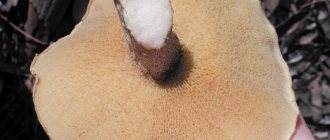
Often, when preparing dishes from boletus, an unpleasant situation may arise due to the fact that the boletus turns pink during cooking. This does not frighten experienced mushroom pickers at all, but beginners may be wary and even refuse to eat their favorite delicacy of mushrooms. Next, we will consider what causes this phenomenon, whether it is dangerous, and how it can be dealt with.
How to properly process flywheels?
Trim the base of the mushrooms, remove debris from the cap and stem. If the bottom of the stem is dirty, scrape and remove the skin at the bottom of the mushroom. If there are places on the mushroom that have been eaten by slugs, then this place should be trimmed. Rinse the flywheels under running water.
Interesting materials:
What does the Qr code of the receipt contain? What is registration at the place of residence? What are accounting registers? Parents' Saturday, what kind of holiday is this? Russia how many time zones? What is hand luggage that you cannot take on a plane? What can you take as hand luggage on a plane? Rufus how to use? What is Romanian deadlift? Russian Railways additional food service, what is it?
Why do boletus turn pink when cooked?
There are few reasons why fruiting bodies change their color; if the butter dish turns pink during cooking, most likely the species composition of the contents of the pan, kettle or cauldron included more than just representatives of this species.
Other mushrooms are the first reason why boletus turns red or pink when cooked
Oilseeds are unique representatives of the mushroom kingdom - this is perhaps the only genus that does not have poisonous false counterparts. That is, there are many varieties whose fruiting bodies are similar to them, and these closely related species are very easy to confuse.
The substances that make up such twins are capable of changing the color of the fruiting bodies during heat treatment. And since the chemical composition of these species, as well as all representatives of the Boletaceae family, is the same, and they are all boiled in the same container, then, naturally, everything is colored, regardless of species.
Important! Mostly the color of the mushroom broth matches the color of the spores. Therefore, if a reddish or purple speck of spore suspension is visible around the fruiting body, this specimen does not belong to Maslenkov and will most likely lead to a change in the color of the broth and the bulk of the mushrooms.
Should I be concerned if the butter turns pink during cooking?
There is no reason to panic if the boletus turns pink after cooking, and besides, the taste of the dish will not even change. Almost all of their counterparts are edible and have similar physiology and, therefore, taste characteristics.
Of course, many will not like the color of pink or purple fruiting bodies in a dish, but this is not so critical, in addition, you can always use some kind of sauce or gravy to change the color scheme of the dish.
How to cook boletus without turning pink or red
To ensure that the fruiting bodies do not change color during heat treatment, you should carefully consider the preliminary preparation of the harvested crop for cooking. It is necessary to carefully examine the fruiting bodies before heat treatment and identify undesirable species among them:
- grates, which cause the butter to turn pink when cooked;
- moss mushrooms, which cause the boletus to turn red during cooking;
- goats that turn neighbors in the pan purple.
It is relatively difficult to distinguish these species from each other, but it is possible. Kozlyaks, unlike many Boletovs, do not have a skirt. The lattice has a cap of smaller diameter with a pronounced tubercle in the middle. The flywheel has a thicker cap.
If all checks have been passed, but you want additional guarantee that the color of the dish will not change, it is recommended to add 0.2 g of citric acid per 1 liter or 15 ml of 6% vinegar to the same volume of water during cooking.
Attention! You can use any type of vinegar - table, grape, apple, etc.
Beneficial features
Purple mushrooms contain many vitamins, as well as other microelements, for example, zinc, manganese and copper. It also contains stearic acid and ergosterol.
This group has a lot of medicinal properties. They are used to create drugs to combat fungal diseases, as well as to produce antibiotics and agents to control hypoglycemia. The mushroom is great for lowering glucose levels.
It quickly and efficiently relieves inflammation and improves immunity. With the help of the vitamins contained in the composition, the mushroom ensures stabilization of the gastrointestinal tract and protects the body from infectious diseases.
Products created on the basis of cobwebs give strength and energy, protect against overwork and increased fatigue.
Yellow types of inedible russula
The confusion with the edibility of russula is such that mushroom pickers often classify some yellow russula as questionable. For example, light yellow russula (R. Claroflava) has a bright yellow cap, and its initially white flesh turns gray when cut, and even darkens when cooked, and this is not typical for most edible russulas.
Even after studying edible and inedible photorussula, a mushroom picker can most likely confuse them. For example, ocher russula (R. Ochroleuca) with value (R. Foetens), since both mushrooms prefer moist forests. In R. Ochroleuca, when broken, the flesh also darkens slightly, has no smell, but has a very pungent taste. It differs from the yellow russula in color: while the latter has a clear and bright color, the ocher russula has a dirty yellow color.
False boletus: their difference from an edible mushroom
Boletus mushrooms are suitable for frying, stewing, and canning. They have a very pleasant taste. However, when collecting boletus, you need to be extremely careful. These mushrooms, like many others, have their own “double” that is unsuitable for consumption.
False butterfly is a very poisonous mushroom and can cause severe poisoning. In addition, it is quite easy to confuse it with a real oiler. However, upon careful examination, several distinctive features of this mushroom can still be detected.
What does a real oiler look like?
This tasty mushroom begins to grow in the forests around mid-June. The butterdish mycelium bears fruit 3-5 times during the season.
The last time mushroom pickers can pick these mushrooms is in September. Distinctive features of the oiler are:
- light brown or light yellow cap;
- tubular under-hat layer;
- yellowish-white color of the pulp (like butter).
Butterflies grow in groups of several. The space under the cap of young mushrooms of this variety is covered with a thin film. In older people, this formation is torn and forms a white ring on the stem. Some varieties of oilseed do not have such a formation.
The caps of good real butterfish are covered with a thin film, which becomes slippery when wet. This is where the name of this mushroom actually comes from.
Description of the false oiler
You can distinguish real boletus from their poisonous “brother” first of all by the color of the cap. In false butterflies it has a cool, slightly purple tint.
A mushroom found in the forest, among other things, also needs to be turned over. In a false oiler, the lower surface of the cap is not tubular, but plate-shaped. In addition, this area in such mushrooms usually has a pronounced creamy-yellow color.
The rings on the stem also differ in appearance between these two varieties of mushrooms. In a regular oiler, this formation, as already mentioned, is white. Its false “brother” has a ring, like the cap, that is slightly purple and hangs down the stem.
Among other things, the ring on the stem of a poisonous mushroom very often looks dried out. In real butterfish it almost always remains alive and elastic.
You can also distinguish a false butterdish from a real one by the color of the flesh at the break. This mushroom is slightly reddish. In addition, the cut flesh of false butterflies usually darkens very quickly.
How not to be confused with the panther fly agaric
The danger of an inexperienced mushroom picker can lie in wait in the forest because of the panther fly agaric. Such mushrooms are also very similar in appearance to boletus and are also extremely poisonous. In this regard, they are even more dangerous than false boletus. And, of course, a mushroom picker must also know what a panther fly agaric looks like.
Adult panther fly agarics can be easily distinguished from boletus mushrooms by the presence of white spots on the cap. In order to distinguish a young fly agaric from an oiler, you should carefully examine its leg. This poisonous mushroom has a significant thickening at the bottom.
Varieties
There are more than 250 varieties of butterweed in nature, but there are only three most common:
- Larch - this representative belongs to the inhabitants of deciduous forest. The color of the mushroom is gray or red-red.
- Late - has a yellowish tint. There are rough spots on the stem, which are also called warts.
- Kozlyak is a yellow-brown mushroom. This species does not have warts on the stalk and a typical ring. The hat becomes wet after rain.
Cooking recommendations
Pour cold water over the mushrooms, place over high heat and bring to a boil.
As soon as they boil, drain the broth and transfer the mushrooms to another saucepan with boiling water, where we add more spices and salt.
Cook the butter until tender for 30 minutes.
If you do not drain the first broth, then the time required is 40 minutes. I cook in two decoctions, since there are still sand particles left on the mushrooms, which easily disappear after boiling. Cool the boiled boletus, season it with oil and add garlic petals.
After cleaning and soaking, you can begin further preparation. Any housewife should know how long to cook boletus mushrooms. Heat treatment time will depend on the method of further use. They are used for:
Where to look
Butterfly should always be looked for near trees, usually in the undergrowth or along the edges of paths and roads, because the fungus loves sunlight. It prefers to grow near pines and spruces or birch trees; mushrooms often grow as if in a path. There are both singles and “family” ones.
Mushrooms grow from the beginning of June to the end of September; sometimes they can still be found in October, provided the ambient temperature remains high. Their appearance is associated with rainy days; after the rain passes, the mushrooms quickly jump in size. People say that boletus grows during certain periods, which coincide, for example, with the flowering of pine or linden.
Before looking for information on how to properly cook boletus, you need to know how to clean it after returning from the forest, because they are quite dirty, but very tasty. Before work you need to prepare yourself and the kitchen:
- Cover the work surface with newspaper or oilcloth.
- Prepare two containers and a knife.
- Put gloves on your hands. Otherwise, you will have to walk around with black nails for several days.
Use a knife to scrape off debris from the stem and remove the film from the cap. It is important at this moment to throw away any wormy mushrooms that accidentally ended up in the general pile. After that, water is poured into the container with butter and kept for 20 to 30 minutes. The settled water is drained and clean water is collected, after which they begin cooking.
Conservation
Marinated boletus is an extremely tasty product. Not every housewife knows how simple it is. In order to prepare delicious pickled butter, you need to take:
- mushrooms - 2.5 kg;
- allspice - 5 pcs.;
- cloves - 2 pcs.;
- bay leaf - 4 pcs.;
- vinegar 9% - 60 ml;
- water - 1.25 l;
- salt - 2 full tablespoons;
- sugar - 1 tsp;
- sunflower oil - 0.5 tbsp. l.
How much butter to cook for marinating is usually determined by eye. On average, this is about 20 minutes. After cooking, the butter is placed in a colander. For the marinade, all ingredients are mixed and brought to a boil. Add mushrooms and cook for 25 minutes. Then the mushrooms are placed in jars and covered with metal lids.
Source
What mushrooms are similar to champignons?
Poisonous mushrooms similar to champignons
- Death cap. At a young age, it can easily be confused with champignon; this is the most dangerous of its twin mushrooms.
- The fly agaric is smelly. In appearance, this deadly mushroom is very similar to champignon, however, it also has its own distinctive characteristics.
- White fly agaric.
Interesting materials:
How are ferns different from algae? How is a variable resistor different from a potentiometer? How does fertile soil differ from black soil? How is polyethylene different from cellophane? How do political parties differ from other public organizations? How does time-based wages differ from piece-rate wages? How do Provencal herbs differ from Italian herbs? How is radial runout different from full radial runout? How is baking powder different from dry yeast? How does a real set of crimes differ from an ideal set of crimes?
Honey mushrooms - what are the benefits and contraindications
Some consider mushrooms just a snack. And they are wrong. Mushrooms are healthy - they contain more than 300 useful substances that strengthen the body's defenses. And also - valuable protein, of which mushrooms contain more than 30%, which is more than meat. And fiber improves digestion. As well as vitamins and amino acids. So those who care about a healthy diet have already managed to include all kinds of mushrooms in their diet.
In fact, honey mushrooms are parasitic mushrooms that infect almost all trees. If they settle on a healthy tree, sooner or later it will die.
In addition to its taste, honey mushrooms have another advantage: healing properties. Autumn honey mushrooms are used as a laxative, and winter ones have antiviral and anticancer effects, and are also rich in proteins.
Honey fungus pulp can destroy Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli, and also has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Just 100g of these mushrooms per day can satisfy our need for elements such as zinc and copper, which are involved in hematopoietic processes.
But honey mushrooms also have contraindications. Mushroom protein, due to its “heaviness” for digestion, is contraindicated for those who have problems with the liver, gall bladder and pancreas.
Nowadays you can find both frozen and pickled honey mushrooms in stores. We may disappoint you a little: frozen mushrooms lose most of their beneficial substances (just like those that have been subjected to long-term processing).
How to determine whether pickled mushrooms are of high quality?
Firstly, honey mushrooms should be whole, and not cut into 2-4 parts. Secondly, they must be uniform in size, without damage. Thirdly, without wormholes, burns and other stains. The taste and smell of high-quality honey mushrooms should correspond to this type of mushroom, with a spicy aroma (and not a cloying spicy one). Taste: sour or slightly sour, but not sour.
One of the disadvantages of wild mushrooms is the ability to absorb heavy metal salts from the environment. This is why artificially grown mushrooms are often preserved.
Popular articles Lunar flower - annual and perennial plant species