The forests of the Kaluga region are rich in edible mushrooms. Fruiting lasts from late spring and ends with the onset of the first frost. Every year, mushroom pickers collect baskets full of protein, rich in vitamins and microelements. And 2022 was no exception to the rule. Quiet hunting began in May and will continue throughout the summer and autumn until the cold climate takes the lead. Having chosen the right mushroom places in the Kaluga region in 2022, every mushroom picker will be able to go mushroom hunting with baskets and buckets, either by train or personal car, or by bus.
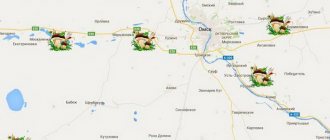
Mushrooms on the area map 2022
On city forums and social networks, you can find real reviews and messages revealing mushroom places in the Kaluga region. Such tips will allow not only beginners, but also experienced lovers of quiet hunting, to find new gathering places rich in mycelium. In the list of popular walking areas, local residents note the following:
- a forest belt passing through the territory of the city of Balabanovo;
- in the areas: Bolshiye Kozly, Balabanovo, Ferzikovo and even Blue Lakes;
- area in the village of Kostino (the count includes not only the forest, but also fields where meadow mushrooms and umbrellas are found);
- the most popular place in the last few years is the Maloyaroslavsky district, bordering Bryansk and the Moscow region. Conditional and edible mushrooms belonging to different families grow there.
In order not to confuse forest gifts with false brothers and not to accidentally collect poisonous mushrooms in the basket, it is recommended to first familiarize yourself with the distinctive features and description of each variety.
Important!
Before you go mushroom picking, you should pay attention to the weather. Myceliums bear fruit only after rain, depending on the time of year. For example, boletus can be collected not only in the fall, as many are accustomed to thinking, but also in the spring, when the air warms up to 20-23 degrees Celsius. It is better to go searching 2-3 days after precipitation falls.
Map of mushroom places
The southern part of the region will delight you with its gifts
Experience shows that the largest number of mushroom places are located in the southern part of the Kaluga region.
Boletus and honey mushrooms
In 2022, forums are literally full of messages about boletus and boletus mushrooms in the Borovsky district. It's worth visiting these places before summer ends. Closer to autumn there is almost no harvest left.
They are also found in old apple orchards near Dyagelevka and towards the village of Sukhinichi.
For honey mushrooms they go to the village of Leo Tolstoy. They can also be found at the exits from the miniature town of Bolshie Kozly, near Obninsk and in the Kolyupanovsky forests. Slightly smaller mushrooms are found in the Maloyaroslavets district or in the aforementioned Borovsky.
According to folk wisdom, the best sign that it’s time to go out for honey mushrooms is the appearance of fogs for several days in a row.
An abundance of fruiting bodies is observed in the town of Tikhonova Pustyn, but the places are scattered 10-20 km from the village, so you will have to walk a lot. The same problem occurs near the town of Balabanovo. But mushrooms are not found there every year. And 2022 did not turn out to be a productive year.
In the villages of Slyadnevo and Zherlovo, rare satanic mushrooms, boletuses, honey mushrooms, porcini mushrooms, boletus or chanterelles are found.
The satanic mushroom in appearance is very similar to the pink-golden boletus. An inexperienced mushroom picker can easily confuse these species. The flesh of young specimens of satatninsky boletus has a faint spicy odor, but old ones are distinguished by the “aroma” of rotten onions or dead rotting flesh (carrion).
You can also find mushrooms in Kaluga along the perimeter of many highways: the most productive are considered to be the sides of the Tula Highway and roads in the Maloyaroslavets direction.
But you shouldn’t grab the harvest right from the edge of the roadway, no matter how tasty and tempting the mushrooms look. The fact is that they easily absorb exhaust gases and all toxic products of human activity like sponges. It’s better to move a little further from the road at a distance of half a kilometer and start picking mushrooms there. But those who want to be sure that they will collect and bring home a “clean catch” can walk even further, leaving the route 1 km behind them.
What's the best way to get there by car?
The easiest way to find mushroom places in the Kaluga region in 2022 is if you have a personal car. The car allows you to go searching in almost any area if the tank is full.
Unfamiliar territories are better conquered thanks to a GPS navigator. It can be installed on your phone and used not only to find the right place, but also as a compass so as not to lose your car parked in the forest. To do this, it is enough to set a point of the original location in order to return back, despite the distance traveled.
When looking for the best gathering place, in addition to those listed above, you can pay attention to the Kozelsky district, passing along the Kaluga-Kozelsk highway. An alternative option is pine forests and forest belts located on the road to the Moscow region.
The basic rule is to exclude the collection of mushrooms growing near highways and other polluted places, which allow the fruits to absorb carcinogens and poisons that are hazardous to health. We are talking about the territory of factories, cemeteries and garbage dumps.
Conditionally edible
In addition to edible ones, there are also conditionally edible mushrooms. They are classified in a separate category because they produce a bitter juice or contain poison in very small quantities.
Such mushrooms must be subjected to special processing before cooking, namely:
- soak (from 4 to 7 days);
- boil (15-30 minutes);
- scald with boiling water;
- dry;
- salt (50-70 g of salt per 1 liter of water).
Among conditionally edible mushrooms, even with special processing, it is recommended to consume only young specimens, without signs of aging or rotting.
Some mushrooms may only be inedible if eaten with other foods. For example, dung beetle is not compatible with alcohol.
How to get there by minibus?
To avoid confusion, you should choose a bus that can get to a station or stop close to the forest. Do not be afraid of the unknown, as in the case of a car, GPS will allow you to get back, marking the original point on the map of the area.
If you are worried about poisoning on a minibus, you can consult with local residents who leave advice in social networking groups dedicated to mushroom picking. Fans of quiet hunting will probably tell you how best to get to Tikhonova station or the Slyadnevo platform, any village or forest clearing.
There are times when local residents agree to go on a search together to keep each other company, exchange accumulated knowledge, or simply meet new acquaintances who share a favorite hobby.
Time to grow
The timing of collecting certain mushrooms depends on the climatic conditions of the region. Real mushroom pickers conduct observations, identify places and study them.
- Autumn honey mushrooms grow in forests of different types. Their time is in May-October, they meet often. Delicious freshly prepared, marinated and salted. Only caps are used. They differ from pseudo-hospitals by the presence of a ring on the stem and a scaly cap.
- Boletus mushrooms grow in forests with birch trees and are rare. Their time is in May-October. Tasty in stir-fries, soups, marinades, and dried.
- Mushroom pickers readily collect boletus, like boletus, until late autumn for pickling and drying. They are found in aspen, and less often birch, thickets.
- In July, a family of russulas of various colors grows. In August, lilac-lilac, blood-red, gray-olive, bluish, greenish, yellowish ones fall into the baskets of mushroom pickers.
- Milk mushrooms appear in July. It is the most delicious of salted mushrooms. For harvesting for future use, white loading pads are also very popular. For loading, you can go to any forest - to a birch and aspen forest, to a mixed and not very dense coniferous forest. In August, mushroom pickers collect yellow, black and aspen milk mushrooms for pickling and pickling.
- Porcini mushrooms (boletus), considered the best edible mushrooms, grow in coniferous forests and oak groves. Their time is July-November. Fresh mushrooms are odorless, but very aromatic when dried. Suitable for any processing method.
- Butterflies grow in deciduous and coniferous forests. Their time is in July-October. Freshly prepared, salted and pickled are good.
- Russulas grow in deciduous and coniferous forests. Their time is in July-October. A good edible mushroom. Tasty freshly prepared, salted and pickled.
- Saffron milk caps are more often found in spruce forests. They can be immediately noticed by their bright color. Ryzhiki are delicious both salted and pickled. Dishes made from fresh saffron milk caps are also wonderful. Some mushroom pickers eat young mushrooms raw, cut and salted.
The height of the mushroom season, both in terms of the variety of mushrooms and their quantity, occurs at the end of August.
What mushrooms can be found in the forests of the Kaluga region?
Like other regions of Russia, the Kaluga region grows a lot of mushrooms, both conditionally edible and poisonous. Beginners should be extremely careful not to accidentally confuse and collect dangerous representatives of their species into a basket.
Today, more than 450 species of mushrooms grow in Kaluga. Some are popular, others are dangerous to health, and others are so rare that even when meeting them, many mushroom pickers do not risk collecting them for further use as food or creating a tincture used in folk medicine.
Helpful advice!
If you have doubts about whether a mushroom is classified as edible, you should not risk your health and loved ones just to collect baskets full of forest gifts. It is better to leave the forest without mushrooms than to put your health at risk.
The following mushrooms can be collected from spring to late autumn in Kaluga:
1) little boletuses (boletus and boletus); 2) porcini and Polish mushrooms; 3) meadow and autumn honey mushrooms; 4) boletus and saffron milk caps; 5) tinder fungi and russula; 6) slingshots; 7) chanterelles and champignons.
Important!
If you meet Hedgehogs along the way, you shouldn’t pick them. Mushrooms are listed in the Red Book and their reproduction is very important. If the recommendations are not followed, very soon the representative of the mushroom world will disappear.
For lovers of fragrant and valuable honey mushrooms, comparable to weeds in terms of germination, it is recommended to go in search of cleared areas and old forests where many stumps remain. It has been observed by many mushroom pickers to have deposits in the following areas of the Kaluga region: Borovsky and Ilyinsky forests, forests adjacent to the forests of Leo Tolstoy, Kolyupanovsky and Bolshiye Kozlov.
To collect mushrooms of the first category, namely boletus, obabok, and Polish, it is recommended to go searching in mixed zones. It is best if the choice falls on the village of Tishnevo, adjacent to the border of the Moscow region.
Regardless of the choice in favor of certain mushrooms, it is recommended to collect with extreme caution so as not to risk collecting poisonous or false fellows. Before heading into the forest, it is recommended that you carefully read the description of each species and the comparative characteristics that distinguish edible mushrooms from unsuitable ones.
Types of mushrooms
There is an abundance of mushrooms in the region. In different types of forests they differ in their quality, quantity and variety. In total there are about 500 species. Among them there are inedible, edible, conditionally edible and, of course, poisonous. But there are still the most common ones.
Coat of arms and flag of the Kaluga region
Edible
Ruby oiler
Butter
It is difficult to confuse this species with another. The name itself speaks for itself. Brown-chocolate color, sometimes gray-olive or yellow-brown.
The thin skin is covered with mucus, like vegetable oil. The stem is usually lighter than the cap, and a ring is located closer to its center.
Golden boletus
Borovik
Quite common and the most desirable type. Long, thickened leg at the bottom. Smooth, dry top, unevenly colored brown with a red, sometimes chestnut tint.
Half-shod champignon
Champignon
Height from 4 to 11 cm. In the center, closer to the base, there is a ring. The color is the same as the top, white or light brown.
The champignon is smooth to the touch, less often with scales. The plates are initially whitish, then become pinkish, and then light brown.
Honey mushrooms late and early
Autumn honey fungus
The word late means that these are winter mushrooms. But the early ones are harvested in the summer. Late ones can be distinguished from summer ones due to their bright color. Yellow, honey or dirty orange.
Hemispherical in shape, the diameter of which ranges from 5 to 7 centimeters. The legs of winter honey mushrooms have a dense structure and a brownish-velvety hue. Also, unlike summer ones, there is no ring.
But summer ones, in addition to the ring, have dark scales. The size of honey mushrooms is 3-6 cm. The skin of early honey mushrooms is smooth, matte, honey-yellow with dark edges. During wet weather, the skin becomes translucent.
Summer honey fungus
Real morel
Morels
An unusual mushroom in the shape of a cone or candle with cells that look like a honeycomb. A grey-brown hue that may change to olive-black over time. The hat from below grows to the leg.
Ordinary stitch
Stitches
The body of the conditionally edible fruit is 4 centimeters high and 12 centimeters wide. The hat is irregular in shape, with folds resembling the insides of a walnut.
Boletus
Pine boletus
The cap, tightly squeezing the leg, is hemispherical in shape. The boletus is red and resembles a thimble worn on a finger. The leg is usually tall, porous, and covered with black or brown scales.
Saffron milk caps
The diameter can reach up to 12 cm, and over time the flat shape becomes funnel-shaped, the edges of which are noticeably curved inward. The cap is dry, but after rains you can see mucus.
Sometimes olive-colored streaks will form on the orange or dull apricot surface. When cut, a bright carrot or orange milk is released.
It is important to know that saffron milk caps are collected in the early stages of growth, since over time insects lay larvae in them.
Red saffron milk cap
Loadings
Loader white
Also known by its middle name, Dry Milk. It received this name because it looks like a common milk mushroom. But their main difference is that the loading surface, no matter what, remains dry.
White, can reach up to 30 centimeters in diameter, but such sizes are rare. The convex shape of the top with a peculiar pit in the center.
From time to time, a red coating may appear. The color changes depending on its age; if the young fruit is white, the old one will be brown.
The plates are also white, thin and narrow. They can change their color from turquoise to greenish. The wide leg tapers towards the top and is also decorated with brown spots.
Real milk mushroom
Common milk mushroom
The diameter of the cap is from 5 to 20 centimeters. Flat-convex, smoothly turning into a funnel. The edges are turned down. Wet, milky skin.
The leg is small in size, 3-7 cm in height. The cylindrical shape is covered with yellow spots or pits.
Valuy
Valuy.
The upperparts are dark yellow, sometimes dotted with gray. Radial stripes form along the edge. The skin is covered with mucus, which can be easily removed.
A distinctive feature of the plates is that they secrete a clear liquid, which dries over time and becomes brown in color.
Inedible mushrooms
Russula is caustic
Depressed tuberous apex with ribbed edges. The skin is smooth and shiny, but in wet weather it becomes sticky. The shade can be bright red or pale pink, but there is something that does not change - these are light ocher spots.
The white leg turns yellow over time, this is especially noticeable in its lower part. The plates are wide and weakly attached to the stem.
Russula pungent
White row
White row
The diameter of the cap is small, maximum size 12 cm. Smooth, matte surface. It is lowered down, and in the center there is a blunt tubercle.
The white color becomes pale gray over time, but with age the center turns yellowish-brown, which is covered with gray spots. This species can be recognized by a crack on the stem.
Honey fungus brick-red
False honey fungus brick-red
Red brick. Smooth, convex cap, with creamy yellow edges. The leg is white, and closer to the edge it is reddish. The plates are pale yellow, grow to the lower part and are covered with a blanket, and over time they change their color to gray-green.
Poisonous
Every mushroom picker must know poisonous mushrooms and how to distinguish them from edible ones.
Death cap
Death cap
Also known as green fly agaric. The most common fruit size is from 6 to 10 cm. The toadstool has an ovoid shape at a young age, and then acquires a hemispherical appearance with smooth edges that are slightly curled down.
The legs of the pale grebe are tall, reaching 15 centimeters. The shade is pale green. There is a “skirt” on it.
Fly agaric red
White patches cover a bright orange spherical cap. Sticky mucus can often be observed. There may be stripes on the edges. The plates are 6-12 mm wide, the color of which is often white, but in the old mushroom they become yellowish.
Fly agaric red
Waxy talker
Waxy talker
The young fruit has a convex appearance and is tucked inward, over time it becomes flat and with a barely noticeable tubercle in the center. At the end it takes the shape of a funnel. A waxy layer covers the body, and underneath it a flesh-colored or brown-colored surface is visible.
Sometimes a waxy coating forms, which seems to look like marble. The leg can be either white or dirty ocher. The upper part is covered with hairs and a whitish coating.
Thin pig
Thin pig
The Russian people describe it as the snout of a pig. The height of the pig does not exceed 10 cm, and the diameter is 20 cm. The shades are always different: olive, gray-brown, yellow-brown, reddish-brown.
But the bottom is slightly yellow or red-brown. The edges of the pig are turned down, and the surface is rough to the touch, but after rain it will become sticky.
False honey fungus gray-yellow
It is often confused with edible honey mushrooms, but you need to be careful, as this crop poses a serious danger to human health. Their size is small, ranging from 2 to 6 cm.
Representatives of the kingdom grow in groups. The tops are flat, gray-yellow, the plates are the same color. The leg is the same color along the entire base, but is brown at the bottom. They have an unpleasant smell.
Sulphur-yellow false honey fungus
Real reviews + photos
Having learned in detail the mushroom places where mushrooms grow in the Kaluga region in 2022, it is worth reading the real reviews left over the last year by local residents who went on a quiet hunt at least once.
- Valentina, 54 years old
The day before yesterday I walked in the forest and found only a few saffron milk caps. The drought did not allow us to collect our favorite honey mushrooms and boletus.
- Yulia Dmitrievna, 62 years old
Despite the modest harvest from recent trips, I took amazing photos for my social networks. What a pity that now families are less and less likely to go for walks in the fresh air rather than to the shopping center.
Tasty or dangerous
People have been collecting mushrooms since time immemorial. They are dried, boiled, stewed, fried, salted, pickled, frozen. However, the edibility of various mushrooms is still controversial.
“We must remember that mushrooms, being plants by the nature of their main characteristics, contain substances found only in animal products. Thus, the shell of mushrooms contains chitin, but humans do not have an enzyme capable of processing this substance. Therefore, mushrooms are, of course, heavy, difficult to digest food for humans. Extractive substances that give mushrooms a unique taste and aroma cause increased secretion of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to exacerbation of existing chronic diseases. This means that the most common mushroom, when consumed, can cause ailments of varying severity,” said the department of Rospotrebnadzor for the Penza region.
Mushrooms absorb many harmful substances from the environment (salts of heavy metals, radionuclides, etc.), so it is better to refuse to collect old, overgrown, late-harvested and wormy mushrooms.
Mushrooms and dishes made from them are perishable products due to the rapid proliferation of microorganisms, so their shelf life is limited: a fresh product must be processed no later than 3-4 hours, and dishes made from mushrooms are not recommended to be stored for more than two hours; it is advisable to consume them after cooking.
Mushrooms are quite heavy food. Therefore, elderly people and those who suffer from chronic gastrointestinal diseases should not eat mushrooms, since even non-poisonous mushrooms can cause an exacerbation of these diseases. And of course, mushrooms should not be given to children under seven years of age.