Is it possible to eat a porcini mushroom if it has turned pink?
To ensure that the fruiting bodies do not change color during heat treatment, you should carefully consider the preliminary preparation of the harvested crop for cooking. It is necessary to carefully examine the fruiting bodies before heat treatment and identify undesirable species among them:
- grates, which cause the butter to turn pink when cooked;
- moss mushrooms, which cause the boletus to turn red during cooking;
- goats that turn neighbors in the pan purple.
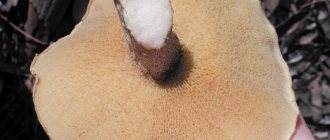
It is relatively difficult to distinguish these species from each other, but it is possible. Kozlyaks, unlike many Boletovs, do not have a skirt. The lattice has a cap of smaller diameter with a pronounced tubercle in the middle. The flywheel has a thicker cap.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JfO-PFj5ttA
If all checks have been passed, but you want additional guarantee that the color of the dish will not change, it is recommended to add 0.2 g of citric acid per 1 liter or 15 ml of 6% vinegar to the same volume of water during cooking.
I'm planning to go again this weekend. About 50 small white crepe mushrooms are frozen raw for the winter; I really love fresh mushrooms in winter)))
Yes, there are a lot of mushrooms this year, in the reports on mushrooms there are a lot of decent photos. Moreover, the layer has grown quite vigorously, there are a lot of large old white ones, but there are also young ones. 300pcs is of course a lot, they just came in very well, and I think it’s not difficult to plan the basket.
Our program for pickling whites is closed, but I plan to dry and salt whites starting Saturday - Sunday.
I don’t look at the photos, I’m not a masochist. There are a lot of mushrooms, white ones are in short supply as always. Do you walk far or somewhere near the road?
I collected within 10 - 15 minutes from the car
hmm, I have other information
Required: 1 kg of mushrooms, 45 g of salt, greens, 1 liter of water Preparation: Wash the mushrooms thoroughly in running water, peel off the leaves, place them in prepared containers in layers 5-7 cm high with caps on the bottom, sprinkle each layer with salt, add greens (dill, parsley mint) Place a wooden circle with a weight on top of the mushrooms, let it settle, after a few days add a new layer of mushrooms, sprinkle with salt, and put the weight again, do this until the container is full. Place the mushrooms tightly, cover with salt solution and put in a cold place. place 2-3 weeks and the mushrooms are ready!!
Hot pickling of mushrooms
The mushrooms are boiled before salting.
Method 1. Butter mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, honey mushrooms, goat mushrooms, boil for 5-8 minutes, white mushrooms, champignons, aspen mushrooms - 8-10 minutes, chanterelles - 12-15 minutes, valui - 15-20 minutes.
Method 3. Boletus and boletus are boiled for 1-2 minutes, chanterelles and boletus - 20-25 minutes, white and boletus are first poured with boiling water, kept in it for half an hour, change the water and boil for 15 minutes.
Hot salted mushrooms are ready to eat in 2-3 days.
Yes According to the subject, mushrooms containing bitterness or toxic substances are salted in this way: milk mushrooms, bitter mushrooms, rubellas, valui, some rows, talkers, cobwebs, pigs, blue-green stropharia, champignons and some russula.
After cleaning and washing the mushrooms, boil them in lightly salted water for 20 to 30 minutes. Then drain the water in which they were boiled, rinse the mushrooms in cold water, place in a sieve, colander, or place in a bag made of thin fabric and hang to drain.
Mushrooms prepared in this way should be placed in dishes (tubs, jars) and salted at the rate of 45-60 g of salt per 1 kg of boiled mushrooms and covered with a wooden circle with pressure. As a seasoning, you can add garlic, onion, horseradish, tarragon or dill to the mushrooms.
In the same way, tubular mushrooms are salted: porcini mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, goat mushrooms, oak mushrooms and boletus mushrooms, boiling for 10-15 minutes.
If the boletus turns pink during cooking, it is better to refrain from eating it. This effect can be produced by an inedible double, which changes its color at elevated temperatures.
Moreover, you need to throw out all the specimens that were in the pan. False boletus is characterized by increased bitterness, which permeates everything that was nearby.
When collecting and preparing, you need to be extremely careful, since any suspicious specimen can cause severe intoxication of the body. If in doubt, check whether the flesh changes color to pink when exposed to air.
Description
To be sure which fruiting body is found, you need to know what the kid mushroom looks like. The slightly cushion-shaped caps of goats are colored from red-ocher to light yellow-brown. They are smooth and hairless in dry weather, slimy after rain. Young specimens have convex caps, old specimens have flat caps, sometimes concave in the center. Their edges are thin. The diameter ranges from 40 to 110 millimeters.
The skin that goes over the edge and tucks into the tubes peels off from the caps when cleaning, like tiny shreds. The tubes of mushrooms that have just broken through the ground are gray-yellow. As the fruiting bodies grow, they turn yellow. Aged mushrooms acquire a brown color. The height of the tubes is 6-10 mm. They usually grow to the legs. They are difficult to separate from the cap flesh.
The legs of mullein are cylindrical, solid, with a thickened bottom. Their height is 30-100 mm, and thickness is 5-20 mm. The top of the longitudinally fibrous legs is yellowish or ocher-rusty, the base is brownish-red.
The cap has dense flesh, colored in white and yellow tones. The flesh of the legs is usually fibrous, brownish-red in color. It turns red when cut. It has a pronounced mushroom smell and pleasant taste. The pulp is endowed with powerful bactericidal properties. It is rich in vitamins, phosphorus, carotene and amino acids.
Oiler mushroom granular. Butter, how to collect, clean and cook
Cooking: 20 minutes
Butterflies have one unpleasant feature: when collected, and especially when cleaned, they get your hands very dirty; a black oily coating appears on your hands, which eats into the skin and is practically not washed off. Therefore, if a manicure is dear to you, but the prospect of walking around with black hands for 2-3 days is not to your liking, then do not forget to wear gloves. And this applies to all types of butter.
If you believe sources from the Internet, then I was lucky enough to find the granular oiler, which is usually found in young pine forests. It was in such a forest that we found our beauties.
The granular oiler does not have a ring or skirt, although some mushrooms, especially young ones, have a thin film that connects the bottom of the cap to the stem. When cut, boletus does not change color.
You can often find droplets of liquid on boletus mushrooms, especially under the cap and on the top of the stem. Butterworts usually grow around young pine trees, at a distance of up to 2 meters from the tree.
After you have collected the mushrooms and come home, it is advisable to start processing them as soon as possible.
Mushrooms are very poorly stored; in addition to the fact that they quickly deteriorate, worms breed in them very quickly. Although, if necessary, freshly picked mushrooms can be stored in the refrigerator for 10-15 hours.
Collected mushrooms should not be stored in a basket or bucket, as this will heat them up and spoil faster. It is best to spread the mushrooms in an even layer on a piece of cloth or newspaper. It is convenient to clean boletus with a small knife.
Do not wash or soak butternuts before cleaning, otherwise they will become slippery and difficult to clean. Oils must be cleaned dry and, if necessary, rinsed in water.
To the question of how long to cook butter, I never found a clear answer. In one cookbook they write 5-8 minutes, in another 10-15 minutes (from the moment the mushrooms boil), and in some sources on the Internet they advise cooking 2 times for 40 minutes. I boiled the butter in salted water for 20 minutes after boiling, everyone remained alive and no one complained of digestive problems.
Boiled mushrooms can then be prepared according to any recipe; such a semi-finished product can be pickled, salted, fried, boiled, or frozen for future use. We fried ourselves a frying pan of aromatic mushrooms with sour cream, and marinated the rest and froze for the winter.
Preparation
Before freezing, mushrooms should be carefully prepared. Preparation is a completely simple procedure and includes several stages.
- To begin with, the mushrooms are carefully sorted.
- The top film from the cap is carefully removed from the boletus, the stem is cleaned and cut. If the mushroom is wormy (identified by small dots-channels that can be seen on the cut of the cap or stem), then it is better to throw it away. Using the handle of a knife and tapping the mushroom cap, remove excess sand or sawdust.
- During cleaning, mushrooms can be sorted into small and large.
- The further process depends on the freezing method. The mushrooms are either left as is or soaked and washed.
How to avoid poisoning from mushrooms and recognize the poisonous ones among all?
This question is asked not only by amateurs and beginners, but also by avid mushroom pickers.
Of course, mushrooms purchased in a supermarket in raw or canned form are 99% free of toxic substances. The only nonsense is improper storage. Such a dish can cause frustration or slight malaise. But what about products that are collected with your own hands? How to recognize poisonous ones among them? After all, poisoning from poisonous mushrooms is equivalent to poisoning from snake venom. The consequences can have a detrimental effect on human health, and sometimes cause death.
There are a lot of misconceptions about recognizing or identifying edible mushrooms.
Types of poisonous mushrooms.
- Firstly, a big and common misconception among many novice mushroom pickers is that young mushrooms, despite the variety and variety, are always edible. For example, the pale grebe, even at a very early age, already has a sufficient amount of phalloidin poison. With a single dose of 20 mg you can die. There have even been cases where a very small dose of this substance entering the human body led to serious complications associated with the gastrointestinal tract and problems with the body as a whole. Of course, when picking mushrooms it is better to avoid old and loose ones, but this does not mean that all young ones should end up in the basket. The best method is to study the type and characteristics of edible mushrooms and collect only those that are probably familiar.
- Secondly, there is a misconception about the bad and pungent smell of poisonous mushrooms. A mushroom with poison does not necessarily have to smell bad; its smell may be no different from champignons that are grown artificially. Don’t forget that everyone’s sense of smell is different, so you shouldn’t rely on mushroom smells when determining edibility.
- Thirdly, there is another common belief that poisonous mushrooms are not eaten by insects. Mushroom pickers take mushrooms slightly spoiled by worms or snails into a basket, concluding that they do not contain poison. This is a wrong opinion. Dangerous poisonous mushrooms can be spoiled by insects, while edible ones, on the contrary, can remain completely intact. Mushroom pickers do not take wormy specimens only because they are difficult to process for cooking and most often there is little left of the trimmed part.
- Fourthly, another misconception is that spoiled or poisonous mushrooms cause milk to sour. Pepsin, the enzyme that sours milk, can be found in both edible and poisonous mushrooms. All of them contain a lot of organic acids, which also affect the oxidation of the dairy product.
- Fifthly, it is widely believed that drinking mushrooms with alcohol will neutralize the poison if it gets in. This is the most false and especially dangerous misconception, because alcohol, on the contrary, enhances and aggravates the effect of poison on the human body. According to statistics, people who drink poisoned food with alcohol are more likely to die.
- Sixthly, there is a common misconception that any mushroom, if thoroughly boiled, will become non-toxic and all poisons will be removed from it. This works for some, but there are also poisons that are resistant to even the highest temperatures. Therefore, even one mushroom can cause severe poisoning.
Popular articles Features of the Fat Albert spruce variety
Delicious recipe! Tatar cuisine recipes with photos step by step
Signs of poisoning
Even when collecting edible boletus, you can get poisoned, although this happens infrequently.
Main causes of poisoning:
- Oilseeds were collected in the wrong place (along roads or near hazardous enterprises).
- The cooking technology and sanitary standards were violated.
In case of poisoning, nausea and abdominal pain occur. The victim must be given an adsorbent, given water to drink and rest, and in severe cases, urgently call emergency help.
Another danger to human health is the so-called false butter. Due to inexperience, novice mushroom pickers may put false doubles in their baskets. And this is fraught with serious consequences, since the toxins contained in them can lead to poisoning and disruption of the entire body.
- dizziness,
- heat,
- intestinal disorders.
If such a problem happens to you, you need to urgently go to a medical facility and rinse your stomach.
Almost all edible mushrooms have poisonous counterparts, which are not recommended to be consumed.
Contraindications
The property of mushrooms, like a sponge, to accumulate minerals in their tissues can be dangerous. When collecting mushroom crops near busy highways or factories, an increased concentration of heavy metal salts - lead, rubidium and cesium - is observed in the tissues. Therefore, these mushrooms, like others, are collected in environmentally friendly areas.
Eating the oily, slippery skin is contraindicated for people suffering from metabolic disorders and a tendency to allergic reactions.
Mushroom dishes with minimal heat treatment - marinades and pickles - are useful for preserving vitamins. However, excess salt will adversely affect the health of hypertensive patients, and excess acids of marinades are contraindicated for gastritis with high acidity.
At the same time, with low acidity of gastric juice and dysfunction of the pancreas and gall bladder, the body will not be able to cope with the breakdown of mushrooms, which will lead to indigestion and digestive disorders.
These products should not be included in the diet of children, pregnant or lactating women.
Cooking recipes
It is not recommended to cook overripe fruits; it is better to take younger ones. If the mushrooms are very large, it is better to cut them. What to do with it and how to process it?
Fried mushrooms
Preparing this simple but very tasty dish will take about 40 minutes. You can eat them as a separate dish, or with a vegetable side dish, with cereals and pasta. And fried boletus with potatoes will not leave anyone indifferent.
- 2 kg butter;
- 2 onions;
- 40 g vegetable oil (approximately);
- salt and pepper to taste;
- dill and parsley.
- Boil the peeled mushrooms for 15 minutes in salted water.
- Rinse and leave in a colander or sieve to remove excess moisture.
- Fry the onion, cut into half rings, until golden brown.
- Add mushrooms and fry over medium heat for a quarter of an hour, stirring constantly.
- Cover with a lid and simmer for another 10 minutes.
- Salt and pepper.
- When serving, top with chopped herbs and add sour cream if desired.
Watch the video! How to deliciously fry butter
Marinated boletus for the winter
In order to enjoy the taste of butter in winter, which is so reminiscent of summer, you can marinate them. There are many pickling recipes, but this one is one of the simplest.
- 2 kg of mushrooms;
- 2 liters of water;
- 1 tbsp. spoon 9% vinegar;
- 3 tbsp. spoons of salt;
- 4 tbsp. spoons of sugar;
- 3 cloves of garlic;
- 1 clove;
- 10 peas of allspice;
- dried dill;
- Bay leaf.
- Peel the mushrooms and rinse them in several waters.
- The first time, boil for 10 minutes in salted water, adding 3 drops of vinegar. Pour out the water.
- The second time, cook for 20 minutes in new water, with spices, salt, sugar and vinegar according to the recipe.
- Place the butter in jars and pour in the marinade.
- Use sterilized jars for pickling. The sterilization process can be carried out over steam, in the microwave, or in the oven.
- Store in a dark and cool place.
Watch the video! How to properly marinate boletus for the winter
Freezing butter
- Before freezing boletus, it is necessary to peel, rinse and boil it.
- Then place on paper towels to drain excess moisture.
- Pack enough mushrooms into containers for one preparation. Indicate the freezing date.
- Frozen boletus can be stored for up to 1 year.
You can also freeze fresh mushrooms, but they take up a lot of space in the freezer. You can also fry mushrooms and freeze them. To enjoy fried mushrooms in winter, you just need to warm them up.
Salted mushrooms
Salted butter is also a very popular and tasty product. These mushrooms will be a good snack and can also be used to prepare various salads.
To prepare you will need:
- 2 kg of mushrooms;
- 8 cloves of garlic;
- 5 tbsp. spoons of salt;
- 8 black peppercorns;
- 6 bay leaves;
- 4 dill umbrellas.
- Peel the mushrooms and boil for 20 minutes in salted water.
- Strain and rinse well.
- Prepare the brine. Add garlic, bay leaf, salt and pepper to the water. Boil.
- Drop the mushrooms and cook for 7 minutes.
- Place in jars, add garlic and dill, add brine, and screw on the lids.
- Leave the jars in a cool place for 30 days until completely cooked.
To remove excess salt from the finished product, you can rinse it. If mushrooms are served as a separate appetizer, then it is better to add vegetable oil, vinegar and onions to them.
Watch the video! How to salt boletus
Website about the dacha
Butterfly (Suillus) is an edible mushroom that is popular among people for its excellent taste and yield. During the period of massive growth, many tiny butterflies appear. They are sometimes collected while kneeling. Otherwise, it is difficult to see slippery coin-sized balls in the grass.
Late oiler, photo from Wikipedia
The oiler has a characteristic shiny surface with a sticky cap skin. The light film on the back of the cap of young boletus is also noteworthy. During rainy weather, the skin becomes snotty. The species of the butterdish and its growth conditions affect the color of the cap, stem and other characteristics of the mushroom.
Butterflies grow in waves. The beginning of the first wave occurs at the time when the rye begins to ear. Spike mushrooms appear: not only porcini mushrooms, but also boletus mushrooms. The mushrooms pour out and disappear instantly, as if the Master of the forest gave them a command. I found confirmation of my observations from V.A. Soloukhina. On a warm June day, he and his wife managed in a short time to collect twelve buckets of strong butternuts growing in a pine forest not far from the village. We could have taken more, but we still had to drive the car to take the mushrooms home.
Not for the sake of mushrooms, but for the sake of curiosity, two days later we visited our pine trees and were amazed. It’s as if everything we saw two days ago was something we dreamed about or happened in a fairy tale. Even if we had wanted to, we would not have taken a single mushroom from the pine trees now. The forest was clear of mushrooms. A fresh person would never have believed that just two days ago... Yes, we ourselves somehow couldn’t believe it, but at home we had clear evidence of this little mushroom miracle (V.A. Soloukhin “The Third Hunt”).
Types of butter
Mushroom pickers usually know only a few types of mushrooms. in the genus Suillus, which belongs to the Boletaceae . The most famous of them are three types.
Late oiler (real, ordinary, yellow)
Late oiler (Suillus luteus) is also called true, ordinary, yellow. In Central Russian forests this is the most common species. The name of the mushroom can be misleading, since late oiler does not appear in late autumn, but from June to October. True, the time of mass collection actually occurs in the fall (in some years even in November). Late oiler is a mushroom of pine forests. It can also be found in places where, in addition to pines, there are other coniferous trees.
Late butterwort is very productive, it grows in large groups. This mushroom is prepared fresh (fried, boiled, stewed), dried, salted and pickled.
Hat. The shape of the mucous cap (up to 12 cm in diameter) in young fungi is cushion-convex and hemispherical. In adults it is wide-conical. Its edges are down. The surface color of the cap is chestnut brown, red-brown or dark brown. The tubular layer is golden yellow or lemon yellow in color. Old mushrooms develop an olive tint.
Cap flesh. The color of the thick pulp is white or yellowish. It has a pleasant smell and a slightly sour taste.
Leg. The height of the solid cylindrical stem of the late butterdish is up to 10 cm, thickness - up to 2 (3) cm. In adult mushrooms it has a white or grayish-violet ring. Above it the color of the leg is white, below it is brownish.
Summer oiler, grainy
Summer butterwort , granular (Suillus granulatus) is also productive. It is suitable for fresh use (it is fried, boiled and stewed), drying, salting and pickling. The mushroom is collected in the summer (June - July) in coniferous forests, where there are many pine trees. Some summer boletus appear from the end of May.
Hat. The shape of the mucous cap (up to 10 cm in diameter) is convex in young mushrooms, and flat in adults. The skin color ranges from yellowish-brown to ocher-brown. The tubular layer is yellow or light yellow.
Cap flesh. The color of the thick pulp is yellowish-white. It has a pleasant taste and smell.
Leg. The height of the solid cylindrical leg is up to 8 cm, thickness is up to 2 cm. The color is yellowish. The leg has a granular surface (hence the name of the species). There is no ring on the leg, which is a distinctive feature of the species. Small watery drops protrude from the upper part of the stem.
Larch oiler
Larch butterfly (Suillus grevillei) is more often found in areas where larches and cedar pines grow. This type of butter dish is fried, boiled, dried and pickled. This species is considered very beneficial to health, almost a medicine for people suffering from arthritis.
Hat. In the larch butterfly, the cap (up to 10, less often up to 14 cm in diameter) changes its shape depending on the stage of growth of the fungus (from convex to flat). The mucous skin is yellow-orange or yellowish-brown. The tubular layer of young and strong mushrooms is yellow; as the butterdish ages, it becomes olive-brown.
Cap flesh. The color of the pulp is white or yellowish. When cut, the tissue may acquire a brownish tint.
Leg. The height of the leg is up to 10 (12) cm, thickness is up to 1.5 cm. It has a cylindrical shape, solid. The color of the leg is from golden yellow to light brownish above the ring. Below the ring a reddish and reddish-brown tint appears. On the stem of young mushrooms there is a white or yellowish hanging ring. As the mushroom matures, it becomes less noticeable and almost completely disappears in older mushrooms.
Larch oiler, photo from Wikipedia
Less well known among us are the white butterdish (Suillus placidus), the cedar butterdish (Suillus plorans) and the Siberian butterdish (Suillus sibiricus). There is the marsh oiler , or yellowish one (Suillus flavidus), a category IV mushroom. Another species, yellow-brown butterfly , also variegated (Suillus variegatus), is very similar to flywheel, it is considered a mushroom with a mediocre taste. American oiler (Suillus americanus) is an edible mushroom that grows in Chukotka and in the thickets of dwarf cedar.
Oiler yellow-brown, photo from Wikipedia
the gray larch butterfly (Suillus aeruginascens) grows every two years It is also called blue oiler . It has a hemispherical cap (up to 12 cm in diameter), which becomes almost flat as the mushroom grows. The surface of the cap is mucous, light gray-brown in color. Old mushrooms have a pale cap that is dirty gray in color. There are few mushrooms, they are very different from those standard butter mushrooms that we find in the forest. Gray larch butterfly is an edible mushroom of category III. It is this species that I would classify as twin mushrooms, since there is a lot of incorrect information about the toxicity of larch gray oiler.
Delicious boletus and their inedible counterparts
Does the oiler have inedible or poisonous counterparts? The usual types of boletus are delicious mushrooms. They have a characteristic cap. Only the yellow-brown buttercup, whose flesh turns slightly blue when cut, can disappoint gourmets due to its mediocre taste. Some Western reference books define it as inedible (but not poisonous!). Siberian oiler is also considered a non-toxic, inedible mushroom.
There are no poisonous butterflies in our forests. But it is quite possible to confuse the delicious butter dish with the pepper mushroom (Suillus piperatus). This mushroom is called: pepper butterdish . It contains bitterness, but is not poisonous. Mushroom pickers who put pepper butter in the basket say in their defense that the bitter taste is greatly reduced when cooked for 15 minutes. After this, the mushroom is fried along with other mushrooms. Pepper oil grows not only next to pine trees, but also in spruce and deciduous forests.
Butternuts turned pink (reddened) during cooking: why, how to cook so as not to turn pink
Butternuts are considered one of the best mushrooms, due to their excellent taste, variety of processing methods and excellent digestibility by the body. They gained popularity among mushroom pickers due to their high yield and the absence of poisonous counterparts. However, there is one point that raises doubts among beginners in the mushroom business - the redness of mushrooms during cooking.
Causes of pinkness
All mushroom pickers who begin processing the harvest after harvesting should remember that boletus mushrooms will never turn red or pink during heat treatment.
If the crop turns partially pink during cooking, do not be upset, since baby goats, like all butter goats, are harmless and do not particularly differ in taste. The only problem in this situation is the unappetizing appearance of the finished dish, however, this can also be used as an original addition.
Is it possible to get poisoned
All lookalike mushrooms are edible and have the same properties and taste characteristics, which means that there is no reason to worry when discovering similar mushrooms. The boletus family is absolutely impossible to confuse with poisonous mushrooms, so there can be no danger.
Mushrooms that have changed their color during heat treatment do not change the taste of the dish, are quite edible and in terms of processing methods and preparation for the winter are no different from butter mushrooms.
Popular articles How to properly plant and grow bacopa from seeds at home?
Processing rules
At the time of preliminary preparation of the harvested boletus, it is possible to identify unwanted specimens that will color the rest of the crop. This is not very easy to do, but perhaps you just need to carefully examine the mushrooms and identify the following differences:
- if the cap is smaller in size, with a pronounced bump in the middle, it is a mushroom that turns pink when cooked;
- if there is no skirt, it is a goat, giving the finished dish a purple color;
- if the cap is thicker than usual, it is a moss mushroom; it will turn red when cooked.
To get a guarantee of color constancy, even after a visual inspection, it is better to play it safe and add 2 tbsp to the cooking water. l. 6% vinegar or 0.2 g citric acid. You can use any type of vinegar - table, grape, apple, etc. If such mushrooms are used in broth or gravy, you can add tomato paste, which will make the color natural.
Often, when preparing dishes from boletus, an unpleasant situation may arise due to the fact that the boletus turns pink during cooking. This does not frighten experienced mushroom pickers at all, but beginners may be wary and even refuse to eat their favorite delicacy of mushrooms. Next, we will consider what causes this phenomenon, whether it is dangerous, and how it can be dealt with.
Oilseeds are unique representatives of the mushroom kingdom - this is perhaps the only genus that does not have poisonous false counterparts. That is, there are many varieties whose fruiting bodies are similar to them, and these closely related species are very easy to confuse.
The substances that make up such twins are capable of changing the color of the fruiting bodies during heat treatment. And since the chemical composition of these species, as well as all representatives of the Boletaceae family, is the same, and they are all boiled in the same container, then, naturally, everything is colored, regardless of species.
There is no reason to panic if the boletus turns pink after cooking, and besides, the taste of the dish will not even change. Almost all of their counterparts are edible and have similar physiology and, therefore, taste characteristics.
Of course, many will not like the color of pink or purple fruiting bodies in a dish, but this is not so critical, in addition, you can always use some kind of sauce or gravy to change the color scheme of the dish.
Application
False boletus can be eaten
Fruiting bodies have long been used by people for a variety of needs. Now there is renewed interest in them. A science arose - fungotherapy. Scientists have become seriously interested in the opportunities that can be extracted from the mushroom kingdom for breakthroughs in medical and pharmaceutical science.
In cooking
False boletus is a lower grade mushroom species. But they are also valued for their taste and nutritional properties. After undergoing appropriate processing, false boletus mushrooms become safe and acquire a pleasant, rich taste. Only after this, mushrooms are used to prepare culinary dishes: they are fried, boiled in soups, and made into fillings for baked goods.
Spruce weed is used as food after heat treatment. It is necessary to remove the mucous film from her cap and rinse thoroughly. Many gourmets fry the mushroom without boiling it first. In our country, spruce moth is considered a third-rate species. In European countries it is well known and is a popular delicacy.
Moss mushrooms are also edible if boiled before cooking. They are salted, pickled, and various dishes are prepared from them. Before salting, moss mushrooms are doused with boiling water and then dipped into boiling liquid. This way, the mushroom pulp will not turn black during cooking and will retain its appetizing appearance.
In medicine
Many false species are used in folk medicine. They are used in the pharmaceutical industry to obtain drugs. The spectrum of their action is wide - from antiviral, antibacterial to antitumor. Mushroom pulp contains a powerful anti-cancer substance that is stronger than all known natural compounds.
If you remove the mucous film from the cap of the mucus and apply it to the wound, the healing process will significantly speed up. Mushroom pulp tincture strengthens the immune system, memory, improves blood composition, eliminates headaches and nervous disorders.
Moss fly contains rare enzymes and essential oils that facilitate and speed up the digestion of food. This species significantly improves the functioning of the digestive tract. It also has diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties, and contains large amounts of vitamin D. Such characteristics make moss mushroom beneficial for the kidneys. Regular consumption of mushroom pulp regulates the functions of the paired organ and prevents the development of pathologies.
Butter soup puree
To prepare the puree soup, it is better to use fresh mushrooms, but the recipe will not lose its flavor if you use frozen ones.
So, for the puree soup, take:
- fresh mushrooms – 150 g;
- carrots – 1 pc.;
- onions – 1-2 pcs.;
- celery (root) – 200 g;
- milk – 100 ml;
- garlic – 1-2 cloves.
Take salt and spices to taste, and also prepare vegetable oil for frying. Sort the mushrooms, rinse, peel, and remove the films from the cap. Place the mushrooms in a saucepan, bring to a boil, strain, and add fresh water. After boiling, add salt, add the whole onion, then cook for about 20 minutes.
Cut the garlic into thin slices, peel and chop the onion and carrots. Saute the vegetables in hot vegetable oil for about 10 minutes, then pour in a little mushroom broth and simmer over low heat for 5 minutes. Peel, rinse and chop the celery root, place in a saucepan along with sautéed vegetables, continue cooking until the celery is ready. Turn off the heat.
Using a slotted spoon, remove all ingredients from the broth and place them in a blender bowl. Add the broth in small parts and blend everything with a blender until smooth. The consistency should be quite thick. Pour hot boiled milk into the butter soup, bring to a boil, add spices, simmer for just a couple of minutes over low heat, stirring constantly. Make sure the soup doesn't burn!
Add fresh herbs before serving. You can serve the creamy soup with croutons, but put them on a plate immediately before serving. This way the crackers will get a little soggy, but will retain their crunchiness.
You can leave a few cooked whole mushrooms to decorate the dish. When using frozen ingredients to prepare puree soup, they can be boiled in one water (provided that you froze them after pre-cooking), and the cooking time for mushrooms can be reduced to 10 minutes.
Panther or gray fly agaric (Amanita pantherina)
Found in the second half of summer and autumn. The cap of the mushroom is up to 12 cm in diameter; in youth it is bell-shaped, but then becomes prostrate. Its color varies from light brown to olive, the entire surface is strewn with multiple white spots. The flesh is also white with a repulsive odor.
Panther fly agaric. Photo from wikigrib.ru
The thin and hollow stalk reaches 13 cm in length. It narrows at the top and thickens at the bottom. The mushroom is similar to the harmless gray-pink fly agaric , but it is deadly poisonous. Poisoning occurs quickly: within 20 minutes to 2 hours after eating.
Is it possible to eat wormy mushrooms?
As noted above, if the mushroom is slightly damaged and it is subjected to simple processing, then no harm will be done to the body, but on the contrary, our body will receive maximum benefit due to the presence of a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements in the mushrooms.
If the mushroom is simply teeming with worms and it will not be subjected to additional processing, then the possibility of infecting the body with helminthiasis
This disease can be detected in a person by conducting a series of diagnostic studies: conducting an ultrasound of the intestines and x-rays, donating blood, sputum and feces for analysis, conducting an endoscopy of the intestines and performing a biopsy of its tissues.
If such a serious disease as helminthiasis is detected, it is necessary to immediately begin its treatment
But it is important to remember that treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist
What poisonous specimens can be found in our country?
Here is a partial list of them:
Pale grebe. Perhaps one of the most famous and most poisonous mushrooms in the world. Toadstool is dangerous because of its similarity to champignon, because even after heat treatment, a small piece of toadstool can kill an adult. Fly agaric and its subspecies (red, stinking). It would seem that the fly agaric, known to everyone since childhood, cannot be confused with anything, but it has many species, and some of them can easily be mistaken for edible. False honey fungus is sulfur-yellow. It is not difficult to guess from the name that this species masquerades as its edible fellow honey mushroom. False fungus grows almost all over the globe, and it will be extremely difficult for a non-professional to recognize it. Cobweb. He's very good looking
The correct shape of the cap and a beautiful, even color can attract attention, but only an inexperienced mushroom picker will cut it off, because it has no non-poisonous counterparts. Red champignon. An inedible type of champignon, it can be distinguished by its unpleasant smell and reddish color of the flesh.
Its use will not lead to death, but poisoning for several days is guaranteed. False boletus or gall mushroom. Quite often found in Russia. It is incredibly similar to its edible counterpart and it is sometimes impossible to distinguish them by appearance. But you will immediately understand that you made a mistake with your choice, because... False boletus tastes very bitter.
Beneficial features
Purple mushrooms contain many vitamins, as well as other microelements, for example, zinc, manganese and copper. It also contains stearic acid and ergosterol.
This group has a lot of medicinal properties. They are used to create drugs to combat fungal diseases, as well as to produce antibiotics and agents to control hypoglycemia. The mushroom is great for lowering glucose levels.
It quickly and efficiently relieves inflammation and improves immunity. With the help of the vitamins contained in the composition, the mushroom ensures stabilization of the gastrointestinal tract and protects the body from infectious diseases.
Products created on the basis of cobwebs give strength and energy, protect against overwork and increased fatigue.
Honey mushrooms - what are the benefits and contraindications
Some consider mushrooms just a snack. And they are wrong. Mushrooms are healthy - they contain more than 300 useful substances that strengthen the body's defenses. And also - valuable protein, of which mushrooms contain more than 30%, which is more than meat. And fiber improves digestion. As well as vitamins and amino acids. So those who care about a healthy diet have already managed to include all kinds of mushrooms in their diet.
In fact, honey mushrooms are parasitic mushrooms that infect almost all trees. If they settle on a healthy tree, sooner or later it will die.
In addition to its taste, honey mushrooms have another advantage: healing properties. Autumn honey mushrooms are used as a laxative, and winter ones have antiviral and anticancer effects, and are also rich in proteins.
Honey fungus pulp can destroy Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli, and also has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Just 100g of these mushrooms per day can satisfy our need for elements such as zinc and copper, which are involved in hematopoietic processes.
But honey mushrooms also have contraindications. Mushroom protein, due to its “heaviness” for digestion, is contraindicated for those who have problems with the liver, gall bladder and pancreas.
Nowadays you can find both frozen and pickled honey mushrooms in stores. We may disappoint you a little: frozen mushrooms lose most of their beneficial substances (just like those that have been subjected to long-term processing).
How to determine whether pickled mushrooms are of high quality?
Firstly, honey mushrooms should be whole, and not cut into 2-4 parts. Secondly, they must be uniform in size, without damage. Thirdly, without wormholes, burns and other stains. The taste and smell of high-quality honey mushrooms should correspond to this type of mushroom, with a spicy aroma (and not a cloying spicy one). Taste: sour or slightly sour, but not sour.
One of the disadvantages of wild mushrooms is the ability to absorb heavy metal salts from the environment. This is why artificially grown mushrooms are often preserved.
Popular articles Lunar flower - annual and perennial plant species
Edible varieties
This group includes several tasty subspecies that are readily used in medicine and cooking.
Cobweb
The lamellar mushroom is popularly called violet or fat mushroom.
An autumn species, prefers to grow in deciduous and coniferous forests.
The characteristic includes several special qualities:
- head cushion-shaped or convex with a circumference of 15 cm;
- in adult and old mushrooms the cap is spread out, the edges are wavy, covered with scales, the color is dark purple with a gray tint;
- the plates are wide, sparsely spaced, purple;
- the height of the cylindrical leg is 12 cm, thickness - 2 cm, the upper part is scaly, the lower part is tuber-shaped;
- the flesh is bluish or with a pronounced nutty taste without a mushroom aroma.
Purple webwort forms mycorrhiza with several types of deciduous trees - beech, oak, birch. It can also be found next to spruce, pine, under fallen leaves, in places where mosses grow, where the soil is acidic and humus.
Peak fruiting occurs at the end of summer and ends in mid-autumn.
Purple dog
Another edible variety that belongs to macromycetes. It grows mainly in groups in places of old fires and fire pits. It begins to bear fruit in the spring and continues until mid-summer.
- the cap is of two types - disc-shaped or cup-shaped, the circumference of the apex is from 1 to 3 cm;
- the surface is smooth, lilac or reddish-violet;
- in some species a false leg may form;
- The pulp is brittle, pale purple, thin, odorless and aromaless.
Mushroom pickers rarely collect representatives of this species due to their low taste.
Cooking technique
There are many known ways to cook butter. Using them, you can get different shades of taste of the dish.
Until ready
Butter as an independent dish is prepared within half an hour. This way you can easily get ingredients for salad and broth for soup.
- Clean the dirt and chop the mushrooms, put them in a saucepan, add water so that it completely covers them.
- Place the pan on the fire, add salt, bring to a boil, reduce the flame and cook for 30 minutes. The finished boletus will sink to the bottom.
- Place the mushrooms in a colander and leave to drain. Use further for cooking.
- Strain the broth through a sieve. It makes an excellent base for soup or sauce.
Boiled boletus is used to prepare various dishes.
Before frying
Boiling is necessary in order to reduce the concentration of harmful substances. Forest mushrooms absorb everything that gets into the soil, groundwater, and air. Therefore, it is not recommended to collect them near highways and in areas with poor ecology. Young boletus collected away from roads does not need to be cooked before frying. But if you doubt their quality, go for it.
- Clean the mushrooms, including the film, and rinse. Cut large specimens into pieces.
- Fill with cold water at the rate of 2 parts water to 1 part mushrooms.
- Place on the fire, wait until it boils, skim off the foam.
- Cook for 15–20 minutes depending on the size of the mushrooms. To make sure there are no false oils, place the onion in water when cooking. If there are poisonous specimens in the pan, it will turn blue.
- Drain the finished mushrooms in a colander to drain the liquid and transfer to a frying pan. Drain the broth.
For marinating
To preserve, cook the mushrooms as usual until tender. But you can also use a special recipe in which they are cooked directly in the marinade.
- boletus – 2 kg;
- salt – 50 g;
- sugar – 80 g;
- 6% table vinegar – 100 ml;
- water – 1 l;
- black and allspice – 5 peas each;
- 2 clove buds;
- 1 bay leaf;
- vegetable oil.
- Pour water into a deep saucepan, add salt, sugar, vinegar and spices.
- Bring the mixture to a boil, hold over high heat for 3 minutes.
- Add the peeled butter and cook for 20 minutes over medium heat.
- When the mushrooms settle to the bottom and the marinade becomes transparent, divide the product into jars. Pour in the marinade so that it covers the future appetizer.
- Pour in 1 tbsp. l. vegetable oil into each jar, cool to room temperature.
- Cover the jars with parchment and tie with twine.
- Store the jars in the refrigerator.