summer. A separate article is devoted to all of them: “Where saffron milk caps grow: forests, places and times of collection.” Here, as an example, I will consider a typical species, the most widespread and popular among mushroom pickers.
The saffron milk cap is real
An autumn-summer mushroom that forms mycorrhiza with pine and loves young forests. It is found both in June and October , including before the appearance of stable snow cover. But camelina bears fruit en masse in mid-summer , and especially in early autumn .
Mushroom places in the country
Autumn mushrooms are collected in many areas of the country.
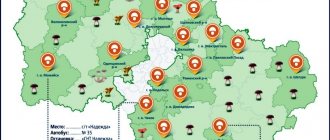
Places near Moscow
Boletuses, chanterelles, and boletus grow along the Savelovsky direction. It covers areas around Ozeretskoye, Fedoskino, Sholokhov.
In the Kazan direction, around the Chernaya station there is a pine forest. It is not recommended to collect boletus and chanterelles here: they absorb toxic compounds and heavy metal salts from the environment.
Along the Leningrad direction in the areas of Firsanovka, Nazaryevo, the village of Elino, Leningradskoye Highway, there is a mixed forest. Honey mushrooms, porcini mushrooms, and saffron milk caps grow in it. At the beginning and end of October, mushrooms have different yields.
Orenburg direction
The Orenburg region is rich in mushrooms
Many edible species grow in Orenburg and the region. Mushrooms of this direction can be collected from the end of October until November. This:
- White mushroom;
- saffron milk caps;
- milk mushrooms;
- boletus;
- honey mushrooms;
- boletus;
- chanterelles;
- Champignon;
- oyster mushrooms
Tambov Region
In the Tambov region there are forests rich in berries, medicinal herbs and mushrooms. In autumn these places abound with different types of mushrooms; here you can find:
- boletus;
- goats;
- White mushrooms;
- flywheels;
- boletus;
- boletus;
- milk mushrooms;
- chanterelles;
- Polish mushrooms;
- saffron milk caps;
- poplar rows;
- honey mushrooms;
- Russula.
Voronezh region
The following edible mushrooms will grow in the Voronezh region in October:
- oyster mushroom;
- talker;
- oakwood;
- winter mushroom (Flammulina velvetypodia);
- milk mushroom;
- wave;
- White mushroom;
- chestnut mushroom;
- fox;
- honey fungus;
- May mushroom;
- oiler;
- flywheel;
- boletus;
- boletus;
- champignon;
- saffron milk cap
Crimea
Crimea in autumn is rich in edible species. On the peninsula in October you can find:
- chanterelles;
- saffron milk caps;
- mountain white mushroom (giant talker);
- “little mice” or gray rows;
- raincoats;
- boletus.
Chanterelles
These mushrooms, remarkable for their canary-like appearance, grow quite steadily in the fall and can now bear fruit no less en masse than in the summer. The same can be said about other varieties of chanterelles, of which not all have a yellow-orange color. A separate article is devoted to all of them: “Chanterelles: varieties, places and times of collection,” so I see no point in considering them here, except perhaps for the most famous chanterelle.
Common chanterelle
Photo 30. Chanterelles are typical summer mushrooms; they grow in smaller quantities in the fall, but at times they grow very harmoniously.
It is found everywhere in coniferous and mixed forests, enters into symbiosis with various types of trees, especially with pine , spruce , oak , and beech . The fruiting season is from early June to October , but these mushrooms usually appear most abundantly closer to July and in September.
Application
Traditional and official medicine uses them to create medicines and treat various diseases. Mushrooms have not been fully studied by scientists. They are considered a separate kingdom, which received its name - Mushrooms and is located systematically between plants and animals, because they have characteristics of both. Some experts think that underground mycelium covers the entire globe, while others are sure that they are an extraterrestrial life form. The work on studying the properties does not stop. Many are used to obtain active antimicrobial drugs and antibiotics.
The antibiotic lactarioviline was obtained from camelina, and mycomecitin was obtained from govorushka. Anthelmintics are made from chanterelles. Extracts from some of the cap mushrooms treat staphylococcus and blood poisoning.
Honey fungus is used to combat intestinal and thyroid problems.
Honey mushrooms
There are several varieties of honey mushrooms (namely real honey mushrooms, and not other representatives of the mushroom kingdom that are similar to them). Some of them begin to bear fruit in August, and summer honey fungus, for example, can even appear in the spring, but all honey mushrooms have one thing in common - these mushrooms grow in the fall, and it is during this period that many of them experience the most massive fruiting. We have dedicated a separate article to honey mushrooms: “Honey mushrooms: summer, autumn, winter and others.” Here I will mention the autumn honey fungus - the most widespread and popular among mushroom pickers.
Autumn honey fungus
It is found in many forests - on stumps, at the base of trees, on their roots and butt, on all kinds of woody remains - always in clusters of several pieces. It appears in August and continues to be found in the forest until November , and when the autumn is warm - even until December . The most massive fruiting is observed in August-September, in separate three “layers” - as knowledgeable mushroom pickers say.
What edible mushrooms grow in the fall, at the beginning and end of November: photos, list, names
In November it is already quite cold and out of all the summer abundance, very few mushrooms are found. These are mainly resistant varieties that grow on tree trunks or stumps. Because there is frost on the ground surface. Usually, the mushroom season ends with the first snow. Occasionally you can see oyster mushrooms on the trunks.
List of November mushrooms:
- greenfinch
- Honey mushrooms
- Oyster mushrooms
- Gray row
greenfinch
Honey mushrooms Oyster mushrooms
Greenfinch
It is also a row of green , yellow or lemon . Cinderellas are typical autumn mushrooms that bear fruit until the very first light frosts - when other edible mushrooms are no longer available. It happens that greenflies are collected from under the snow.
Mycorrhiza forms with coniferous trees, mainly with pine trees. Prefers to grow on sandy or sandy loam soils. It appears most abundantly in forests from September to November .
Lately there has been talk around the greenfinch about its toxicity. European researchers claim that it can be poisoned, especially if you eat a large amount of mushrooms. In our country, this mushroom has been considered edible for centuries, however, experts strongly recommend consuming greenfinch only after pre-treatment (boiling) and in moderate quantities.
Rules for collection and use
Each species has its own location: under trees, on forest edges or on stumps. You should not neglect the rules of collection, because if you do not follow them, it is easy to get poisoned even by edible mushrooms.
These organisms accumulate toxins if they grow near the road. Do not place damaged, “rotten” mushrooms next to healthy ones. You should not collect them in plastic bags, from which forest organisms will absorb chemical compounds that are harmful to humans, especially released by artificial materials in hot weather. In addition, in such a package they will suffocate within a few hours of your journey through the forest.
It is best to collect mushrooms away from the highways, in proven and familiar places. They need to be placed in wicker baskets made of natural materials, immediately selecting the good ones, and throwing away the rotten and wormy ones without pity.
Before cooking, the fruiting bodies should be sorted again and then soaked. After frying or boiling, eat immediately, do not store in the refrigerator for several days, and do not reheat on the stove several times. They serve as a good environment for the growth of bacteria when stored in finished form.