Bashkiria is quite rich in various types of mushrooms. Fans of “quiet hunting” in this region can thoroughly enjoy collecting milk mushrooms, honey mushrooms, chanterelles, boletus and boletus.
- Borovik
- Ryzhik
- Death cap
When does the mushroom season begin in Bashkiria?
The mushroom season in Bashkiria, as in most other regions, begins from the moment the snow melts and continues until the onset of a steady cold snap. From spring to autumn, you can collect various types of mushrooms in the forest.
To better understand how and when to collect, you should use the mushroom picker’s calendar. Depending on the time of year, it indicates the approximate timing of the appearance of certain species. But first things first, let’s get acquainted with the mushroom places of this region.
The mushroom season in Bashkiria, as in most other regions, begins from the moment the snow melts and continues until the onset of steady cooling
Real milk mushroom
A cunning mushroom of impressive size that can easily camouflage itself under a layer of fallen leaves. Most often it grows in coniferous and birch forests. There are several types of milk mushrooms, each of which is valued in its own way:
- Yellow milk mushroom. Of all the milk mushrooms, it is the easiest to notice. The cap of young mushrooms has a convex shape, but straightens over time. It is smooth to the touch, but can become slimy when it rains. It has a bright brown or golden color. The leg is hollow, but at the same time strong, sticky, bright yellow. There are characteristic notches on the entire surface of the leg.
- Pepper mushroom. Dense and fleshy cap, whitish in color, velvety. The leg is very dense, solid, and can be smooth or slightly wrinkled. This mushroom is classified as conditionally edible, but before eating, many mushroom pickers recommend soaking it well or even boiling it.
- Bitter mushroom. This mushroom is slightly smaller than its counterparts, so it is a little more difficult to find. Over time, the flat cap straightens and a small tubercle forms in the center. As a rule, the cap is brown or reddish in color. The leg is thin, cylindrical in shape. Covered with light down, a thickening of the leg can be seen at the base. It is strictly forbidden to collect such mushrooms in areas of increased radioactive contamination, since they are capable of accumulating harmful substances.
- Red-brown milk mushroom. The cap is matte, at first round, and over time it acquires a depressed shape. Typically light brown in color. The leg is quite strong, velvety, and has the shape of a cylinder. The color usually does not differ from the color of the cap. This milk mushroom is very tasty when fried and salted.
- A real milk mushroom. “King” of all milk mushrooms. The cap of young specimens is flat, but over time it can take the shape of a funnel. Typically white or yellowish in color. The edges of the cap are curved on the inside. The stem is hollow, cylindrical in shape, and usually does not differ in color from the cap. This mushroom is truly impressive in size, but it can be overlooked due to the adhesion of plant debris.
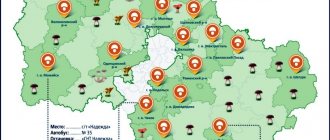
Mushroom places in Bashkiria
Bashkiria is a paradise for real mushroom pickers. Its territory is quite vast and includes 5 different climatic zones. Therefore, the range in species is quite huge. For example, if you need milk mushrooms, you should go to the village of Osorgino, well known to local residents.
Boletus mushrooms grow in abundance on the territory of the Chishminsky district. Askarovo is famous for various types of mushrooms. There are enough mushrooms on the territory of Bashkiria, but when choosing a particular place for collection, you must be guided by the following rules:
- Do not pick mushrooms along busy roads and highways.
- Do not use areas near populated areas for collection.
- The deeper into the forest, the better.
Volnushka (volnyanka)
Popularly called Volyanka. This specimen is quite common, but is most often found in mixed and birch forests. There are two types:
- The wave is white. A convex hat with rolled edges, white. The leg has the shape of a cylinder that tapers at the base.
- Pink wave. The cap can be convex, but sometimes it is completely flat. The leg is cylindrical, hard and strong.
An oil can is very similar to a wave. It is difficult to confuse it with others because it has a very slimy skin, which is covered as if with vegetable oil. The cap (olive or brown) of a young oiler has the shape of a hemisphere, but over time it becomes prostrate. Only sometimes the edges of the cap are raised. The leg is straight, solid and fibrous, cylindrical in shape. It has a slightly lighter color than the cap. Grows next to trees in almost all types of forests. Almost never found in mountainous and rocky areas.
Gallery: mushrooms of Bashkiria (25 photos)
Description of edible mushrooms in Bashkiria
There are quite a lot of edible mushrooms on the territory of Bashkiria. The most popular and common ones are described below.
Spring
Traditionally, the mushroom season in Bashkiria begins with the first spring mushrooms. After a long winter, they are the most desirable and long-awaited for lovers of quiet hunting.
Also read: Edible, poisonous and inedible mushrooms of the Moscow region in June
Common morel
A widespread species growing in mixed deciduous forests. It is characterized by an egg-shaped cap and a hollow, fragile stem. The surface of the cap consists of irregularly shaped cells. The pulp has a pleasant smell and taste.
Common morel
Morel cap
It grows in deciduous forests; especially large concentrations of this mushroom can be found in birch or aspen forests. The period of mass fruiting occurs at the end of April - beginning of May. Characterized by a sinuous, irregularly shaped cap. Can be eaten without prior heat treatment.
Line
Conditionally edible mushroom. Requires pre-boiling before cooking. It has a shapeless winding cap and a short stem. The inside of the cap is hollow; if you cut it lengthwise, you can see a hollow space with numerous folds. The pulp of Stok is fragile, waxy with a characteristic smell of dampness.
Line
Summer
After warm thunderstorms, summer mushrooms begin to appear en masse.
Borovik
Considered the “king of mushrooms”. Mentions of it can even be found in ancient Russian fairy tales. Valued for its excellent taste and unique aroma. Prefers to grow on the edges of birch forests and along forest paths. Usually there are whole groups of these mushrooms; individually, the porcini mushroom practically does not grow. It is characterized by a wide dark brown cap and a massive stem.
Chanterelle
Massively growing mushrooms that actively begin to develop after warm summer rains. The main harvest of chanterelles occurs at the end of summer. They prefer to grow in mixed birch forests . The fungus is quite light-loving, so its main accumulations are in forest edges, roadside areas and clearings.
Chanterelle is one of the few fungi that does not produce worms or accumulate harmful substances. These mushrooms also have a peculiar chanterelle smell. Their caps at a young age are round and slightly convex; at an older age they become funnel-shaped.
Chanterelle
boletus
Popularly also known as obabok. Mass fruiting occurs in the first half of June. It is characterized by a thin stalk, which becomes quite hard and fibrous in old age, and a brownish-brown cap. The mushroom has the ability to age very quickly. Young boletus mushrooms are best suited for culinary processing. They can be fried, pickled or dried.
Also read: Spring edible and poisonous mushrooms of Ukraine
Boletus
Also known as redhead. Boletus is one of the most productive tubular mushrooms. Its fruiting lasts from June to October. A distinctive feature of boletus is its dense flesh, which turns blue when cut. This mushroom is characterized by a round cap of rich orange color and a stalk with gray scales. Most often it can be found in young aspen growth or in deciduous small forests.
What mushrooms can be found in the forests of Bashkiria (video)
Autumn
Autumn is a busy time for mushroom pickers. A walk in the forest at this time leaves the most pleasant impressions. Pesky mosquitoes disappear in the forest, and the summer heat subsides.
Ryzhik
Camelina is considered the royal mushroom. Raw lightly salted saffron milk caps are a real delicacy. This mushroom grows in pine plantings and mixed coniferous forests. Moisture is very moist for its development, so mass fruiting begins only after heavy autumn rains.
The saffron milk cap is characterized by a rounded cap of rich orange color . When the fruiting body is broken, the milky juice of saffron milk caps turns green very quickly.
Oiler
A massive mushroom, the first wave of fruiting occurs in July. But you can collect especially a lot of oil in early September. Prefers to grow on the edges and in young pine plantings. You can distinguish it by the characteristic sticky skin on the cap.
Oiler
Honey fungus
One of the most favorite autumn mushrooms. It grows in huge groups on stumps, fallen and dead trees. Young specimens with caps that have not yet unfolded are especially valuable. The color of the mushroom caps varies from light brown to darker with an obligatory black center. The purpose of honey mushrooms is universal; they are equally suitable for pickling, frying or drying.
Real milk mushroom
Milk mushrooms are traditional mushrooms for pickling. When their cap is broken, milky juice is released. Due to its constant wet cap, it is also called a wet milk mushroom. In air, its milky juice turns yellow very quickly. It is a mycorrhizal species, therefore it mainly grows in birch and mixed with birch forests. Characterized by a rounded cream-colored cap and a hollow stem. Along the edge of the cap there is a kind of fringe of yellowish fibers.
Also read: Beautiful and tasty: how to properly collect and prepare russula
Real milk mushroom
Common morel
This mushroom is found in forests of various types. It is not picky, so it can grow on almost any soil, even sandy ones. These mushrooms can be found most often on the edges of forests, as well as along roads. In addition to food, they are also used in medicine. Different morels look different:
- Common morel. The cap resembles an egg, is divided into cells, hollow, brown or ocher in color. The leg is very brittle, also hollow, smooth.
- Morel hat. The cap is bell-shaped with a wrinkled surface, brown or bright yellow. The leg is thin, tall, cream-colored (can be pure white).
- The morel is conical. The cap has a characteristic cone shape with a ribbed surface and is olive, brown, and often brown in color. The leg is fragile, hollow, white.
Inedible and poisonous mushrooms of Bashkiria
In addition to edible species, poisonous mushrooms also grow on the territory of Bashkiria. Very often, the excitement of mushroom pickers is so great that, out of ignorance, even unfamiliar species are sent into the basket. Some of them can be deadly poisonous.
Death cap
A deadly poisonous species, only a quarter of its cap can kill a healthy adult. Its main distinguishing feature is a characteristic pouch at the base of the leg. It grows almost everywhere, but it can be especially often found in mixed forests. The pale toadstool can also be identified by a peculiar blanket around the leg, which breaks as it grows .
fly agaric
Red fly agaric is one of the most common poisonous mushrooms. Prefers mixed birch forests, where it can be found in fairly large groups. Fatal cases of poisoning by it are quite rare , but it can still cause significant harm to health. Very often, a medicinal tincture is prepared from fly agarics.
fly agaric
Polypore (chaga)
A parasitic fungus that grows on trees, mainly in deciduous forests. But even among such parasites there are those that can be safely eaten. But there are only 2 types:
Having a whole closet of so much beloved shoes, you have to walk around in shapeless moccasins and trampled ballet flats. And it's all about the protruding bones on the feet, which bring simply unbearable pain in general in any shoes. If you wear slightly thicker shoes than moccasins, a size too large, the inflammation will last for several more days. How to deal with bunions, read our material.
- Sulfur-yellow tinder fungus. It itself is flat-rounded and has a yellowish tint. The leg is very dense and instantly woody.
- Variegated tinder fungus. Saddle-shaped, with brown scales over the entire surface. The leg is shortened and thick, dense, dark brown in color at the base.
Important rules for quiet hunting
In order for the collection to bring only positive emotions and not end with a visit to the doctor during a “silent hunt”, the following rules must be followed:
- If there is even the slightest doubt about the species of a mushroom, it is better to get rid of it immediately. Before collecting, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with the most common poisonous species.
- It is advisable to take a compass and map with you into the forest, especially if you are going to an unfamiliar place. You should not rely on a GPS navigator alone. Its battery can run out at the most inopportune moment.
- Mushrooms have the ability to accumulate heavy metals and various toxic compounds, so under no circumstances should they be collected along busy highways and large industrial facilities.
- Before going to the forest, you should notify your relatives about where you will be and the approximate time of return.
How to distinguish edible species
Mushrooms are not only tasty, but also very healthy food. They contain substances such as salts, glycogen, carbohydrates, as well as vitamins of groups A, B, C, D. If the mushrooms are young, then they also contain many microelements: calcium, zinc, iron, iodine. Their intake has a beneficial effect on the body's metabolic processes, increasing appetite, functioning of the nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
In fact, there are no exact criteria by which one can distinguish safe mushrooms from poisonous ones. Only existing knowledge about the appearance, characteristics and names of each species can help in this matter.
Characteristics of edible mushrooms
General criteria for edible mushrooms include:
- No sharp bitter smell or taste;
- They are not characterized by very bright and catchy colors;
- Typically the inner flesh is light in color;
- Most often they do not have a ring on the stem.
But all these signs are only averaged, and may have exceptions. For example, one of the most poisonous representatives, the white toadstool, also has no pungent odor at all and its flesh is light.
Another important point in this matter is the growing area. Typically, edible species grow far away from their dangerous counterparts. Therefore, a proven harvest location can significantly reduce the risk of encountering poisonous mushrooms.
Common Misconceptions
There are many popular signs and non-standard ways of determining the safety of mushrooms. Here are the most common misconceptions:
- Silver spoon. It is believed that it should darken upon contact with an inedible mushroom;
- Onion and garlic. They are added to the mushroom broth and if they darken, it means there is a poisonous species in the pan. It is not true;
- Milk. Some people believe that when a mushroom that is dangerous to humans is placed in milk, it will definitely turn sour. Another myth;
- Worms and larvae. If they eat certain types of mushrooms, then they are edible. But in fact, some species edible by worms can harm human health.