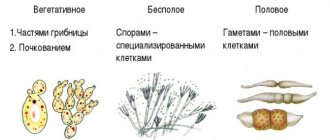
Mushrooms
0
1587
Article rating
Kira Stoletova
When going to the forest, people should know the rules for collecting mushrooms, their shelf life, appearance and taste. This harvesting guide will be useful for both experienced mushroom pickers and beginners who need to know how to pick mushrooms correctly.
Rules for collecting mushrooms
Rules for picking mushrooms for children
1. Collect only those mushrooms in the forest that you know for sure are edible.
2. Never eat or taste mushrooms that you do not know or that are in doubt.
3. Never collect or eat those mushrooms that have a tuberous thickening at the base of the stem, surrounded by a shell (such as the red fly agaric), and do not taste them.
4. When picking mushrooms, especially russula, try to take them with a whole stalk, so as not to lose sight of the important feature indicated in the previous rule.
5. If you collect champignons in the forest, which are called pecheritsa in some places, pay special attention to the color of the plates located on the lower surface of the cap.
Never collect or eat “champignons” that have white plates. In real edible champignons, the plates quickly turn pink and then darken.
The deadly poisonous pale toadstool, similar in appearance to a champignon, has always white plates.
6. If you collect mushrooms, nigella, white mushrooms, milk mushrooms, podgruzdi and other mushrooms containing milky juice for pickling, be sure to boil or soak them before salting in order to extract bitter substances that irritate the stomach.
The same should be done with valuy and russula, which have a caustic and bitter taste, as well as with pigs.
7. When collecting strings and morels, you must always remember the need to neutralize them before cooking. These mushrooms should first be boiled for 7-10 minutes in water; Be sure to throw away the decoction containing the poison. After this treatment, the stitches and morels can be boiled or fried.
8. Never collect or eat mushrooms that are overripe, slimy, flabby, wormy or spoiled.
Don't eat mushrooms raw.
10. Mushrooms brought home should be sorted into individual types on the same day and carefully examined again. All questionable, as well as overripe, flabby and wormy mushrooms should be thrown away. The lower part of the legs, contaminated with soil, is cut off and the mushrooms are thoroughly washed to remove sand and debris. For some mushrooms (butter mushrooms and mokrukhs), the film covered with mucus is removed from the cap.
Mushrooms must be cooked on the day of collection or no later than the next morning.
Rules for collecting mushrooms: 1. Collect only those mushrooms that are familiar to you and which you can definitely distinguish from poisonous ones. 2. Do not collect old, wormy ones that have absorbed water after long rains and are covered with mold. 3. Carefully inspect the mushrooms before adding them to the basket. 4. Remember that even the best and, of course, edible mushroom, if it is overripe, begins to rot, or has been left untreated for a long time, can become poisonous.
The shelf life of fresh mushrooms should not exceed 18-24 hours at a temperature not exceeding +10 degrees. 5. Do not collect mushrooms that appeared after the first frost. 6. Do not pick mushrooms along roads or near industrial enterprises: they accumulate heavy metals and radioactive substances in their fruiting bodies that are hazardous to health. 7. Do not use plastic bags or other plastic containers that do not allow air to pass through to collect mushrooms. 8. At the first signs of poisoning, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Before he arrives, you need to drink a lot of warm water and induce vomiting.
Any avid mushroom picker will say that “silent” hunting is a great pleasure, and not just an opportunity to replenish household supplies.
Of course, it’s nice to leisurely wander through the morning forest in search of caps shining with dew hidden under the trees, blades of grass and leaves.
However, we must not forget that mushrooms can be not only edible, but also poisonous, so you need to collect them very carefully so that when you bring them home, they will only benefit you.
Mushrooms and forests - they go together
Three types of mushrooms live in the forests of Russia:
- Saprophytic fungi destroy (rot) dead plants. These fungi are essential for the recycling of nutrients in the forest. Morels are believed to be saprophytic mushrooms.
- Parasitic fungi attack living plants, causing disease and death of forest organisms.
- Mycorrhizal fungi coexist with forest trees. The mycelium of the fungus, together with the roots of the trees, forms mycorrhiza (fungus root). This network of roots and mycelium increases the surface area through which trees can absorb water and nutrients. The mycelium, in turn, receives nutrition from the tree. Both trees and mushrooms depend on this partnership for survival. Chanterelle is an example of mycorrhizal fungi. The pine fungus is suspected to be mycorrhizal, but further research is needed to confirm this.
Rules for collecting mushrooms
Here are some useful tips and recommendations that will be useful even for an experienced mushroom picker.
It is best to go to the forest before full sunrise, i.e. around 6 am. Firstly, the sun will not blind you, and secondly, the dew that has not dried on the caps will make them more noticeable.
It is best to collect mushrooms in a basket woven from willow twigs or birch bark.
Take a small handy knife with you. You should also take care of protection from mosquitoes and ticks. For collection, do not choose places near industrial enterprises, roads and railways.
The basic principle that should be followed while hunting is “If you’re not sure, don’t take it!”
Never test the edibility of a mushroom!
It's best to leave it in the forest if you're not sure it's edible. Also, you should not take obviously old or wormy copies, or those left by other people.
Quite often people become victims of so-called false mushrooms.
They look edible in appearance. If the base of the leg has a thickening surrounded by fringe rings, then this is a sign of toxicity. False honey mushrooms, so often mistaken for real edible mushrooms, have a very thin stem without velvety rings. They are also much smaller than real mushrooms. There is no slippery film on the cap and no scales.
There are two ways to collect mushrooms: cut or twist. Both methods are acceptable for preserving mycelium. Thus, tubular species (boletus, boletus, boletus), growing singly, are better to be carefully twisted out.
If they grow in families, then in order not to damage the mycelium you need to cut them off at ground level. The mushrooms, saffron milk caps, and milk mushrooms have very thin and fragile stems, so it is better to cut them off with a knife.
In any case, you need to cut or unscrew it very, very carefully.
The preserved mycelium will delight you with a new harvest in the same place. That’s why true lovers of “quiet” hunting hide their “fishing” spots so carefully in order to return there again and again for a full basket.
As soon as you return home from the forest, immediately sort and clean the mushrooms. Those that contain milky juice (volnushki, milk mushrooms) should be soaked before cooking - then they will not taste bitter.
However, it is better not to take them for drying. Freshly collected and peeled caps and legs should be cooked for at least an hour over moderate heat.
When they settle to the bottom, it means they are ready. Any foam that forms should be skimmed off. You can change the water once.
For freezing fresh mushrooms, only a freezer with a quick deep freezing system is suitable. They can be stored in a regular refrigerator for no more than three days!
Remember and follow these simple recommendations, and mushroom hunting will bring you both a great mood and the opportunity to please yourself and your loved ones with freshly prepared and stored “forest” meat for future use.
Mushroom picking. Time and place for collecting mushrooms. Rules for collecting mushrooms. Mushroom season
Mushroom picking has long been popularly called mushroom hunting or silent hunting. And this is not at all surprising, because you still need to be able to find a healthy mushroom - large, fresh, strong.
In a quiet hunt, not only information about edible/poisonous mushrooms is important, but also knowledge about the rules of collection. There are plenty of tricks in a quiet hunt!
The mushroom picker's shoes and clothing should in no way restrict movement, since mushroom picking involves constant moving from place to place..
Due to incorrectly selected shoes, your feet can suffer greatly: it is best to give preference to sports shoes or any worn-in shoes. To avoid chafing your feet, you should choose cotton or wool socks (depending on weather conditions). It would not be superfluous to provide additional protection from rain and wind. Mushroom hunting is often carried out in large forest areas. For such trips, it is advisable to have matches, a knife, a whistle, a compass, paper and a pencil with you.
But when picking mushrooms, the forest itself requires special attention .
It is necessary not only to carefully search for the object of collection, but also to vigilantly monitor the surroundings and the road under your feet, as there is a risk of tripping over brushwood and roots overgrown with grass, falling into a hole, or getting caught on a sharp branch, because mushrooms grow in thick grass.
An indispensable companion for any mushroom picker will be a basket made of willow, bast or birch bark.
Under no circumstances should they be replaced with a backpack, a plastic bag, a bucket or other container in which the mushrooms can become wrinkled - picking mushrooms requires care.
It is very important not to damage the integrity of the mycelium, so the collection object is cut with a knife so that the lower end of the leg remains in the ground, which is subsequently sprinkled with earth and compacted. This will prevent you from losing yield in the next mushroom season.
How to pick mushrooms like a pro
Have you noticed your friends posting pictures of mushroom caps, straw baskets and rubber boots on Instagram? Yes, mushroom season has arrived, and its devotees are happy to tell others about it. If you are bored indoors, you can easily join the crowd of collectors, this will help you avoid the mistakes of a novice collector.
Forget about summer shoes
Having the right clothes and equipment is half the battle. If you don't, nature might just get the best of you. Be sure to bring waterproof shoes, a hat, a basket or bucket, a knife for cutting mushroom stems, drinking water and a long stick. It is also recommended to wear trousers if you encounter nettles or biting insects. Also bring a light jacket.
“Everything should be easy. You'll likely have to walk several kilometers, and the worst part will be sweating under layers of clothing. You'll need a hat to protect you from cobwebs, bugs, and other nasties that fall from trees. Remember, all this will not protect you from the tick - it will always find a way if it wants to bite you. Boots are a must because if you step on a snake, they will be your only salvation from being bitten. You'll need a stick to clear all those leaves around the mushrooms, instead of putting your hand in the dark."
Don't choose the wrong varieties of mushrooms
Almost all mushrooms have an inedible counterpart that is poisonous to humans. A “false” mushroom will grow where a real one is unlikely to grow, but they look similar in appearance. The edible stem of red-capped garlic (leccinum aurantiacum) will quickly turn blue and look "like it's been covered in ink" after its stem is cut. The fake one will retain its pinkish tint.
All my life I had no idea that foxes had a doppelgänger. And many people don't know this. Edible chanterelles are richly colored and, most importantly, when turned over, their gills hang down like stalactites in a cave. And first of all, it was necessary to remember that chanterelles, as a rule, do not like spruce forests.”
“It’s better not to pick a mushroom if you don’t know what it is. Or you can cut a small piece and put it on your tongue. The false mushroom will taste bitter and burn your tongue. However, do not swallow the saliva. . ”
What to do if you encounter a wild animal
It is better to immediately head in the opposite direction if you accidentally stumble upon a wild animal in the forest. To avoid the boar, do this:
“You should not run away, but smoothly move away from the boar. Female boars can be very aggressive - they can bite through human bones as easily as we can break a match. Don't look them in the eye.
And you can’t come closer than 30-40 meters to the elk. One day I came across one - a young animal two meters tall. He started snorting in my direction. Horrifying scene. You should get away from the moose by walking backwards as quickly as possible.”
Mushroom picking time
You need to start picking mushrooms early in the morning in order to catch them before they heat up under the sun.
This will allow them to be stored for a longer time. If mushrooms heated by the sun are spread over the surface in a thick layer, they will quickly deteriorate - they will become covered with mucus and begin to emit an unpleasant odor.
It is a mistake to assume that mushrooms grow in the forest only in autumn. Already from mid-May you can collect morels, in July - russula, and in early August - boletus, milk mushrooms, boletus and boletus.
Beginning in September, boletus mushrooms, moss mushrooms and honey mushrooms appear. But a dry June foreshadows a mushroom-free July.
Mushroom season
All mushrooms grow in “layers” or “waves”. From mid-May, the first spring mushrooms of the year begin to appear. In July, in the last ten days, in the forests where birches are found, you can collect veils, which are well known as constant companions of porcini mushrooms; in small-leaved and relatively light-colored ones - pigs, in broad-leaved ones - pepper mushrooms and podgrudki.
The harvest of porcini mushrooms in July is not rich, since their layer is waiting for its time.
During the summer in central Russia there are approximately three to four layers of mushrooms, with August being the main mushroom month.
At this time, all July varieties begin to actively bear fruit, and in addition to them are added the most valuable, new ones - boletus, aspen boletus, saffron milk caps and boletus mushrooms.
The white wave is the first herald of the approaching autumn. Therefore, in part, September and August in general are the time when you can actively begin quiet hunting.
At what age can children eat mushrooms?
Pediatricians do not recommend giving mushrooms collected in the forest to children under 7 years of age. Some doctors insist that mushrooms are not recommended for children under 14 years of age.
In addition to possible poisoning, the reason is that the child’s gastrointestinal tract is not able to digest all the substances contained in mushrooms, and especially chitin, which is sometimes difficult for even an adult body to cope with. This means that this can lead to severe digestive disorders. Moreover, children should not be given mushrooms in any baby food or in any form, be it mushroom soup or pies with them.
But cultivated mushrooms, for example, champignons and hangers, can be given to children in various dishes, starting from 3 years old.
In addition, please note who should also not eat mushrooms:
- for allergy sufferers
- people with severe dysbiosis
- pregnant women
- To old people
- people with diseases of the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
Mushroom picking places
The most mushroom places are traditionally considered to be light deciduous groves - birch, aspen, etc.
Porcini mushrooms can be found near anthills and fly agarics. It should also be remembered that in dry summers the mushroom grows as close to the trunk as possible, and in damp summers it grows away from it.
Most of them grow to the north of the tree, to the west and east there are slightly fewer of them, and on the south side of the trunk they are generally extremely rare.
When picking mushrooms, you need to remember that excessive caution will not hurt in this matter.
You should not take an unknown mushroom or try a well-known one. Based on the same precaution, it is best to give preference to a young harvest, since the old one tends to accumulate toxic substances: pickling, salting and drying require exclusively whole and strong mushrooms.
For greater convenience, the search can be carried out using a stick, reaching a length of about 1 meter, with a spear located at the end.
Mushrooms, especially tubular ones, are placed in a basket so that their caps are facing upwards, and small mushrooms are left whole, while the cap of large ones is cut off and placed next to the stem.
Once a mushroom is found, it must be cleared of debris and soil - this will make working at home much easier. In the forest you need to behave calmly and not rush from tree to tree: quiet hunting requires special concentration, attention and patience.
Often where one mushroom grows, many others can be found. But do not forget about the danger of poisonous mushrooms.
Collected mushrooms should not be stored for too long (more than 2-3 hours). This is due to the increased moisture content (about 89-92 percent). The unprocessed harvest is stored in the refrigerator or cellar. If there are none, any cool place will do.
Most mushrooms, including russula and lamellar mushrooms, must be cut off only with the stem. This is done in order to make sure that there is no special membranous ring, which is characteristic of some poisonous mushrooms that are similar in appearance to russula - for example, toadstool, which is considered the most dangerous.
One fourth of her hat is enough to kill her from poisoning.
Before pickling, such mushrooms as conditionally edible ones are placed in a large enamel pan and filled with cool water. The latter helps remove milky juice and bitterness from the fruit.
Aluminum and galvanized utensils should never come into contact with mushrooms. Immediately after delivery from the forest, the mushrooms must be sorted. If this is not possible, then they are doused with salted boiling water. This prolongs their life by a day.
It is important not only to collect...
Advice to mushroom pickers from experienced “hunters” includes processing the harvest. The main recommendations are:
- Upon arrival home, the “catch” must be sorted by type and sorted by quality. “Illiquid” is mercilessly thrown away.
- The bottom of the stem with the ingrained soil is cut off, and the mucous film is removed from the cap.
- Mushroom dishes are prepared, as well as stored, only in non-metallic containers. Pots - only enamel, containers - porcelain or glass, plastic should be avoided.
- Prepared mushrooms should be kept exclusively in the cold. Several hours spent on the table, especially in the heat, can trigger the formation of toxins.
- Mushrooms with milky juice (nigella, milk mushrooms, white mushrooms, white mushrooms) are soaked or boiled before salting.
- Before any cooking, morels are boiled for at least 7 minutes; The broth must be poured out and not used for any dishes.
And one more important note that you need to know about mushrooms: some varieties cannot be used as a snack because they are not compatible with alcohol.
Rules for safe mushroom picking
The forest, as you know, is our wealth. Therefore, natural resources must be treated with care.
So, for example, when coming to the forest to pick mushrooms, you should follow certain rules for collecting them. Below are some recommendations.
Before giving the rules for collecting edible mushrooms, it is worth noting some points that precede a trip to nature. It is better to go to the forest when warm days and nights come after heavy rains.
This has a very beneficial effect on the harvest. You need to go to the forest early in the morning. Of course, there are people who believe that everyone will get mushrooms. This is partly true, but only when places are known where no one has ever been. When going for mushrooms, you need to dress well. You should put on thick trousers and high boots or boots on your feet, and a sweater and a thick jacket on top.
First of all, you should choose the area.
Under no circumstances should you collect mushrooms near large, especially industrial, cities, near cemeteries and factories. You need to go away from highways and railways.
This is due to the fact that in the vicinity of these places there is an active release of heavy metals and other harmful substances. All toxic compounds are absorbed by plants. Therefore, as the rules for collecting mushrooms say, you should choose an area away from the above areas.
Urgent help
Even experienced mushroom pickers may have trouble and one “harmful” mushroom will escape their attention. If, after a meal that included mushroom dishes, one of the eaters experiences alarming symptoms (nausea, vomiting, pale skin, rapid heartbeat), his stomach and everyone who was sitting at the table should be rinsed with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and immediately called " ambulance." You should not put off calling the emergency room, even if the symptoms have weakened: the accumulation of toxins in the body can lead to long and difficult treatment.
Poisonous mushroom or not?
If there is any doubt about the edibility of a mushroom, it is better not to cut it. Poisoning can be very dangerous (depending on the concentration of the toxic substance), and the consequences are unpredictable. It would be a good idea to contact a specialist who can weed out inedible mushrooms.
He could also talk about the signs of poisonous species. You should not put wormy, flabby, overripe or rotten mushrooms in the basket.
In spoiled species, the process of decomposition begins, which is accompanied by the release of harmful compounds. The rules for collecting mushrooms recommend putting the harvest in wicker baskets that are well ventilated. In extreme cases, you can use a bucket. Harvested crops should not be placed in bags. There the mushrooms can “suffocate” and quickly deteriorate.
Some rules for picking mushrooms for children
If a child goes to the forest with his parents, he should be given several recommendations.
This can be done in a playful way. For example, you can tell him: “Make a rule for picking mushrooms.” During the conversation, the child begins to understand how to behave in the forest. Parents explain that mushrooms should not be pulled out of the ground or the roots should be broken.
In this case, next year there will be no harvest in this place. To ensure that the mycelium remains intact, the mushroom should be carefully cut with a knife. You can pull it out if it is under a thick “litter”. However, this must be done extremely carefully, turning and swinging the leg. After this, the hole must be sprinkled with moss.
This way, the open mycelium will not dry out under the bright sun. A new harvest will appear in the same place next year. When telling your child the rules for picking mushrooms, you should definitely tell him that you should not knock down those species that do not fall into the basket. It happens that one person does not know the name of a particular species or thinks that it is poisonous. The other, on the contrary, knows it very well and actively uses it for food.
You must tell your child that you cannot try raw mushrooms. The same applies to berries. If you go into the forest with children, it is necessary that they are visible at all times. It is very easy for a child to get lost, this should not be forgotten.
Mushroom picker signs
Many mushroom pickers pay attention to signs and signs before picking:
- If mushroom pickers go into the forest during a leap year, the forest spirit will begin to take revenge on them.
- There is a superstition that once every 2-3 years the mycelium becomes poisonous and therefore mushrooms cannot be collected. Perhaps in this way our ancestors wanted to give the mycelium a rest and restore its “strength”.
The forest needs annual restoration, so many mushroom pickers change their “golden” places to new ones every year, and during a leap year they take a vacation for the sake of safety. Proper collection is a real art.
Attitude to the forest and its inhabitants
When in nature, you should show respect for it. You don't need to break down trees to start a fire. There are a lot of dry branches on the ground in the forest; they will be quite enough. If stops are organized, after them you should definitely remove all rubbish and put out the fire.
Forest dwellers also need to be treated with care. Under no circumstances should you destroy anthills or bird nests. When going into the forest, you need to know not only the rules for picking mushrooms, but also what to do in case of an unexpected encounter with a wild animal. It is best, of course, to go to already familiar places. However, you can meet some forest dweller, for example, a wild boar, in a well-known area. If this happens, you should not be aggressive or panic. No need to make loud noises.
As a rule, wild boars do not attack people, but when they see them they may stop. The person should also stop moving.
Usually boars go on their way after some time.
Required equipment
Collection rules also include special accessories that you take with you into the forest.
- Clothing: depends on the season (warm, light). All parts of the person's body must be covered. If you wear a short T-shirt and shorts, a person will get injured on branches and suffer from insects (mosquitoes, ticks). Mosquitoes won't do much harm, but ticks will cause health problems.
- Shoes: Light shoes should be worn on your feet. It should be closed and comfortable. In the forest you can find not only insects, but also snakes. If your shoes are closed, you will be able to avoid a snake bite.
- Knife: A mushroom picker can easily cut off the fruiting body and check the mushroom stem and cap for worms.