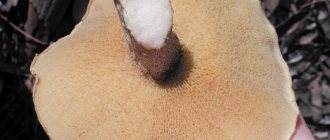
Why do boletus turn purple when cooked?
Every mushroom picker should know that this variety of mushrooms usually does not change color after heat treatment.
During the boiling process, it is not characterized by the appearance of blue, lilac, or brown shades. If the butter dish turns purple during cooking, this indicates that the cooking method was incorrectly chosen. The stems and caps darken from too much heat treatment. When heated for a long time together with water, vegetable protein is destroyed, and boiled mushroom raw materials develop an unusual blue color. Such a change may also depend on the area of growth, when the composition of the soil and illumination can affect the course of chemical reactions during heat treatment.
Pickled boletus turns purple when cooked due to numerous additives in the form of spices, garlic, onion, and pepper. To avoid this, you need to boil the product several times, and be sure to drain the first water. It is recommended to add vinegar and a pinch of citric acid to the marinade.
Read also: The largest locust in the world photo
Other mushrooms are the first reason why boletus darkens during heat treatment
The main reason for the sudden change in color of mushrooms to dark or purple after cooking is the inclusion of other species in the basket that are similar in appearance to boletus. Among the doppelgängers we can distinguish kids (goats, or reshetniks), which are easily confused when collected. This is also an edible variety, which tastes almost no different from the “original”.
Other forest plants also have the ability to change color, including:
False boletus turns black already at the cleaning stage. They differ from real representatives by a different structure of the cap: under it there is not a sponge, but plates.
Violation of cooking rules is the second reason why the butter turned purple
The oiler turns purple due to improper processing technology. In order for the product to retain its original appearance after boiling, you need to prepare it following simple rules:
- large ripe fruits are cleared of film;
- legs and caps are brought to a boil in clean water;
- boil for no more than 5 – 10 minutes;
- Drain the mushroom mass in a colander;
- pour salted water, after boiling, cook for 15 - 25 minutes, depending on the size of the fruit.
During the cooking process, a film may appear on the surface, which must be removed with a slotted spoon. The recommendation to change the water is due to the fact that, as decomposers, boletus absorbs radiation and heavy metals, but during the first boiling they are destroyed.
Should I worry if the butter turns purple during cooking?
Inexperienced mushroom pickers are alarmed by the fact that the collected prey changes its color to purple when the dishes are cooked. This may well happen to edible specimens if you cook them for more than a quarter of an hour. Do not worry if the selected product has all the varietal characteristics. Purple butter, obtained after cooking, does not threaten human health and retains its usual taste.
Areas of application
In cooking
Before cooking, the fruiting bodies are subjected to heat treatment - boiled over medium heat in salted water for at least 20 minutes.
Then they are used to prepare salads, appetizers, first and second courses. They are also excellent marinated and salted.
To get a tasty and aromatic preparation, you should follow clear instructions:
- Peel the mushrooms, rinse, cut into pieces, and boil in salted water for 40 minutes. Then drain in a colander.
- Next you need to prepare a marinade from several ingredients - water (1 l), salt (2 tbsp), sugar (1 tbsp) and 2 pinches of citric acid. Additionally, you can add bay leaves (1-2 pcs.), black pepper - 3-4 peas, a little greenery (dill umbrellas) and 2-3 large cloves of garlic (can be cut into pieces). Mix all ingredients and boil for a couple of minutes. When preparing marinade, it is important to remember that iodized salt is not suitable for these purposes.
- Pour the boiling marinade over the mushrooms, previously placed in clean jars. Sterilize for 15 minutes, pour 1-2 tbsp on top. vegetable oil.
- It is important that the mushrooms are completely covered with the marinade, otherwise they will quickly deteriorate.
- Roll up with tin lids, wrap in a blanket, and after cooling, take out for storage in a cellar or basement.
You can try this preparation only after three weeks, so that it has time to become saturated with all the aromas.
Among the representatives of the mushroom kingdom there are a lot of very unusual specimens, both in shape and color. The purple mushroom is not rare, but due to its appearance it is a rather exotic “inhabitant” of the forest. There are edible, conditionally edible and inedible purple mushrooms, which any mushroom picker should be able to distinguish.
Why did boletus turn blue during or after cooking?
Encyclopedia "Mushroom-Info" Mushroom Picker's Guide Why did boletus mushrooms turn purple after cooking?
Among all varieties of edible mushrooms, boletus is considered one of the best in taste. They are used in all technological processes: freezing, drying, salting, pickling and frying. The excellent digestibility of butter allows them to be used in any dish. After thoroughly cleaning the sand, grass and leaves, you can begin cooking the mushrooms. However, you may find that the butter has turned purple after cooking - why does this happen, and what can be done in such cases?
Why do boletus turn blue after cooking and should I be concerned?
First of all, you need to know that butter is not characterized by a purple, lilac or blue color after heat treatment. This means that along with the butter mushrooms, there were other mushrooms in the pan - goat mushrooms (goats). But in this case there is no need to be afraid. This is an absolutely edible type of mushroom, which in taste and appearance is practically no different from boletus. A tubular mushroom that is part of the genus Butterfly is called a goat mushroom. They are prepared using the same technology as their “relatives”, but when cooked they turn purple. But the acquired color does not make the mushroom worse. Many housewives decorate boring, monochromatic marinades with these purple “butter” after cooking. This aesthetically unattractive mushroom can be boiled, stewed, fried, and also dried. And so that it does not darken too much and retains its original pink color, you need to add a little table vinegar before cooking.
Another reason why boletus turns blue after cooking is too long a heat treatment. With prolonged cooking, the vegetable protein is destroyed, and the mushroom acquires a bluish tint, but it is barely noticeable. As already mentioned, butter oils cannot turn blue or purple when cooked. In such a situation, it is common for them to change their color to beige or light brown. It all depends on its original appearance, which is influenced by the terrain, soil composition and lighting.
How to properly fry and cook butter?
The harvest time for boletus is from June to early November. They grow mainly on young edges of coniferous and deciduous forests. Can be found on roadsides. The first distinctive feature of the mushroom is the cap. In dry weather it shines but is sticky to the touch. With high humidity it becomes covered with mucus.
These two signs are the main ones when collecting:
- Wet hat.
- Presence of film, ring.
If one of the signs is absent, the mushroom is discarded. Oils can be divided into several types:
Edible - the flesh is white or cream. The color of a broken mushroom does not change. The most delicious kind. The mushroom is good for soup and frying. It is prepared for the winter, dried, canned, and frozen. It is recommended to boil the mushrooms first. This is how they acquire a special taste
How much to cook butter for marinating and how much to freeze is very important. More experienced housewives determine the time by eye
On average it takes 10-15 minutes for freezing and 20 minutes for canning. Cooking time may vary depending on the age of the mushroom. Conditionally edible - the flesh of these mushrooms darkens and turns yellow when cut. Sometimes it turns gray. Eating such boletus is not dangerous, but the taste is very different from edible ones. Some mushroom pickers believe that if you boil such a mushroom for a long time, it will become tastier. How long to cook butter before frying or preparing other dishes in this case is unknown. Inedible - when cut, they acquire a purple color. Some varieties have a metallic odor. These mushrooms can also be eaten, but they are not at all tasty.
Not everyone knows how and how much to cook butter. This mainly depends on the type of mushroom and its age. In order to cook butter, just wash them and put them in boiling salted water for 20-25 minutes. If the mushrooms are still subject to heat treatment, then the time is reduced to 10-15 minutes. Boiled boletus is added to salads and various toppings. They are fried and canned. It is also preferable to boil the mushroom before freezing.
Fried boletus is considered an unusually tasty dish. Mushrooms of any age are suitable for their preparation. You can boil them before frying. You can simply put it in a frying pan raw. How long to cook the boletus before frying will depend on how young the mushroom is. Usually this is no more than 10 minutes. Ripe mushrooms take twice as long to cook.
What to do in case of poisoning?
What to do if such a situation does occur? Let's look at what actions should be taken in case of mushroom poisoning . It is necessary to provide first aid in case of intoxication of the body.
There are several simple rules that, if followed, will help alleviate the patient’s condition:
- Call an ambulance immediately! When the first signs of poisoning appear, do not try to cope with the symptoms yourself. This can have very serious consequences;
- Provide the patient with pastel mode;
- It is necessary to drink water in large quantities; gastric lavage helps to eliminate toxins as quickly as possible;
- Activated carbon absorbs harmful substances and alleviates the patient's condition.
Thus, you can never know for sure whether the most dangerous mushrooms ended up in your basket or not. Even the most experienced mushroom pickers may not notice this. When going into the forest, you need to be as attentive and prepared as possible. And without hesitation, leave a dubious mushroom without attention.
Video about 5 deadly mushrooms in central Russia
In this video, Leonid Varlamov will tell you what mushrooms you should be wary of in the forests of central Russia, and how to avoid getting poisoned by them:
In September, completely unexpectedly and contrary to all forecasts, mushrooms appeared in the forests exhausted by the summer drought. The people set off with baskets to mushroom hunt, hoping to stock up on “forest meat” for the winter. And we asked doctors about what is healthy in mushrooms and how best to eat them.
Honey mushrooms with potatoes? Maximum two spoons!
“You can’t call mushrooms “meat” even in quotation marks,” says Marina Kopytko, candidate of medical sciences, chief physician at the Weight Factor health nutrition clinic. – From the point of view of nutritional value, we can only talk about the protein that mushrooms contain, but it is incomplete - unlike the animal protein that meat products provide. So mushrooms cannot be an equivalent substitute for meat. They contain a lot of water, a certain amount of carbohydrates and aromatic substances - they are what give mushrooms the taste and smell for which they are loved. It turns out that the popularity of mushrooms is associated more with taste than with nutritional value - there is nothing particularly useful or important for the body in them.
But it turns out that there is something that is rather detrimental to him. Mushrooms only at first glance seem like a tender and light food. They contain a large amount of chitin, a polysaccharide substance that the human intestine cannot digest. That is why mushrooms are among the so-called heavy foods, which even healthy people should not consume in frying pans, not to mention those who have something to read in their medical records. Three categories of people for whom mushrooms are contraindicated: young children, old people and anyone with gastrointestinal diseases.
“Because of chitin, mushroom protein is very difficult to digest,” explains nutritionist Marina Kopytko. “Only a small percentage of it is absorbed; the rest is of no use to the body, but it still has to make efforts to process such food. This is a serious burden on the organs of the digestive tract, especially the pancreas. Mushrooms also have active choleretic properties and stimulate the production of gastric juice, which is not useful for those who have gastritis with high acidity or peptic ulcers. But allergies to mushrooms are very rare.
How to buy mushrooms correctly
A few words about buying mushrooms at the market. If you don’t have the time or skills to pick mushrooms yourself, you can buy them at the market.
- When purchasing, you need to carefully examine the mushrooms - what condition they are in, whether there are any bruises or damage.
- Do not buy mushrooms that have been pulled out by the roots. Firstly, a person picking mushrooms thus spoils the mycelium, which means he absolutely doesn’t care what grows there after him, and, most likely, he doesn’t care what mushrooms he sells. Secondly, such an incompetent seller can slip (not on purpose, of course) poisonous mushrooms.
- Look at the cut of the leg. It should be fresh, not weathered, the edges should be smooth and not bent.
- The caps should not have any dents or darkened brown spots. If the mushrooms are limp, you should not buy them. At best, they will be tasteless.
- Do not buy mushrooms in plastic bags. This way they spoil very quickly. If they were collected directly into the bag, then they are probably no longer suitable.
We suggest you read: Why do spider mites appear on cucumbers and what to do about it?
If trouble does occur, you should immediately contact a medical facility by calling an ambulance. Before the ambulance arrives, your actions can not only alleviate the suffering of the victim, but also save his life. Act clearly and quickly:
- Don't panic.
- Perform gastric lavage and induce artificial vomiting several times.
- The victim should be placed comfortably in a horizontal position and covered with a blanket.
- Drinking regularly will help prevent dehydration and fight toxins. To do this, you need to drink milk, salted or just clean water.
- Someone should always be near the patient to ensure that the victim is conscious and give ammonia to sniff in case of loss of consciousness, otherwise a coma may occur.
Edible types of purple mushrooms and their descriptions
Before you go on a “quiet” hunt for such exotic mushrooms, you need to protect yourself from mistakes. To do this, it is not enough to know their names; it is important to familiarize yourself with the photo and description of the fruits in order to understand what edible purple mushrooms look like.
Purple dog
Petsitsa is a representative of the genus of the same name. The mushroom has a small fruiting body, 0.5-3 cm in diameter, cup-shaped. This species, as a rule, has no leg, since the arctic fish is a discomycete. However, a small false pedicle may be present. The surface of the arctic fish is smooth, the inner surface of the discomycete is lilac in color, but the outer surface is pale and may have a grayish tint.
The fragile and thin flesh of the mushroom does not have any taste or smell. The color of the pulp is lilac.
Amethyst varnish with purple stem and cap
Amethyst varnish belongs to the family Oryadovaceae and the genus Lakovitsa. Lakovitsa is a small mushroom with a longitudinally fibrous purple stem and a cap, the shape of which changes as it develops. In immature specimens the cap is hemispherical, and later becomes flat. The plates are located directly under the cap and slightly descend onto the stem. The rich color of the varnishes fades and turns pale over time.
The pulp is thin, has a purple color and a rather delicate taste.
Gossamer violet
The purple cobweb is a rare representative of its kingdom, belonging to the Cobweb family. The spider's cap changes shape as it grows. If at first it is convex and with drooping edges, then later it becomes flat and covered with scales. The diameter of the cap does not exceed 15 cm.
The thick leg of the cobweb, the width of which reaches 2 cm, slightly thickens downwards. There are small scales on the upper part of the leg. The length can vary from 6 to 12 cm.
The pulp has a dense texture. In mature specimens, the blue color of the flesh fades to almost white. When exposed to air after cutting, the flesh turns brown. Wide and sparse plates of the cobweb, as if shrouded in a veil. The cobweb has virtually no odor, but has a pleasant nutty taste.
Row with a purple cap and a thick stem
Ryadovka belongs to the Govorushka genus and the Ryadovaceae family. The row has other names, such as cyanosis, titmouse and blueleg.
Titmouse - a row with a rather large purple cap, 6-20 cm in diameter, is a conditionally edible species. The cap of young bluelegs has a convex hemispherical shape with the edge turned down. In mature bluefish, the cap becomes convex and outstretched. The initially bright cap acquires an ocher hue as the fruiting body grows.
The pulp of the row is fleshy and dense. Later, the flesh softens and, like the cap, acquires an ocher-cream hue. The length of the leg can reach 10 cm, and the width – 3 cm. The cyanosis leg has a dense texture and a cylindrical shape. There is a light flocculent coating on the surface of the stem directly below the cap, and purple mycelium is located at the base.
Bluefoot has a specific taste and smell, which disappears after heat treatment.
Species that turn purple when cooked
When cooked, the goat mushroom, or lattice mushroom, turns lilac in color.
The goat belongs to the genus Maslenok. The diameter of the yellowish-brown cap of the trellis varies between 3-12 cm. At first, the cushion-shaped, and later flat cap has a smooth, sticky surface. In damp weather, the cap becomes covered with mucus.
The skin on the cap fits so tightly that it cannot be removed at all or can be removed in patches. The length of the leg can reach 10 cm, and the thickness is only 2 cm. The leg, unlike the cap, is lighter and more matte, and its shape resembles a cylinder.
The pulp is quite elastic, and later becomes rubbery, and does not have a special smell or taste.
Places where purple mushrooms grow in the Moscow region
Spider webs can be found in coniferous and deciduous forests near pine, birch, oak, beech and spruce. On the territory of the Russian Federation it grows in the Primorsky and Krasnoyarsk Territories, but recently the spider web can also be found in the Moscow region.
Lilac lacquer usually grows on well-moistened soils in coniferous forests near moss. But it can also be found in mixed and deciduous forests not far from oak trees.
Lilac lacquer
Petsica, in turn, grows exclusively in areas after fires or bonfires and, as a rule, grows in large groups. The mushroom is widespread not only in the Moscow region, but throughout Europe and North America, although even there it is quite rare.
Rowing is common in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, which corresponds to Siberia and the European part of Russia. It is a saprophyte and grows on rotting leaves, fallen needles and compost heaps. The row can be found in coniferous, mixed forests and even gardens. Blueberry tolerates the first frosts quite well, so it can bear fruit until November. The row most often grows in groups, and sometimes forms “witch circles”.
Useful properties and restrictions on use
The row is rich in B vitamins, as well as manganese, copper and zinc. This species is actively used not only in cooking, but also in medicine, because cyanosis is used for the production of antibiotics and antifungal agents.
In addition, cyanosis reduces glucose levels and has an anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effect. Cobweb has similar beneficial properties as cyanosis, since it contains identical beneficial substances and trace elements.
Gossamer violet
Petsitsa, in turn, has a positive effect on clarity of vision, thins the blood and thereby prevents the appearance of varicose veins and thrombophlebitis. Pepper tincture is used to treat kinetosis. Petsica also contains a large amount of vitamin C, which improves human immunity.
Mushrooms should not be abused by people with gastrointestinal diseases. And in case of serious diseases, such as ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis, you should completely stop using them. Also, this product should not be consumed by children under 10 years of age and pregnant women, since it is quite difficult to digest and absorb by the body.
| Name: | Butter |
| Type: | Edible |
There may be several reasons why boletus turned purple after cooking. To understand what the color change means and whether something can be done, you need to understand the characteristics of these mushrooms.
Silver and garlic
How to check whether a mushroom is poisonous or not? It is said that a silver object can be dipped into a pan containing this product. And if the silver darkens, it means there is a poisonous mushroom there. But this theory is not 100% correct. Since a reaction may occur with a substance that is released from edible mushrooms.
The changed color of garlic added during cooking also does not one hundred percent confirm the presence of dangerous stalks. After all, a reaction with the enzyme tyrosinase could have occurred, again.
Source of the article: https://sadovnic.su/yagody/griby-posle-varki-fioletovye.html
Why do boletus turn purple when cooked?
Every mushroom picker should know that this variety of mushrooms usually does not change color after heat treatment. During the boiling process, it is not characterized by the appearance of blue, lilac, or brown shades.
If the butter dish turns purple during cooking, this indicates that the cooking method was incorrectly chosen. The stems and caps darken from too much heat treatment. When heated for a long time together with water, vegetable protein is destroyed, and boiled mushroom raw materials develop an unusual blue color. Such a change may also depend on the area of growth, when the composition of the soil and illumination can affect the course of chemical reactions during heat treatment.
Pickled boletus turns purple when cooked due to numerous additives in the form of spices, garlic, onion, and pepper. To avoid this, you need to boil the product several times, and be sure to drain the first water. It is recommended to add vinegar and a pinch of citric acid to the marinade.
Other mushrooms are the first reason why boletus darkens during heat treatment
The main reason for the sudden change in color of mushrooms to dark or purple after cooking is the inclusion of other species in the basket that are similar in appearance to boletus. Among the doppelgängers we can distinguish kids (goats, or reshetniks), which are easily confused when collected. This is also an edible variety, which tastes almost no different from the “original”.
Other forest plants also have the ability to change color, including:
- Mosswort
- Grabovik
False boletus turns black already at the cleaning stage. They differ from real representatives by a different structure of the cap: under it there is not a sponge, but plates.
Violation of cooking rules is the second reason why the butter turned purple
The oiler turns purple due to improper processing technology. In order for the product to retain its original appearance after boiling, you need to prepare it following simple rules:
- large ripe fruits are cleared of film;
- legs and caps are brought to a boil in clean water;
- boil for no more than 5 – 10 minutes;
- Drain the mushroom mass in a colander;
- pour salted water, after boiling, cook for 15 - 25 minutes, depending on the size of the fruit.
During the cooking process, a film may appear on the surface, which must be removed with a slotted spoon. The recommendation to change the water is due to the fact that, as decomposers, boletus absorbs radiation and heavy metals, but during the first boiling they are destroyed.
Should I worry if the butter turns purple during cooking?
Inexperienced mushroom pickers are alarmed by the fact that the collected prey changes its color to purple when the dishes are cooked. This may well happen to edible specimens if you cook them for more than a quarter of an hour. Do not worry if the selected product has all the varietal characteristics. Purple butter, obtained after cooking, does not threaten human health and retains its usual taste.
Why do mushrooms turn dark?
It happens that during cooking the caps and stems change color. The fact is that there are several subspecies of these mushrooms:
- if boiled boletus mushrooms turn purple, then most likely it is goat (cow, dry butterdish), it is quite edible and not dangerous;
- if the mushrooms turn red during cooking, then these are flywheels, also edible mushrooms;
- if the collected mushrooms turn pink after cooking, then this is most likely a mushroom, which also belongs to the subspecies of edible butter mushrooms.
If you are going to prepare mushrooms for the winter, then remember that pickled or frozen boletus, previously boiled in water with the addition of citric acid, will remain light in color and will not color the marinade.
False boletus can also change color when cut, but they differ from real ones primarily in that the false ones have plates rather than a sponge under the cap. Based on this feature, you will not pick up inedible or poisonous ones in the forest. But remember that it is better to double-check yourself several times before eating any mushroom.
What to do to prevent boletus from turning black
It is especially unpleasant when the mushroom mass darkens in the jar after salting. The finished product does not look aesthetically pleasing, and the appearance of the dish is not appetizing. Experienced foresters advise adding a little citric acid and vinegar to the marinade. Before serving the roast, sprinkle the dish with lemon juice. This will add a subtle sour taste and preserve the beautiful appearance of the butter.
How to cook butter without turning brown
It is recommended to boil the product before any further use:
- before frying;
- freezing;
- slicing for salads;
- for soup.
To prevent the butter from darkening during cooking, there are several tips for the housewife:
- Mushroom raw materials should be kept in boiling water for no more than 30 minutes.
- Before frying, boiling time should be reduced to 15 minutes.
- It is important to first defrost the frozen preparation, and then cook it in the same way as fresh mushrooms.
- Before freezing, the butter must be boiled a little, dried, and put into bags. It is permissible to harvest raw fruits.
- When preparing soup, the first water must be drained, and the base of the dish will be the following broth. Boiling time should not exceed 30 minutes.
- When cooking, add 1 tsp. citric acid.
- It is recommended to simmer butter in a slow cooker for about 40 minutes.
There is no need to worry if the butter mushrooms turn purple after cooking: all the taste characteristics of the mushrooms will remain unchanged, and the dish will turn out just as appetizing as usual.
How long to cook butter
Different dishes will require a certain amount of pre-processing time. How long to boil the butter in one case or another depends on the specific recipe.
Before frying
There is no consensus on how long to cook butter in this case. Many people prefer to fry mushrooms right away. In this case, the butter has a denser consistency and tastes better.
However, you should not do this, because the pulp of the mushroom tends to accumulate radiation and heavy metals. It is better to protect yourself and your family by pre-boiling the butter for 15-20 minutes. Drain, dry slightly and then fry according to the recipe.
Until ready
The simplest, fastest and lowest-calorie dish is made from boiled butter. If not further cooked, they should simmer for about 30 minutes. The readiness of the butter is determined as follows: as soon as they have sunk to the bottom of the pan, you can stop cooking.
To make the dish more aromatic, 5 minutes before turning off, add roots to taste (carrots, celery or parsley), a pinch of ground black pepper and 2-3 pcs. peas, 1-2 cloves, 1 bay leaf. Boiled boletus is best combined with stewed vegetables or rice. These mushrooms are prepared in the same way for use in various salads.
Before freezing
Butter can be prepared in this way without prior boiling. They store well, but take up a lot of space. Once boiled, the mushrooms can be formed into small rectangular briquettes, placing them tightly in plastic bags. This way the butter will take up less space, and it will be more convenient to divide them into portions for further use.
To preserve maximum beneficial properties, boil mushrooms for no more than 10-15 minutes before freezing. Then they are well drained, dried, packaged and sent to the freezer for long-term storage.
For marinating
There are two ways to prepare butter in this case.
Pre-boiling
The mushrooms need to be boiled for at least 20 minutes, then drained, rinsed well, poured with hot marinade and put on fire for another 5-7 minutes. Pour boiling water into prepared jars, close tightly with lids and leave in a warm place until completely cooled.
Cook immediately in marinade
To do this you will need (for 1 kg of butter):
- 1 tbsp. l. with a heap of salt;
- 1/3 tbsp. Sahara;
- 0.5 tbsp. 6% acetic acid;
- 3 pcs. black and allspice;
- 1 carnation inflorescence;
- 1 bay leaf;
- 2 tbsp. water;
- odorless vegetable oil.
How to cook:
- Boil the marinade, adding all ingredients except oil, cook for 3-5 minutes.
- Dip the peeled and washed boletus into the boiling marinade for 0.5 hours, reducing the heat to medium.
- When the mushrooms sink to the bottom of the pan, pour them into prepared jars, add 1 tbsp to each. any vegetable oil, close with tight-fitting lids.
Butter marinated in this way should be stored in the refrigerator.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=7bASfupXV9Q%3F
For soup
If you are preparing the first course, there is no need to boil the butter twice. They have such a rich aroma and characteristic taste that it would be a pity to lose it through unnecessary processing. However, it is still necessary to bring the first water to a boil and drain it in order to protect yourself from radiation and heavy metals accumulated by mushrooms.
Then you need to cook the butter for 30 minutes and only after that add all the ingredients required by the recipe. Mushrooms go best with vegetables and noodles. Greens will enhance the specific taste of butter, especially parsley.
Butter cooked in a slow cooker is very tasty. Soup, roast, and pilaf turn out surprisingly tasty and aromatic. First you need to boil the mushrooms for 3-5 minutes, rinse and use according to the recipe recommendations. When cooking butter in an oven or double boiler, boiling for 5 minutes is also necessary.
Edible varieties
This group includes several tasty subspecies that are readily used in medicine and cooking.
Cobweb
The lamellar mushroom is popularly called violet or fat mushroom.
An autumn species, prefers to grow in deciduous and coniferous forests.
The characteristic includes several special qualities:
- head cushion-shaped or convex with a circumference of 15 cm;
- in adult and old mushrooms the cap is spread out, the edges are wavy, covered with scales, the color is dark purple with a gray tint;
- the plates are wide, sparsely spaced, purple;
- the height of the cylindrical leg is 12 cm, thickness - 2 cm, the upper part is scaly, the lower part is tuber-shaped;
- the flesh is bluish or with a pronounced nutty taste without a mushroom aroma.
Purple webwort forms mycorrhiza with several types of deciduous trees - beech, oak, birch. It can also be found next to spruce, pine, under fallen leaves, in places where mosses grow, where the soil is acidic and humus.
Peak fruiting occurs at the end of summer and ends in mid-autumn.
Purple dog
Another edible variety that belongs to macromycetes. It grows mainly in groups in places of old fires and fire pits. It begins to bear fruit in the spring and continues until mid-summer.
- the cap is of two types - disc-shaped or cup-shaped, the circumference of the apex is from 1 to 3 cm;
- the surface is smooth, lilac or reddish-violet;
- in some species a false leg may form;
- The pulp is brittle, pale purple, thin, odorless and aromaless.
Mushroom pickers rarely collect representatives of this species due to their low taste.
Ryadovka
For many mushroom pickers it is known as violet lepista or naked. Popularly called titmouse or cyanosis.
- the top is fleshy, with a circumference of 16 to 19 cm, hemispherical or convex with thin edges turned down;
- adult fruiting bodies take on a prostrate or depressed shape, the edges are curved, in some specimens the caps are wavy-curved;
- the surface is glossy, in young mushrooms it has a rich purple hue, in old ones it fades and becomes ocher;
- pulp with a mild mushroom taste and aroma reminiscent of anise;
- the plates are violet, thin, densely located;
- the legs are dense, cylindrical in shape, with a thickened base, fibrous structure. In old mushrooms, cavities appear in the thickness of the stem;
- The main difference between the mushroom is the flaky coating and pubescence at the bottom.
Purple rowers are quite large; they prefer to grow under fallen, rotting leaves. They are found both singly and in groups.
Amethyst lacquer
Lakovitsa is listed in the Red Book
This mushroom of the Rowadovaceae family belongs to the group of edibles, but is rare in our country, therefore it is listed in the Red Book. Likes to grow on moist soil in coniferous forests.
It has several distinctive features:
- cap circumference - 1-5 cm depending on age;
- in young specimens the cap is hemispherical, in old fruiting bodies it is flat;
- the main color is lilac-violet, fades with age;
- the plates are thick, the same color as the cap, later becoming white;
- cylinder leg, fibrous, purple;
- In cross section, the fruiting body is purple.
Late oiler (real, ordinary, yellow)
Late oiler (Suillus luteus) is also called true, ordinary, yellow. In Central Russian forests this is the most common species. The name of the mushroom can be misleading, since late oiler does not appear in late autumn, but from June to October. True, the time of mass collection actually occurs in the fall (in some years even in November). Late oiler is a mushroom of pine forests. It can also be found in places where, in addition to pines, there are other coniferous trees.
Late butterwort is very productive, it grows in large groups. This mushroom is prepared fresh (fried, boiled, stewed), dried, salted and pickled.
Hat. The shape of the mucous cap (up to 12 cm in diameter) in young fungi is cushion-convex and hemispherical. In adults it is wide-conical. Its edges are down. The surface color of the cap is chestnut brown, red-brown or dark brown. The tubular layer is golden yellow or lemon yellow in color. Old mushrooms develop an olive tint.
Cap flesh. The color of the thick pulp is white or yellowish. It has a pleasant smell and a slightly sour taste.
Leg. The height of the solid cylindrical stem of the late butterdish is up to 10 cm, thickness - up to 2 (3) cm. In adult mushrooms it has a white or grayish-violet ring. Above it the color of the leg is white, below it is brownish.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Lemon for the liver: benefits and harm
Color changing mushrooms
In nature, there is one such species - the goat or lattice. This mushroom is a representative of the Buttercup genus and has a yellowish-brown cap covered with mucus, the circumference of which varies from 3 to 12 cm, depending on age.
At the beginning of growth, the surface of its cap is cushion-shaped, later it becomes flat, smooth and sticky.
The leg is 10 cm long, not too thick - up to 2 cm, elastic, cylindrical, a couple of shades lighter than the head, matte. In cross-section, the fruit body is light, does not lose any smell or aroma, and is dense.
If after cooking such mushrooms become dark lilac or purple in color, do not worry, this is a common occurrence.
Summer oiler, grainy
Summer butterwort (Suillus granulatus) is also productive. It is suitable for fresh use (it is fried, boiled and stewed), drying, salting and pickling. The mushroom is collected in the summer (June - July) in coniferous forests, where there are many pine trees. Some summer boletus appear from the end of May.
Hat. The shape of the mucous cap (up to 10 cm in diameter) is convex in young mushrooms, and flat in adults. The skin color ranges from yellowish-brown to ocher-brown. The tubular layer is yellow or light yellow.
Cap flesh. The color of the thick pulp is yellowish-white. It has a pleasant taste and smell.
Leg. The height of the solid cylindrical leg is up to 8 cm, thickness is up to 2 cm. The color is yellowish. The leg has a granular surface (hence the name of the species). There is no ring on the leg, which is a distinctive feature of the species. Small watery drops protrude from the upper part of the stem.
How to distinguish from false ones
Not only edible, but also poisonous varieties can have a purple color. To learn to distinguish them, you need to read the description.
Camphor milk mushroom
This species is classified as conditionally edible. The fruiting body contains muscarinic substances, which are poisonous and can cause severe intoxication.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
When muscarine poisoning occurs, a whole complex of symptoms occurs, which experts call “muscarinic syndrome.” Signs of it appear within 30 minutes to 2 hours after eating mushrooms containing these compounds. Studies have shown that the mechanism of action of muscarine on the human body is comparable to that of the poisonous gas Sarin.
The cap of the fruiting bodies is light chestnut or pale yellow with a purple tint, turning brown where pressed.
After some time, the cut purple flesh acquires a red-brown tint and emits the smell of camphor, so it is difficult to confuse it with other species, although completely inexperienced mushroom pickers can do this. When broken, the mushroom releases clear juice.
Umbrella purple
This is not a poisonous mushroom, but due to the unpleasant aroma and the presence of bitterness in the pulp, it is not eaten.
The description includes several features:
- the cap is semi-round, later becoming prostrate;
- the surface is slightly wrinkled, dry, scaly;
- its circumference varies from 5 to 10 cm;
- at the beginning of growth, the color of the cap is snow-white with a slight purple tint and scales, later it acquires an amethyst-brown tone;
- the leg is cylindrical, often curved, whitish, contains a powdery coating at the top, and is covered with numerous light brown scales at the bottom;
- the plates are white, slightly wavy.
Goat's web
This lamellar poisonous mushroom is often confused with the purple cobweb.
The external characteristics are similar, but there is one main difference - the unpleasant smell of acetone, which is emitted by the inedible mushroom.
Goat's web spiders have purple, sometimes even blue, caps. Another distinctive feature is the presence of a skirt with a leg in the form of a belt.
Mycena pure
Mycena pure is very dangerous
This dangerous double of the amethyst lacquer belongs to hallucinogenic mushrooms and is characterized by the presence of muscarine.
The main difference is the presence of whitish or gray-yellow plates under the cap. This species produces a rare aroma (from weak to intense).
Beneficial features
Purple mushrooms are good for the body. because have a rich composition:
- microelements - manganese, iron, potassium, calcium, sodium, copper, zinc;
- thiamine;
- riboflavin;
- vitamins of group B, as well as PP, A, E;
- cellulose.
Fruiting bodies have a positive effect on the functioning of all internal systems, improve the general condition of the skin, nails, hair, increase immunity against various diseases and help eliminate waste and toxins. They help many people lose weight because... considered low in calories.